Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
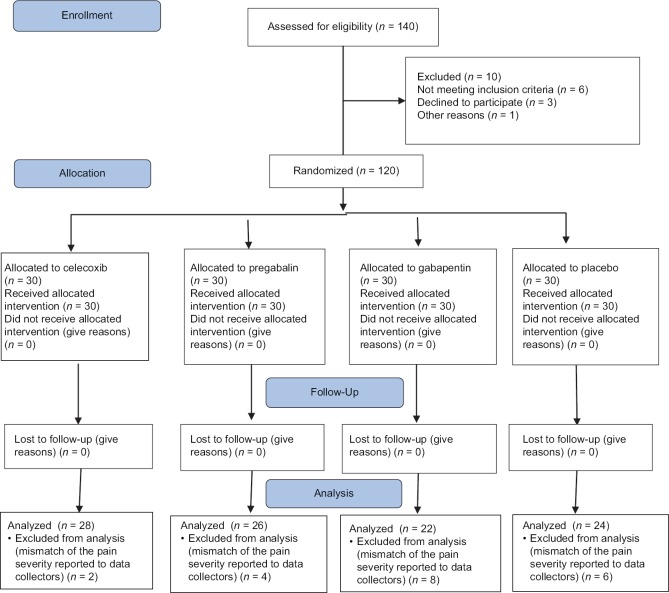 |  |
Background Gabapentinoids are increasingly prescribed in inflammatory arthritis (IA), despite no trial evidence for efficacy at managing pain in this population. Observational studies in non-IA populations suggest gabapentinoids are associated with fractures but are limited by methodological heterogeneity/potential residual confounding. Patients with IA generally have an increased risk of Continuing Education Activity Multimodal pain control is an important modality to control pain in the postoperative period in all patients undergoing surgery or various other procedures. This is especially important in orthopedic surgeries, which often require extensive dissection and fixation of complex periarticular fractures and joint replacement procedures. Multimodal pain control is the Ten other reports were reviewed for the general use of perioperative gabapentin outside of orthopedics, its pharmacology, and the rationale behind its use as an adjunct perioperative pain medication. Gabapentin is routinely used in preoperative multimodal anesthesia to reduce pain following total joint arthroplasty (TJA) surgery. Evolving evidence has shown it is ineffective in reducing postoperative pain and should be used cautiously in this patient population due to its adverse effects. In 2006, Ho et al. performed a review of 16 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) evaluating the use of preoperative gabapentin in controlling postoperative pain (3). This was a very heterogeneous group that included orthopedic, gynecologic, urologic, breast, and head/neck surgeries. Ten other reports were reviewed for the general use of perioperative gabapentin outside of orthopedics, its pharmacology, and the rationale behind its use as an adjunct perioperative pain medication. Conclusion: The preoperative administration of gabapentin appears to be an effective strategy for enhancing postoperative pain control and reducing opioid use in orthopedic patients undergoing spinal anesthesia. Further studies are necessary to determine the optimal dosing regimen and long-term effects of gabapentin in this setting. This systematic review and network meta-analysis evaluates the associations of pain, opioid consumption, and adverse events with different dosages of pregabalin and gabapentin in patients undergoing spine surgery. Gabapentin may be prescribed either before or after surgery to help with postsurgical pain. However, it should be used with caution due to the high risk of abuse. Closely linked with the musculoskeletal system’s functionality is the nervous system. Hence, certain nerve-related drugs, or neuropathic agents, are sometimes used in orthopedics. These include drugs like gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica). We reviewed 8 articles (609 patients) addressing the effect of gabapentin perioperatively (Table) in regard to lower extremity orthopedic surgery. Ten other reports were reviewed for the general use of perioperative gabapentin outside of orthopedics, its pharmacology, and the rationale behind its use as an adjunct perioperative pain medication. The study analyzed gabapentin prescription patterns of orthopedic surgeons from 2013 to 2021 recorded in annual Medicare Part D Public Use Files across the fifty states and Washington DC. Datasets were filtered to only include orthopedic providers. Gabapentin prescriptions were grouped based on state of practice for each surgeon per year for total gabapentin claims, supply in days, and arthroplasty (TJA). The purpose of these guidelines is to improve the treatment of orthopaedic ng a multidis approach on the use of gabapentinoids following primary TJA. The combined clinical practice guidelines are meant to address common and important stions related AAOS Clinical Practice Guidelines and Systematic Review Methodology, the There are meta-analyzes in adults demonstrating the benefits of using gabapentin to improve postoperative pain in orthopedic surgeries. In pediatrics, it has never been studied. The aim of this study was to evaluate the use of gabapentin 10 mg/kg, Gabapentin (1-aminomethyl-cyclohexaneacetic acid) is an amino acid that has the structure of the neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). It is a novel drug used for the treatment of postoperative pain with antihyperalgesic properties and a As gabapentin has been commonly used off-label for pain management in orthopedics, a retrospective analysis was conducted to investigate trends in orthopedic prescriptions of gabapentin considering novel state regulations. Lower extremity pain after orthopedic surgery is so frequent that has led to many treatment modalities. This study aims to compare the prophylactic effects of oral gabapentin, pregabalin, and celecoxib on reducing postsurgical pain of the lower extremity While gabapentin and pregabalin are the most commonly used anticonvulsants used for pain control, there are slight differences between the two medications. 13 Both drugs display dose-response relationships, however gabapentin is absorbed at a slower rate than pregabalin. 14 Additionally, pregabalin possesses a much higher and more consistent Pre-operative Gabapentin Treatment Studies examining patient pain levels following various orthopedic procedures with pre-operative administration of gabapentin were included. In nearly all studies, the visual analog scale (VAS) was used to assess and quantify patient pain scores post-operatively. In three different studies patients were given 300mg of gabapentin or placebo, 2 hours prior to Gabapentin is routinely used in preoperative multimodal anesthesia to reduce pain following total joint arthroplasty (TJA) surgery. Evolving evidence has shown it is ineffective in reducing postoperative pain and should be used cautiously in this patient population due to its adverse effects. The pu
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |