Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
/GettyImages-141483691-4cc225237a5945f8ab949d936f52c48e.jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 | 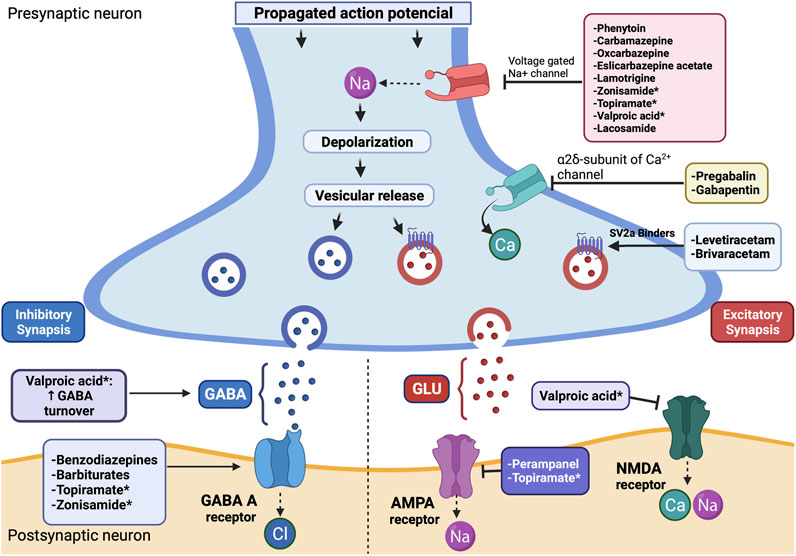 |
Gabapentin is a medication that has gained significant attention for its effectiveness in managing nerve pain. Originally developed as an anticonvulsant, it is now commonly prescribed for various conditions, including neuropathic pain, postherpetic neuralgia, and even restless legs syndrome. Understanding the appropriate dosage, uses, and potential side effects of Gabapentin is essential for Gabapentin is a medication primarily used to treat nerve pain by calming down the overactive nerves responsible for transmitting pain signals. It’s often prescribed for conditions like peripheral neuropathy, post-herpetic neuralgia (pain after shingles), and other nerve-related disorders. Other meds used are Pregablin (Lyrica) which is an epileptic like neurontin and also an antidepressant called Cymbalta. I take a combo of Amitriptyline (an older antidepressant used for nerve pain) and Neurontin. They work somewhat on me for pain however I am on a low dose of neurontin due to its sedating effects. Gabapentin and pregabalin are medicines that are used to treat epilepsy. The neural mechanisms of epilepsy and nerve damage pain have some commonality so the medicines are also prescribed for the treatment of neuropathic (nerve damage) pain such as pain after shingles, diabetes nerve pain and sciatica. They often considered together as ‘gabapentinoids’. Gabapentin is a prescription drug used to treat seizure disorders and nerve damage from shingles. Off label uses (non-FDA approved) include fibromyalgia, headaches, and hot flashes. Common side effects are fatigue, nausea, hostility, dizziness, and tremors. Gabapentin is not an opioid narcotic, but it does have signs and symptoms associated with drug misuse, addiction, and withdrawal symptoms The Link Between Gabapentin and Nerve Damage The primary concern regarding gabapentin revolves around its long-term use. While it's designed to treat nerve pain rather than cause it, chronic use may lead to certain complications that could mimic or exacerbate existing nerve issues. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication prescribed for a variety of conditions. Learn about its uses, side effects, and what you should know if you've been prescribed this medication. Gabapentin, which is used to treat seizures, nerve pain and restless leg syndrome might be linked with increased risk of dementia, a new study says. Gabapentin, originally developed to treat seizures, has become a widely prescribed medication for conditions such as nerve pain, restless leg syndrome, and anxiety disorders. While gabapentin can be effective in managing these conditions, prolonged use of the drug may lead to various long-term effects. What type of nerve pain is gabapentin approved to treat? Gabapentin is approved to treat nerve pain (neuralgia) that results from nerve damage. Gabapentin may be used to treat: Nerve pain caused by a herpes zoster viral infection, also known as shingles. This pain is called post-herpetic neuralgia (PHN), and it can be severe and chronic Abstract Background Gabapentin is commonly used to treat neuropathic pain (pain due to nerve damage). This review updates a review published in 2014, and previous reviews published in 2011, 2005 and 2000. Objectives To assess the analgesic efficacy and adverse effects of gabapentin in chronic neuropathic pain in adults. Search methods For this update we searched CENTRAL), MEDLINE, and Embase Gabapentin is commonly used to treat and prevent seizures in people with epilepsy or to treat nerve pain (postherpetic neuralgia) that can occur after a viral infection called shingles. Gabapentin is approved to treat seizures and postherpetic neuralgia, a type of nerve pain following shingles. It is thought to work by changing how nerves send messages to your brain. It is also used off-label to treat other neuropathic pain conditions. Gabapentin is also sometimes used to relieve the pain of diabetic neuropathy (numbness or tingling due to nerve damage in people who have diabetes), and to treat and prevent hot flashes (sudden strong feelings of heat and sweating) in women who are being treated for breast cancer or who have experienced menopause (''change of life'', the end of monthly menstrual periods). Talk to your doctor Background: Gabapentin is commonly used to treat neuropathic pain (pain due to nerve damage). This review updates a review published in 2014, and previous reviews published in 2011, 2005 and 2000. Objectives: To assess the analgesic efficacy and adverse effects of gabapentin in chronic neuropathic pain in adults. Search methods: For this update we searched CENTRAL), MEDLINE, and Embase for Short & Long-Term Effects of Gabapentin Gabapentin is a widely used medication, often prescribed for conditions like seizures, nerve pain, and RLS (restless leg syndrome). While it can provide relief for many people, gabapentin also carries potential risks. Both short-term and long-term use can lead to side effects that affect the body and mind. Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Gabapentin is available in both branded and generic forms. Receiving six or more prescriptions of the drug gabapentin for low back pain is associated with significantly increased risks of developing dementia and mild cognitive impairment (MCI)—29% and This review is an update of a review published in 2011, itself a major update of previous reviews published in 2005 and 2000, investigating the effects of gabapentin in chronic neuropathic pain (pain due to nerve damage). Antiepileptic drugs are The Connection Between Gabapentin and Neuropathy Gabapentin is often prescribed specifically to manage symptoms associated with neuropathy. However, some patients express concerns about whether gabapentin itself could contribute to nerve damage or worsen their condition. The question "Does Gabapentin Cause Neuropathy?" arises from these concerns.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
/GettyImages-141483691-4cc225237a5945f8ab949d936f52c48e.jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |