Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
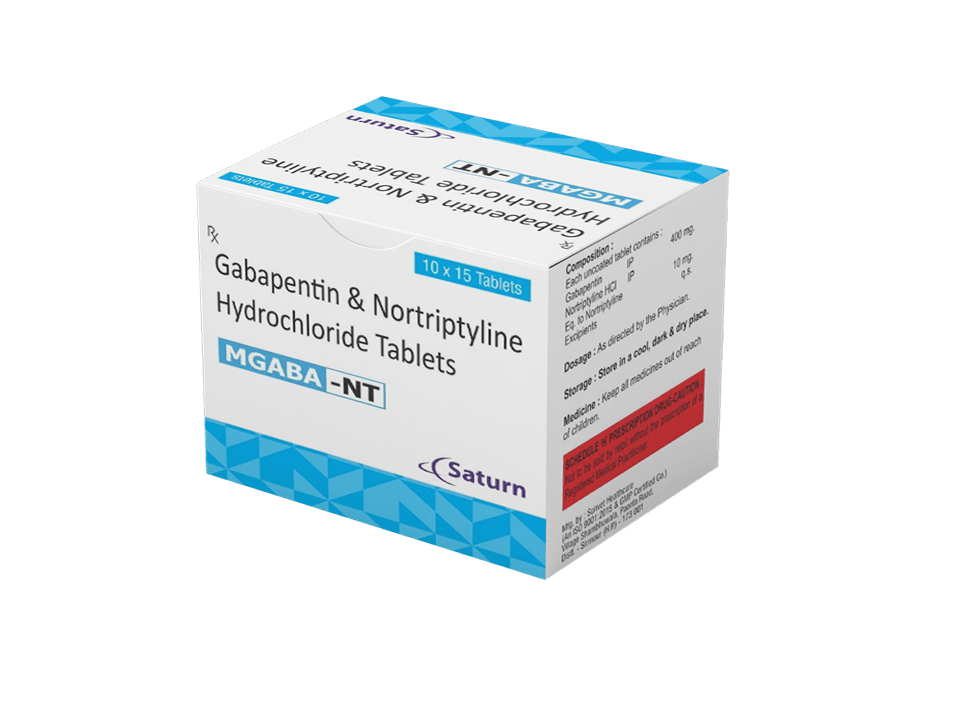
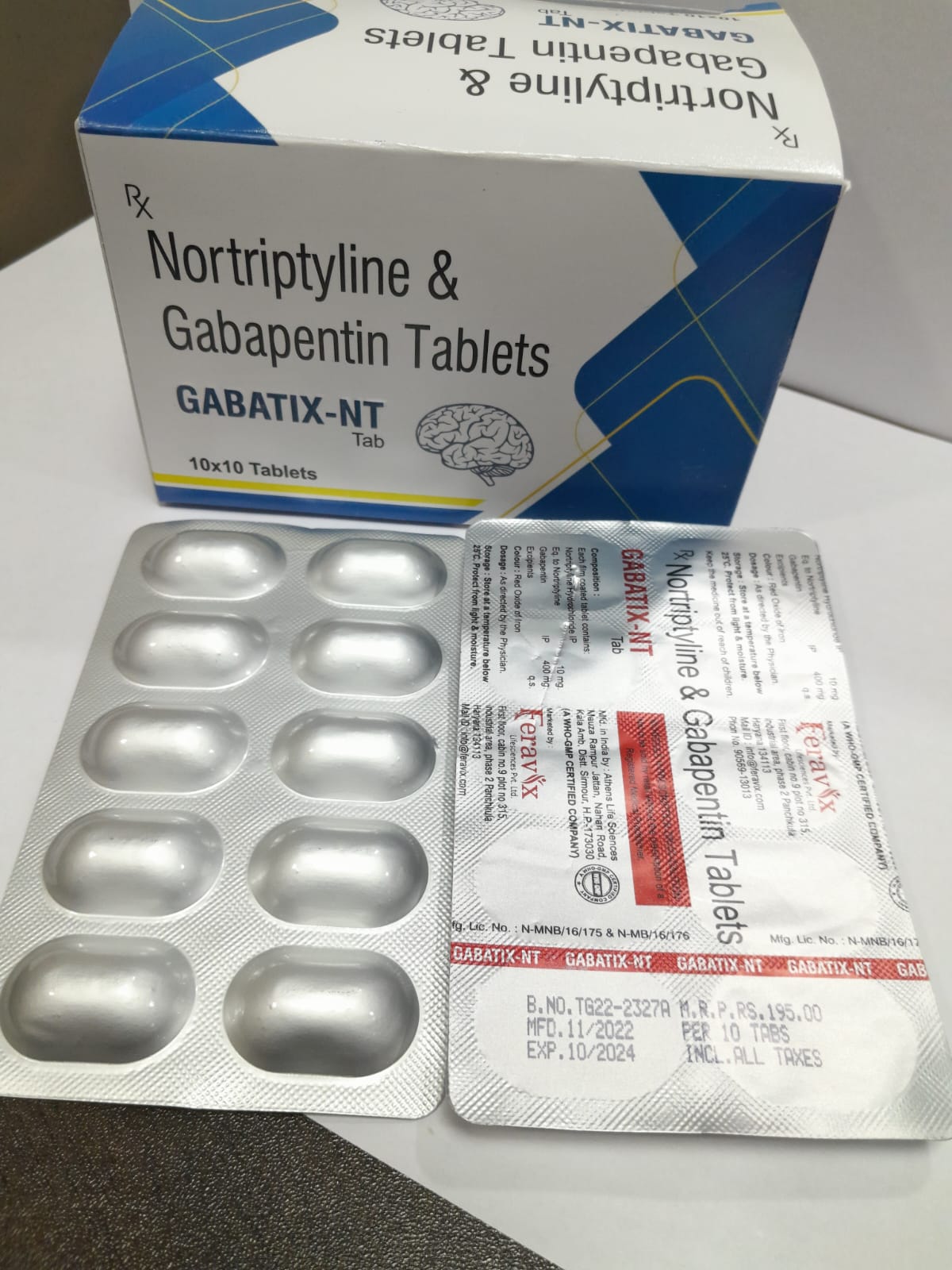
Neurontin (gabapentin) is used to treat seizures and nerve pain caused by the herpes virus. Includes Neurontin side effects, interactions and indications. Learn about Gabapentin Enacarbil, its uses for nerve pain and restless legs syndrome, dosage guidelines, side effects, and how it compares to Gabapentin. Gabapentin is commonly used to treat and prevent seizures in people with epilepsy or to treat nerve pain (postherpetic neuralgia) that can occur after a viral infection called shingles. 2.1 Dosage for Postherpetic Neuralgia - In adults with postherpetic neuralgia, gabapentin capsules may be initiated on Day 1 as a single 300 mg dose, on Day 2 as 600 mg/day (300 mg two times a Gabapentin is used to help control partial seizures (convulsions) in the treatment of epilepsy. This medicine cannot cure epilepsy and will only work to control seizures for as long as you continue to take it. Gabapentin is also used to manage a condition called postherpetic neuralgia, which is pain that occurs after shingles. Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Detailed Gabapentin dosage information for adults and children. Includes dosages for Restless Legs Syndrome, Epilepsy and Postherpetic Neuralgia; plus renal, liver and dialysis adjustments. For adults, your gabapentin dosage varies depending on your medical conditions and which form you’re taking. The maximum dosage is 3,600 mg per day. For children, the dosage is based on age and body weight. There are several ways to save on gabapentin. For instance, GoodRx can help you access Horizant at an exclusive cash price of about $170. Typical starting dosage: 900 mg per day (300 mg, three times per day, spaced evenly throughout the day). The usual maintenance dose is 900–1,800 mg per day, divided into three doses daily. Gabapentin is a prescription drug most commonly prescribed to relieve nerve pain following shingles in adults and the pain of postherpetic neuralgia. Learn about side effects, drug interactions, dosages, warnings, and more. Gabapentin is used with other medications to prevent and control seizures. It is also used to relieve nerve pain following shingles (a painful rash due to herpes zoster infection) in adults. Gabapentin is known as an anticonvulsant or antiepileptic drug. 2.1 Dosage for Postherpetic Neuralgia - In adults with postherpetic neuralgia, gabapentin capsules may be initiated on Day 1 as a single 300 mg dose, on Day 2 as 600 mg/day (300 mg two times a The starting dose is 300 mg three times a day. The recommended maintenance dose of gabapentin tablets is 300 mg to 600 mg three times a day. Dosages up to 2400 mg/day have been well tolerated in long-term clinical studies. Doses of 3600 mg/day have also been administered to a small number of patients for a relatively short duration, and have been well tolerated. Administer gabapentin three Gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) is a medicine used to treat partial seizures, nerve pain from shingles and restless leg syndrome. It works on the chemical messengers in your brain and nerves. Gabapentin is from a group of medicines called anticonvulsants. Medscape - Seizure dosing for Neurontin, Gralise (gabapentin), frequency-based adverse effects, comprehensive interactions, contraindications, pregnancy & lactation schedules, and cost information. Easy-to-read patient leaflet for Gabapentin Capsules. Includes indications, proper use, special instructions, precautions, and possible side effects. Gabapentin is used to control seizures, to treat nerve pain that can happen after having had shingles, and to treat a condition called restless legs syndrome. In addition to these FDA-approved uses, doctors sometimes prescribe gabapentin off-label. Gabapentin is a prescription anti-seizure (anti-convulsant) drug that is used for preventing seizures and for treating post-herpetic neuralgia, the pain that follows an episode of shingles. Doctors do not know how gabapentin works (the mechanism of action). Gabapentin structurally resembles the neurotransmitter gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA). Learn about gabapentin (Neurontin) usage and dosing. Read the latest news and reviews about the drug as well as potential side effects and popular alternatives. Includes Gabapentin indications, dosage/administration, pharmacology, mechanism/onset/duration of action, half-life, dosage forms, interactions, warnings, adverse reactions, off-label uses and more.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |