Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
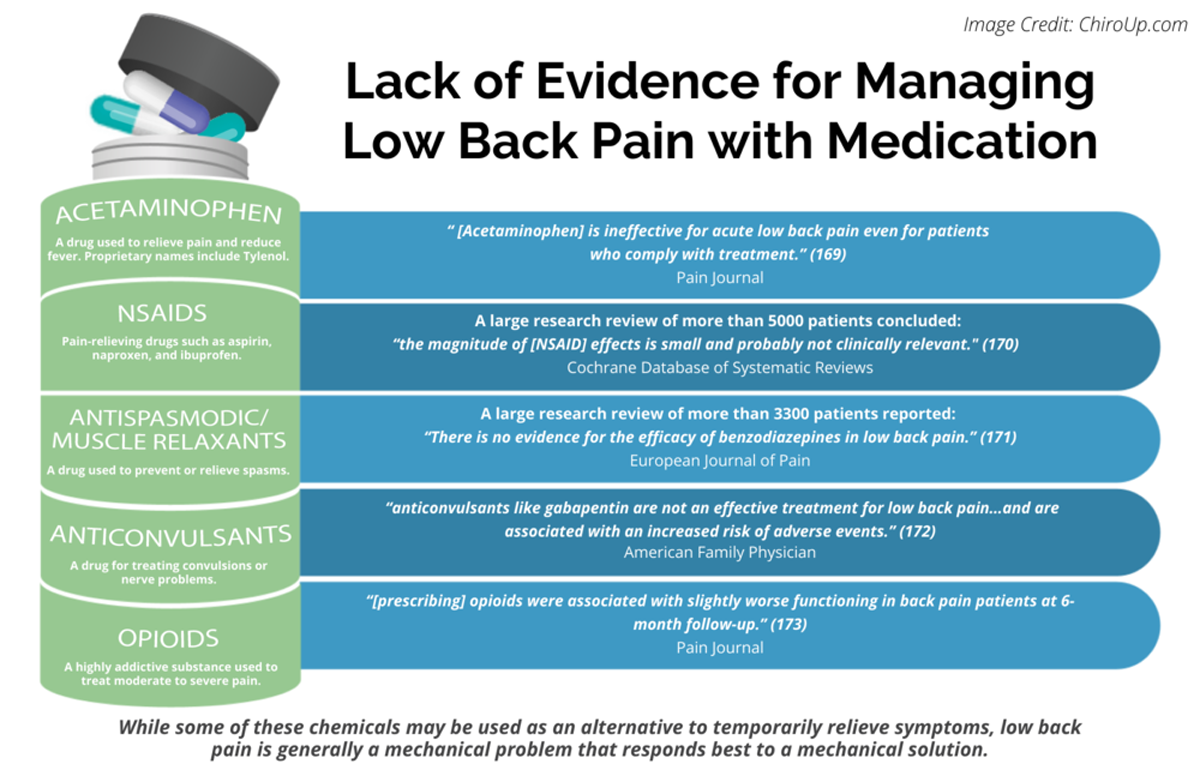
The use of anticonvulsants (e.g., gabapentin, pregabalin) to treat low back pain has increased substantially in recent years despite limited supporting evidence. We aimed to determine the efficacy and tolerability of anticonvulsants in the treatment Although the underlying mechanism of pain is predominantly non-specific, many argue that there is a substantial neuropathic pain element. Neuropathic pain is more severe, with significant disability. Gabapentinoids, including gabapentin and pregabalin, have proven efficacy in some neuropathic pain conditions. In recent years—especially as concern over the opioid epidemic has increased—doctors have turned to prescribing the gabapentinoids pregabalin (Lyrica) and gabapentin (Neurontin, others), which have demonstrated benefit for neuropathic pain conditions but not for nonspecific CLBP. Chronic low back pain (CLBP) is widely prevalent, and in majority it is nonspecific (no clear etiology) in nature. Among chronic conditions, CLBP is noted to be the leading cause of years lived with disability. Gabapentin (GB) and Pregabalin (PG) have been shown to be helpful in neuropathic pain conditions, such as diabetic neuropathy. Gabapentin works in the same way that more interventional treatment approaches like steroid injections do in the case of sciatica, but without some of the downsides that these treatments have, such as injection site injury. How Do I Get My Sciatic Nerve to Stop Hurting – Relieving Sciatica Pain Immediately Other Types of Neuropathic Pain Gabapentin is a drug used to treat chronic lower back Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant used to treat nerve related back pain, such as sciatica. Learn more about how gabapentin is used in sciatica treatment. Gabapentin, an effective analgesic for selected neuropathic pain syndromes, is widely prescribed for non-neuropathic conditions, like chronic low back pain, although there are no published randomized trials supporting this practice. We assessed the efficacy of gabapentin for chronic back pain in a 12-week, two-arm, placebo controlled, randomized clinical trial comparing gabapentin (up to 3600 Back pain has an impact on daily life and drives individuals to seek effective treatments, leading many healthcare providers to turn to gabapentin. Originally designed as an anti-seizure medication, gabapentin has found application beyond its initial purpose, addressing not only back pain but also nerve pain, postsurgical discomfort, and occasional anxiety. Specifically beneficial for those The use of anticonvulsants like gabapentin (Neurontin) for painful conditions has increased greatly in recent years. This review finds good evidence that these drugs are not an effective treatment Is Gabapentin effective for all types of back pain? Gabapentin can be very effective in treating various types of back pains, including: Gabapentin for Sciatica: Sciatica, marked by sciatic nerve compression, presents as lower back pain radiating down one or both legs. While exercise, physical therapy, and NSAIDs prove effective, a study with 747 participants found gabapentin to be less Abstract Background and objective: Chronic Low Back Pain (CLBP) is very common, with a lifetime prevalence between 51% and 80%. In majority, it is nonspecific in nature and multifactorial in etiology. Pregabalin (PG) and Gabapentin (GB) are gabapentinoids that have demonstrated benefit in neuropathic pain conditions. Chronic low back pain (CLBP) is widely prevalent, and in majority it is nonspecific (no clear etiology) in nature. Among chronic conditions, CLBP is noted to be the leading cause of years lived with disability. Gabapentin (GB) and Pregabalin (PG) have been shown to be helpful in neuropathic pain conditions, such as diabetic neuropathy. Gabapentin was originally developed as an anti-seizure medication. But healthcare professionals don’t just prescribe it for back pain. It’s also used for nerve pain, postsurgical pain, and occasionally anxiety. Let’s take a closer look at what the research says about gabapentin for back pain, how to take it, and when to consider further care. Certain medications are safer and more effective than others for treating spine pain in older adults, according to a recent study. Among these are the over-the-counter drugs acetaminophen (Tylenol) and ibuprofen (Advil) and some nerve pain drugs, muscle relaxants, and antidepressants. Background Chronic low back pain (CLBP) is a global health problem, and gabapentin and pregabalin are often used in the treatment of patients without associated radiculopathy or neuropathy. Therefore, determining their efficacy and safety is of Discover if gabapentin can help alleviate back pain. Learn about its effectiveness, dosage, and potential benefits for lower back pain relief. Background: Chronic low back pain (CLBP) is a global health problem, and gabapentin and pregabalin are often used in the treatment of patients without associated radiculopathy or neuropathy. Gabapentin is not effective for the treatment of radicular low back pain and is associated with adverse effects. Back pain is the leading cause of disability in the US (1). With an overwhelming number of available treatments, choosing a medication to treat your back pain can be difficult. If your back pain is nerve-related, then the anticonvulsant drug gabapentin may be a good choice for you. This article will explain how gabapentin works, detail its uses, and go over potential side effects, so that you Gabapentin is prescribed for analgesia in chronic low back pain, yet there are no controlled trials supporting this practice. This randomized, two-arm, 12-week, parallel group study compared gabapentin (forced titration up to 3600 mg daily) to inert
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |