Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 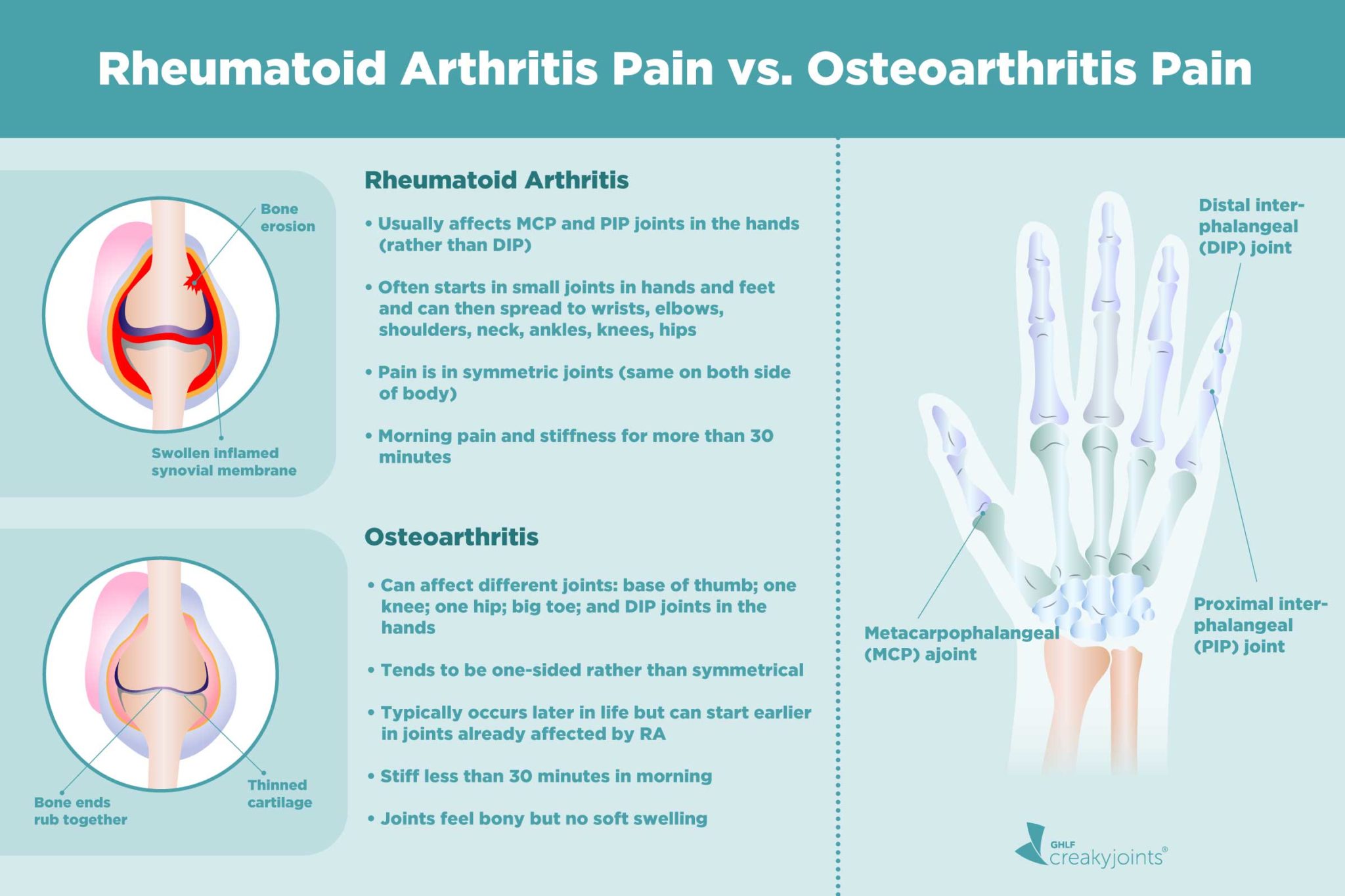 |
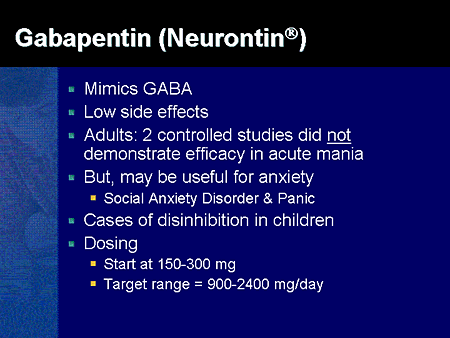
Managing pain from chronic conditions, such as, but not limited to, osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, requires the clinician to balance the need for effective analgesia against safety risks associated with analgesic agents. Osteoarthritis and The Arthritis Today Drug Guide is meant for education – not self-medicating. Arthritis Today, the Arthritis Foundation and the Drug Guide Medical Review Panel do not endorse any products mentioned in this guide. While we endeavor to keep the information up to date, we make no representations or warranties about the completeness of the information provided. Gabapentin: A Detailed Review of Effectiveness, Side Effects, and Comparisons for Treating Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA). In summary, gabapentin is not a first-line treatment for rheumatoid arthritis, but some individuals use it for nerve pain management. For many, arthritis is a daily challenge marked by persistent pain and discomfort. Finding effective pain relief can significantly improve quality of life. Gabapentin, a medication primarily used to treat nerve pain and seizures, is sometimes considered for managing arthritis pain. Let's delve into whether Gabapentin can help with arthritis pain and explore additional resources that may bring Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most prevalent arthritis worldwide and is characterized by chronic pain and impaired physical function. We hypothesized that heightened pain in hand OA could be reduced with duloxetine or pregabalin. In this prospective, Gabapentinoids are increasingly prescribed in inflammatory arthritis (IA), despite no trial evidence for efficacy at managing pain in this population. Observational studies in non-IA populations suggest gabapentinoids are associated with fractures Neurontin (gabapentin), generally prescribed for the treatment of nerve pain, is sometimes used to relieve severe pain caused by knee osteoarthritis (OA). Osteoarthritis, also known, as wear-and-tear arthritis, can often become so severe that joint replacement surgery is needed. Using gabapentin How effective is Gabapentin for Rheumatoid arthritis? Find out results from a study of 22 Rheumatoid arthritis patients who take Gabapentin. Abstract Background: Pain management is a high priority for patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Despite deficiencies in research data, neuromodulators have gained widespread clinical acceptance as adjuvants in the management of patients with chronic musculoskeletal pain. Inflammatory arthritis is a commonly encountered clinical condition, with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and osteoarthritis (OA) being among the prevalent types of inflammatory arthritis (Udomsinprasert et al., 2019). Clinically, the primary manifestations revolve around inflammation and pain, with suboptimal treatment efficacy (Ledingham et al., 2017). The prolonged and recurrent episodes of pain Gabapentin may provide relief for different types of arthritis, including osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Clinical studies have shown potential benefits in reducing pain and improving mobility in these conditions, although results can differ based on individual responses and treatment plans. Discover how gabapentin is being used to treat rheumatoid arthritis symptoms, including pain and inflammation, in this informative medical resource article. Gabapentin is occasionally taken as a pain relief option, but what’s the science behind it? This article will determine whether gabapentin is effective for arthritis pain, how it works, and how to make the most of it. Background Gabapentinoids are increasingly prescribed in inflammatory arthritis (IA), despite no trial evidence for efficacy at managing pain in this population. Observational studies in non-IA populations suggest gabapentinoids are associated with fractures but are limited by methodological heterogeneity/potential residual confounding. Patients with IA generally have an increased risk of Gabapentin, a drug sold under the brand name Neurontin, is not commonly used for rheumatoid arthritis. While it may be useful for treating severe knee osteoarthritis, there is no strong evidence to support its effectiveness in autoimmune forms of arthritis such as rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis. Gabapentin belongs to the class of anticonvulsants and has two approved uses: the Gabapentin is a drug used to treat nerve pain and seizures, but it is not recommended for rheumatoid arthritis. It belongs to the class of anticonvulsants and has two approved uses: treating partial seizures in people with epilepsy and treating tr. Pain management is a high priority for patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Despite deficiencies in research data, neuromodulators have gained widespread clinical acceptance as adjuvants in the management of patients with chronic musculoskeletal
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |