Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | +for+concussion.jpg) |
.jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
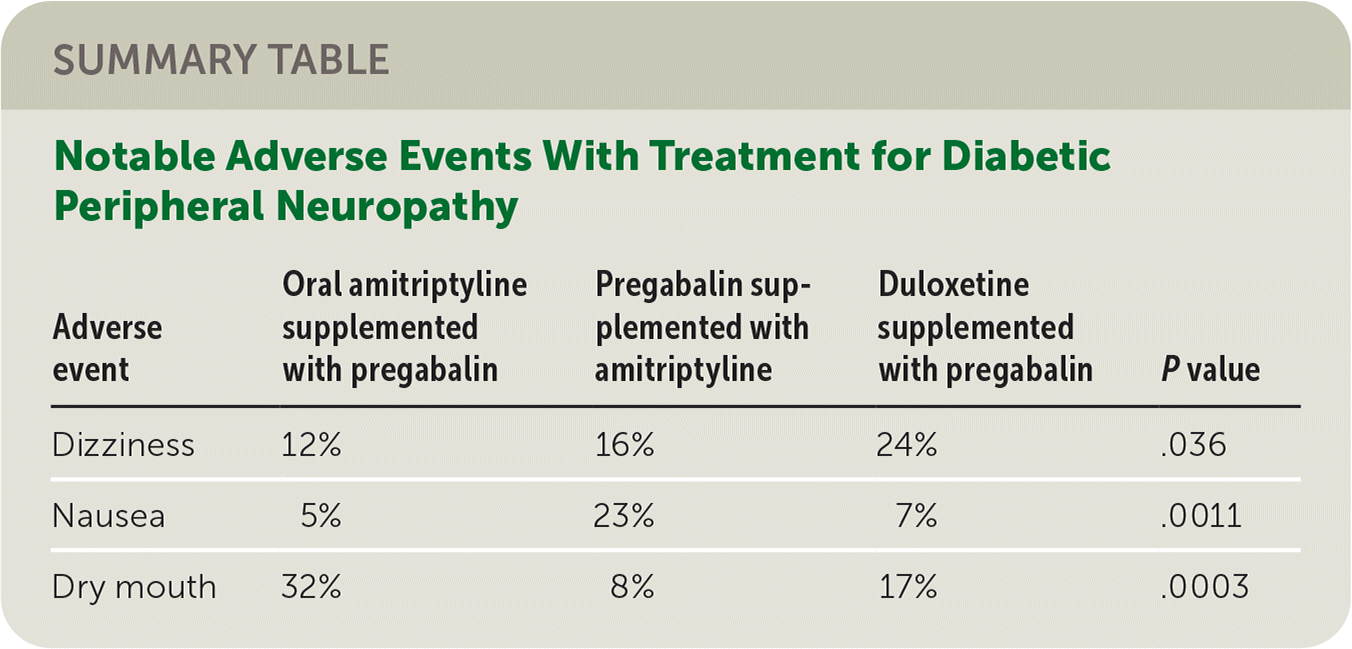
Explore gabapentin or amitriptyline for nerve pain, sciatica, and vulvodynia. Discover the differences, pros and cons, dosage, interactions, and real patient experiences. Gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica) have been found to improve sleep, but the mechanism of action is not clear. 47, 48 A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of adults who Amitriptyline is an tricyclic antidepressants (TCA) and is used to treat depression. Side effects of amitriptyline include fast heart rate, blurred vision, urinary retention, dry mouth, constipation, sexual dysfunction, weight gain or loss, and low blood pressure on standing (orthostatic hypotension). Safety of amitriptyline in pregnancy has not been established. Find patient medical information for Amitriptyline (Amitid, Elavil, Endep) on WebMD including its uses, side effects and safety, interactions, pictures, warnings, and user ratings Conclusion Both gabapentin and amitriptyline are important prescription medications that have a wide range of therapeutic uses, including pain management. They are routinely prescribed for neuropathic or nerve-related pain. Amitriptyline is a tricyclic antidepressant used to treat depression and, off-label, conditions like insomnia, anxiety, migraines, and chronic pain. Amitriptyline, sold under the brand name Elavil among others, is a tricyclic antidepressant primarily used to treat major depressive disorder, and a variety of pain syndromes such as neuropathic pain, fibromyalgia, migraine and tension headaches. [11] Due to the frequency and prominence of side effects, amitriptyline is generally considered a second-line therapy for these indications. [12][13 Amitriptyline is used to treat symptoms of depression. Amitriptyline is in a class of medications called tricyclic antidepressants. It works by increasing the amounts of certain natural substances in the brain that are needed to maintain mental balance. From the Guidelines Gabapentin is generally considered the first-line treatment for neuropathic pain and may be better tolerated than amitriptyline. For most patients, start with gabapentin: Initial dose: 300 mg once daily at bedtime Gradually increase to 300 mg three times daily Can be further increased up to 1800 mg daily in divided doses if needed If gabapentin is not effective or poorly Gabapentin vs. Amitriptyline hydrochloride: side effect and effectiveness comparison (a real world drug study) Summary: We compare the side effects and drug effectiveness of Gabapentin and Amitriptyline hydrochloride. Amitriptyline is often prescribed for sleep. While this is not an FDA-approved use of this medication, doctors may prescribe it for sleep and often do. There are benefits to taking amitriptyline Amitriptyline vs Gabapentin Amitriptyline, with the chemical formula C20H23N and CAS number 50-48-6, is a tricyclic antidepressant commonly prescribed for depression and anxiety disorders. It has also been used off-label to treat chronic pain, fibromyalgia, and insomnia due to its analgesic properties. For example, this trial tells us nothing about how well gabapentin, amitriptyline, or carbamazepine would have performed. Study subjects could be treated with a medication they had taken before the trial, even if it hadn’t worked for them. The quit rate included factors unrelated to how safe or effective the medication was. Amitriptyline is in the tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) drug classification and acts by blocking the reuptake of both serotonin and norepinephrine neurotransmitters. Amitriptyline is an FDA-approved medication to treat depression in adults. The non-FDA approved indications are anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder, insomnia, chronic pain (diabetic neuropathy, fibromyalgia), irritable bowel Amitriptyline is a medication that treats depression. It increases the amount of serotonin and norepinephrine in your brain. Description Amitriptyline is used to treat symptoms of depression. It works on the central nervous system (CNS) to increase levels of certain chemicals in the brain. This medicine is a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA). This medicine is available only with your doctor's prescription. Compare Amitriptyline vs Gabapentin head-to-head with other drugs for uses, ratings, cost, side effects and interactions. Amitriptyline Patient Tips Medically reviewed by Carmen Pope, BPharm. Last updated on Oct 3, 2023. How it works Upsides Downsides Bottom Line Tips Response/effectiveness Interactions FAQ 1. How it works Amitriptyline may be used to treat depression or off-label to relieve chronic pain, fibromyalgia, or insomnia. Experts are unsure exactly how amitriptyline works, although historically it was Gabapentin 600 mg per day and increased upto a maximum of 1800 mg per day, at bed time. Amitriptyline 25 mg per day and increased upto a maximum of 75 mg per day, at bed time. There were four scheduled visits during the study. All study participants were given a diary and necessary scales (Visual analog scale and sleep interference scale). Common side effects of Amitriptyline include: drowsiness, dizziness, dry mouth, blurred vision, constipation, weight gain, and trouble urinating Serious side effects of Amitriptyline include: easy bruising, unusual bleeding, persistent heartburn, shaking, mask-like facial expressions, muscle spasms, severe stomach pain, decreased sexual ability or desire, enlarge or painful breasts, black
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | +for+concussion.jpg) |
.jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |