Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
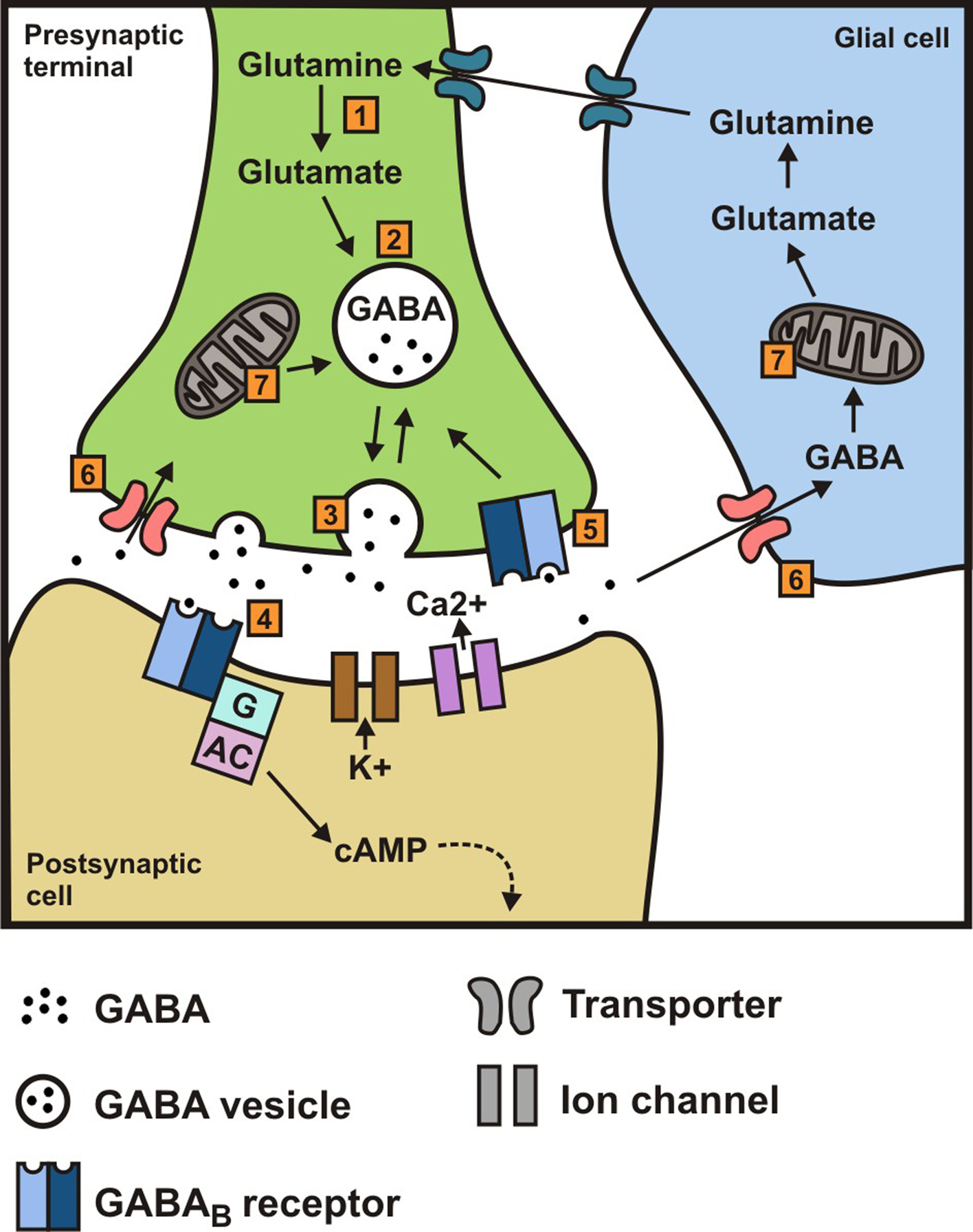 | 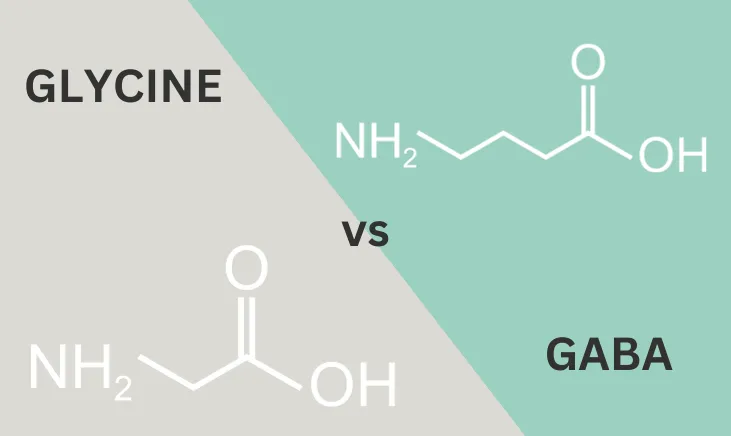 |
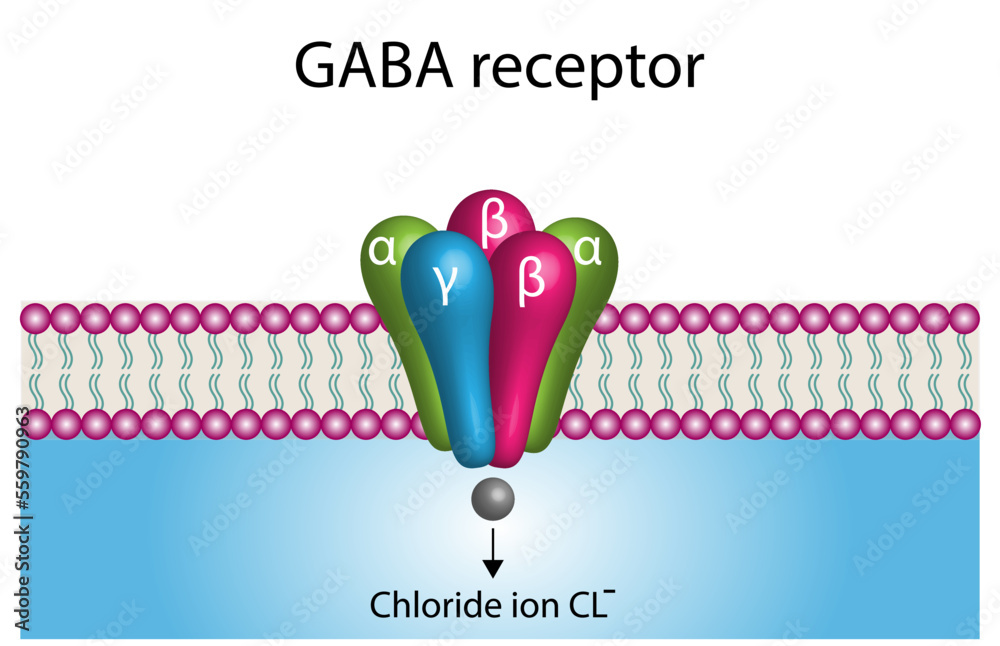
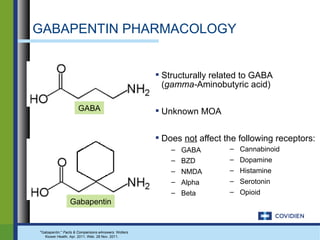
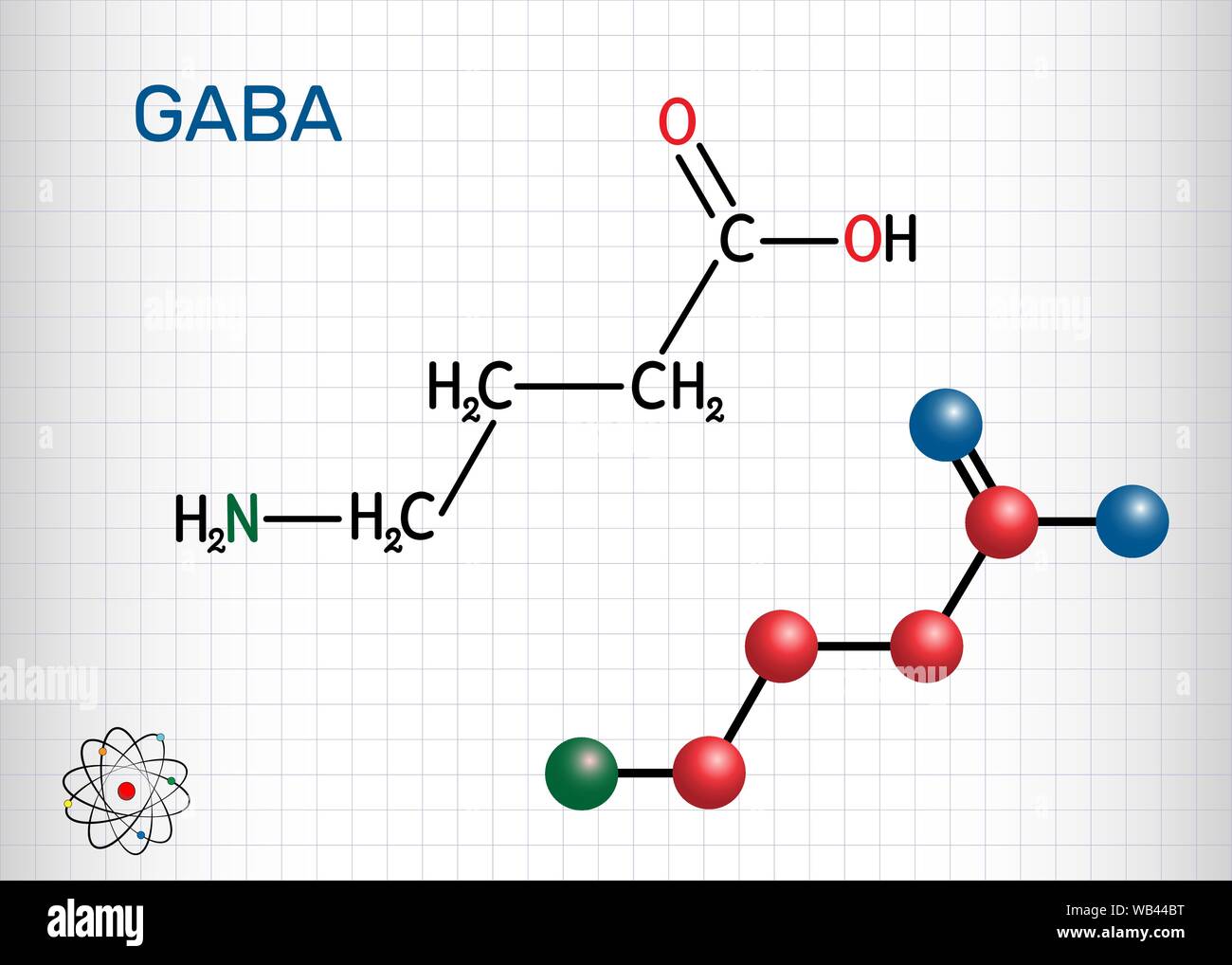
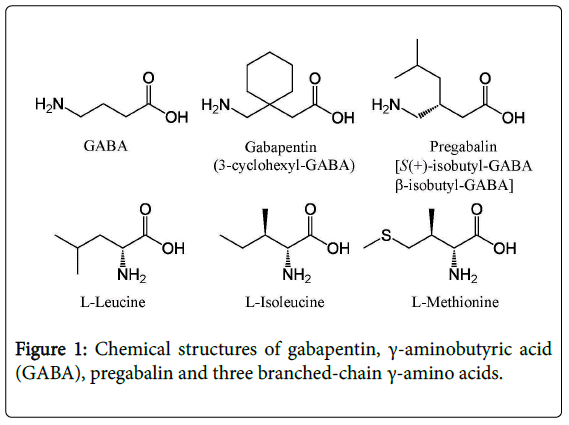
Gamma Aminobutyric Acid vs. Gabapentin: Understanding Their Roles and Differences Gamma Aminobutyric Acid (GABA) and Gabapentin are two substances that often come up in discussions about neurological health, anxiety disorders, and pain management. We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. GABA, or gamma-aminobutyric acid, is an amino acid supplement and neurotransmitter that plays a crucial role in the central nervous system. It helps calm the mind and reduce anxiety by inhibiting the activity of certain brain cells. GABA vs. Gabapentin What's the Difference? GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) and Gabapentin are both substances that affect the central nervous system, but they have different mechanisms of action and uses. GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter in the brain that inhibits or slows down nerve activity, helping to reduce anxiety and promote relaxation. On the other hand, Gabapentin is a Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and glutamate are implicated in numerous neuropsychiatric and substance abuse conditions, but their spectral overlap with other resonances makes them a challenge to quantify in humans. Gabapentin, marketed for the GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) and gabapentin are different substances with some similarities. GABA is a neurotransmitter in the central nervous system that controls nervous system excitability, while gabapentin is a drug designed as a structural analog of GABA. GABA, short for gamma-aminobutyric acid, is the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system (CNS). It plays a crucial role in regulating neuronal activity, reducing excitation, and promoting relaxation. By binding to specific receptors in the brain, GABA inhibits neurons firing, leading to calming effects and promoting sleep. GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) and gabapentin are two substances often discussed in the context of brain health and neurological treatments. While they share some similarities in their impact on the nervous system, they are fundamentally different in terms of their structure, function, and applications. This distinction is crucial for understanding their respective roles and benefits. Dosage Considerations: If someone decides to try a GABA supplement, it's essential to follow recommended dosages and guidelines. Excessive intake of GABA supplements may lead to side effects or interactions with medications. Dietary sources of Gamma-aminobutyric acid Here are you can find some food sources that contain GABA: Fermented Foods. Explore the differences between Gamma Aminobutyric Acid (GABA), a neurotransmitter, and Gabapentin, a medication, despite their similar names. Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is an inhibitory neurotransmitter in your brain, meaning it slows your brain’s functions. GABA is known for producing a calming effect. Gabapentin, marketed for the treatment of seizures and neuropathic pain, has been shown to increase in vivo GABA concentration in the brain of both rodents and humans. Conclusion: Key Takeaways on GABA vs Gabapentin In conclusion, while Gamma Aminobutyric Acid and Gabapentin may share structural similarities and a focus on neurologic functions, they are distinctly different in their action, uses, and safety profiles. What is Gaba? Gaba has active ingredients of gaba (gamma - aminobutyric acid). It is often used in stress and anxiety. eHealthMe is studying from 425 Gaba users for the drug's side effects, drug interactions, effectiveness and more. Check Gaba in the real world. What is Gabapentin? Gabapentin has active ingredients of gabapentin. It is often used in peripheral neuropathy. eHealthMe is studying The entire review is about gabapentin/neurontin and is not about the amino acid GABA at all, even though the search terms used for this paper included: gamma-aminobutyric acid and gaba. This is just one example of many such papers. By Forest Tennant, PNN Columnist “GABA” is short for the neurotransmitter, gamma aminobutyric acid. GABA is the natural (endogenous) biochemical substance in the brain, spinal cord, and all nerves that control electrical conduction. Without proper GABA function, we experience pain. GABA and gabapentin are two fundamentally different compounds that share some important similarities. The first, gamma- or γ-aminobutyric acid (or GABA), is a neurotransmitter that serves as a chemical messenger in the brain. Gabapentin was developed for treating epilepsy by alleviating the excitability of a patient’s nervous system. This also helps with other disorders with neuropathic pain, for example fibromyalgia, insomnia, and bipolar disorder. Another name for gabapentin is Neurontin, and this medication has no effect on the amount of GABA in the brain. Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is a neurotransmitter with a crucial role in the human brain and body. It's recognized for its calming and relaxing effects, and many people use GABA supplements to unwind, alleviate stress, and enhance sleep. Gabapentin, while structurally similar to GABA, is a medication with distinct effects and applications. This blog post delves into the benefits of GABA
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |