Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
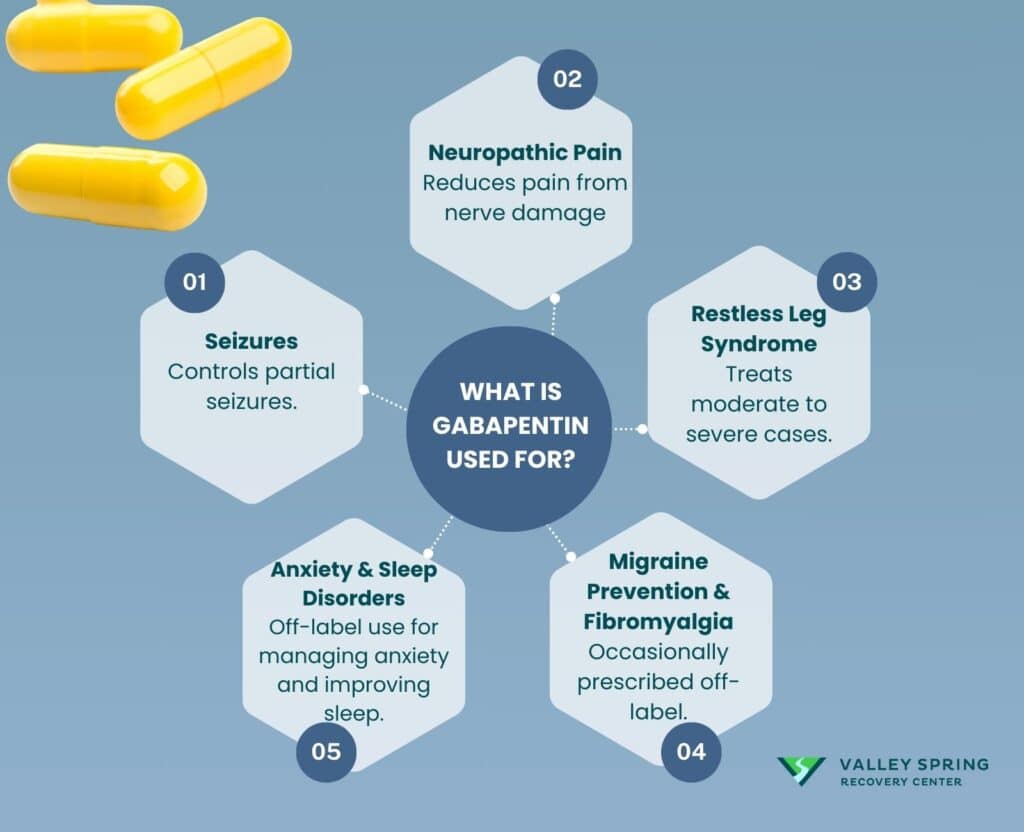 |  |
Gabapentin for management of neuropathic pain, irritability, neonatal abstinence syndrome, rescue sedation, feeding intolerance and visceral hyperalgesia in infants has grown over the past decade. There remains little guidance for indications, This sheet discusses gabapentin use during pregnancy and breastfeeding, offering guidance on potential risks and safety considerations. PURPOSE: Gabapentin, a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) analog with antiepileptic and antinociceptive properties, is increasingly reported in the literature for the treatment of pain and agitation in medically complex patients in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU), despite the paucity of safety and efficacy data in infants. The objectives of this study were to characterize gabapentin However, is hard to know if these problems are from the gabapentin, from the underlying health condition (s) being treated, or other factors. I need to take gabapentin throughout my entire pregnancy. Will it cause withdrawal symptoms in my baby after birth? Studies have not been done to see if gabapentin use alone can cause withdrawal in a newborn. Despite the widespread use, only sparse information is available on the safety of gabapentin during pregnancy. We sought to evaluate the association between gabapentin exposure during pregnancy and risk of adverse neonatal and maternal outcomes. We used gabapentin for the treatment of term and preterm infants with refractory visceral hyperalgesia caused by neurologic and gastrointestinal morbidities. Symptom relief for chronic irritability and feeding intolerance occurred in both populations, as was a reduction in the use of opioids and benzodiazepines. Despite some clinician advocacy for the use of gabapentin to treat neonatal irritability of presumed neurologic origin, the extent of gabapentin administration to hospitalized neonates is unknown. We aimed to identify trends in gabapentin Gabapentin is a γ-aminobutyric acid analog formally indicated for the treatment of epilepsy and neuropathic pain that is gaining increased popularity. Gabapentin has been historically considered a safe medication, including during pregnancy and lactation, with low reported concerns for misuse and us We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Gabapentin and TCAs are considered first line pharmacologic treatment options for patients with neuropathic pain. 20 The following studies describe the use of gabapentin in the treatment of neuropathic pain in pediatric patients. Gabapentin was well tolerated and associated with decreases in pain scores. It's use resulted in decreased requirements for analgesic and sedative medications. Gabapentin therapy appears to be an effective option for neonates and infants with refractory pain and agitation. Gabapentin was well tolerated in infants. Initial gabapentin dosing of 5 mg/kg/dose every 24 hours appears safe and consistent with other published studies in infants. The improvement in outcomes with few adverse events suggests a beneficial role for gabapentin. Gabapentin use in NICU in the United States increased in recent years and varies markedly between institutions. Term infants, ≤28 weeks' gestation preterm infants, and neonates with chronic genetic, neurological, and gastrointestinal diagnoses were more likely to receive gabapentin. Gabapentin is a medication that has been used to prevent and control partial seizures, treat some forms of nerve pain, and treat moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Some brand names are Horizant®, Gralise® and Neurontin®. Gabapentin use in pregnancy is not very well-studied. While the available information does not strongly suggest that it causes problems for the baby, further research is required to prove that gabapentin is safe. Gabapentin is a gamma-aminobutyric acid analog used for numerous neurologic conditions, including neuropathic pain and epilepsy. We describe a 39-week gestational age, male infant with hypotonicity, functional short gut, and microduplication of chromosome 22 who was treated with gabapentin to contro Your child needs to take the medicine called gabapentin. This information sheet explains what gabapentin does, how to give it, and what side effects or problems your child may have when they take this medicine. Gabapentin has been used to treat neuropathic pain related to visceral hyperalgesia in the neonatal population.5,6 Gabapentin, a gamma-aminobutyric acid analog, is thought to inhibit pain via voltage-dependent calcium ion channels in the central nervous system. There is minimal information on the use and side effects of initiating and discontinuing of gabapentin in this population.3,5-7 The OBJECTIVE Gabapentin for management of neuropathic pain, irritability, neonatal abstinence syndrome, rescue sedation, feeding intolerance and visceral hyperalgesia in infants has grown over the past decade. There remains little guidance for indications, initiation, titration and maintenance dosing trends and assessment of outcomes. Gabapentin is well tolerated in neonates and infants. Gabapentin decreases pain scores and the need for other neurosedative medications in neonates and infants. This article is commented on by
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |