Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
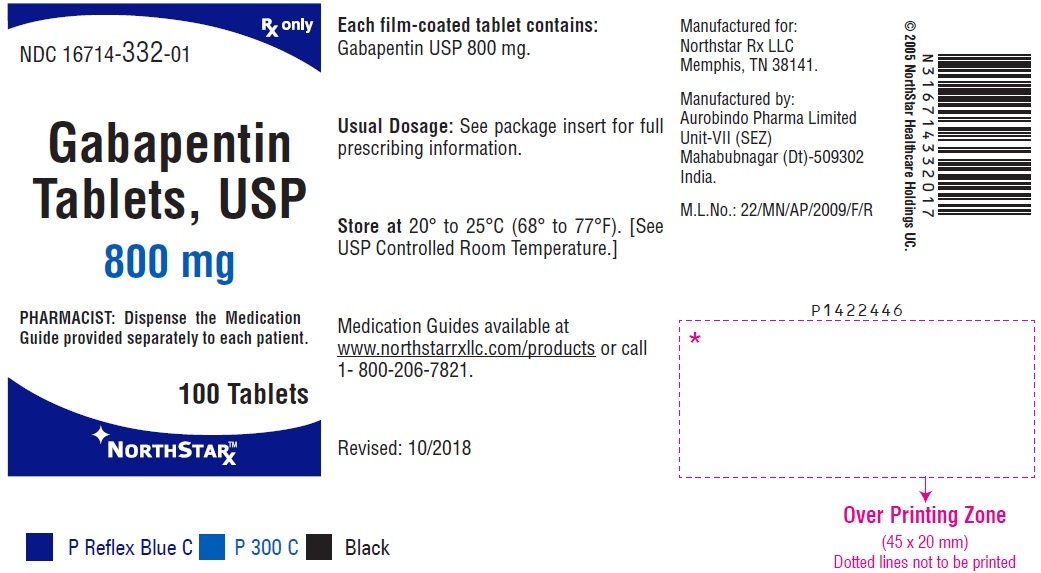
Abstract Objective This article reviews evidence-based psychiatric uses of gabapentin, along with associated risks. Method of Research An extensive literature review was conducted, primarily of articles searchable in PubMed, relating to psychiatric uses, safety, and adverse effects of gabapentin. Results Evidence supports gabapentin as a treatment for alcohol withdrawal and alcohol use Though gabapentin has many potential uses, it can cause side effects. Read more about 13 gabapentin side effects here. Gabapentin can have significant effects on mood, including the potential to cause abnormal changes such as depression, anxiety, and suicidal thoughts. While it is primarily prescribed for conditions like epilepsy and neuropathic pain, its impact on mood should not be underestimated, especially in individuals with preexisting mood disorders. Combination mood stabilizer therapy, the concomitant use of more than one agent, has become commonplace in the treatment of refractory bipolar disorder. This article is a review of the available data for combinations of mood stabilizers. Explore gabapentin's psychological side effects, learn to recognize symptoms, and discover management strategies for improved mental well-being during treatment. 1. Gabapentin may be effective for treating depression and anxiety, among other things. Although gabapentin was traditionally used to treat seizures, it is now sometimes used as a mood stabilizer for depression and bipolar disorder because it calms neurons in the brain, and it may be effective for anxiety too. Clinical trials even found that gabapentin may be a good alternative to Does gabapentin affect your mood and can it cause depressive symptoms? Gabapentin can affect mood and may cause depressive symptoms, though this is considered a rare side effect. While it is primarily used to treat seizures and nerve pain, some individuals have reported experiencing feelings of sadness or worsening depression during treatment. Abstract Objective: Gabapentin is commonly used off-label in the treatment of psychiatric disorders with success, failure, and controversy. A systematic review of the literature was performed to elucidate the evidence for clinical benefit of gabapentin in psychiatric disorders. Data sources: Bibliographic reference searches for gabapentin use in psychiatric disorders were performed in PubMed This article presents the negative side effects of gabapentin such as psychotic and depressive symptoms, which occur shortly after its use. The use of gabapentin in mood disorders is discussed through these side effects. Unveiling Gabapentin's Link to Depression and Suicidal Thoughts Investigating the association between gabapentin use and depression Gabapentin is primarily prescribed as an anticonvulsant for seizures and neuropathic pain, but its role in treating depression remains unclear. Despite being used off-label for mood disorders, significant evidence directly linking gabapentin to effective treatment Discover how gabapentin affects emotions, from potential benefits to side effects. Learn about managing mood changes and the importance of personalized care. Abstract Objective: Gabapentin is commonly used off-label in the treatment of psychiatric disorders with success, failure, and controversy. A systematic review of the literature was performed to elucidate the evidence for clinical benefit of gabapentin in psychiatric disorders. Key takeaways: Gabapentin is a medication that’s used to treat seizures, nerve pain from shingles, and restless leg syndrome. Despite previous marketing claims, there’s no evidence that gabapentin is a good treatment for bipolar disorder. The best treatment for bipolar disorder is therapy and a combination of other medications. These include mood stabilizers, anticonvulsants, and The combination of gabapentin and opioids has been associated with increased rates of hospitalization and even death. Finally, while the rate of gabapentin abuse in the general population appears to be low, there is a much higher risk for abuse of gabapentin in patients with a history of a substance use disorder, especially opioid use disorder. Gabapentin is a nerve pain medication and anticonvulsant that has proven to be effective for people who have hard-to-treat depression or other mood disorders. Gabapentin is not typically considered a mood enhancer. It is primarily used to treat nerve pain, seizures, and, in some cases, mental health conditions like insomnia or bipolar disorder. While gabapentin may help stabilize mood in certain situations, it works in different ways compared to traditional mood enhancers like antidepressants or mood stabilizers. Some people might experience Explore the intricate link between gabapentin and depression. Learn about its effects on mood disorders, mechanisms, and clinical implications.💊🧠 Explore gabapentin's role in mental health treatment, including its uses, benefits, and potential risks. Learn about dosage, effectiveness, and side effects. Objective: Gabapentin is commonly used off-label in the treatment of psychiatric disorders with success, failure, and controversy. A systematic review of the literature was performed to elucidate the evidence for clinical benefit of gabapentin in psychiatric disorders. Data sources: Bibliographic reference searches for gabapentin use in psychiatric disorders were performed in PubMed and Ovid Gabapentin is widely prescribed off label in medical practice, including psychiatry. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) warned of risks associated with gabapentin combined with central nervous system depressant (CNS-D) drugs, which are commonly prescribed in psychiatric treatment. This study examined off-label outpatient gabapentin use for psychiatric indications and concomitant CNS-D
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |