Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/gabapentin-withdrawal-symptoms-timeline-and-treatment-4176217-FINAL-updated-61b1abea5c98489fa075d8fdce211c50.jpg) |
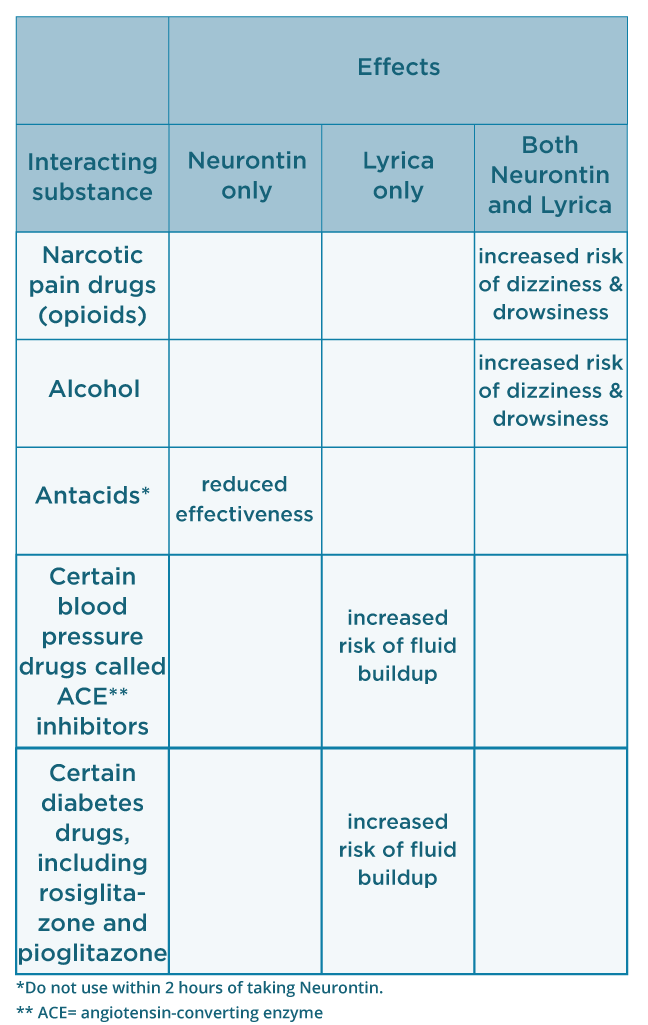 |  |
Gabapentin is prescribed to manage conditions affecting the nervous system, helping to alleviate chronic pain, control seizures, and improve neurological discomfort. Gabapentin alters nerve signaling in the brain to reduce pain and seizures. Beyond its approved uses, Gabapentin is increasingly prescribed off-label for conditions like anxiety, migraines, and fibromyalgia. According to a report Recurrent migraines can be functionally disabling and can impair quality of life. The disabling nature of migraine headaches leads to frequent visits to outpatient clinics and emergency department facilities, causing significant health and financial burdens. Headaches fall in the top five causes of emergency department visits and the top twenty reasons for outpatient visits.[1] The overall Gabapentin isn’t usually prescribed as a primary migraine preventative. It’s typically added to work in conjunction with other therapies, or used when other medications haven’t worked for the patient. As a preventative measure rather than an acute treatment, gabapentin needs to be taken continuously. Gabapentin for Migraines Is an “Off-Label” Use When a drug is used for something Gabapentin is a drug that’s approved to help prevent seizures in people with epilepsy and treat nerve pain from shingles. It’s also sometimes used off-label for migraine prevention. Gabapentin is safe for cats and is commonly prescribed by veterinarians to treat pain, anxiety, and feline hyperesthesia syndrome. It has a low risk of side effects when taken at the correct dosage. Unlocking Gabapentin: What Its Prescription for Your Chronic Headaches Really Signifies Understanding your treatment journey when Gabapentin is introduced for persistent headache management. A new study warns that this prescription drug can significantly increase the risk of dementia and mild cognitive impairment in people taking it for chronic low back pain. Gabapentin is not typically known to cause migraines, but individual reactions can vary. Gabapentin, a medication primarily used to treat nerve pain and seizures, has gained attention for its potential side effects. While it's often prescribed for conditions like neuropathic pain and epilepsy, many individuals wonder about its impact on headaches and migraines. Gabapentin is an effective prophylactic agent for patients with migraine. In addition, gabapentin appears generally well tolerated with mild to moderate somnolence and dizziness. Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Gabapentin is available in both branded and generic forms. Like many other medications used off-label as a treatment for headaches and migraine, gabapentin can be effective when used in combination with other prescribed medications, treatment options, and lifestyle changes as recommended by your doctor. Tension-type, migraine, and cluster headaches are the most common primary headaches. Primary headaches are differentiated by clinical criteria from the International Classification of Headache However, the guidelines state that the evidence is inadequate to recommend the use of gabapentin for migraine prevention. 6 Because gabapentin is not effective and commonly causes adverse effects Migraine headaches are a debilitating condition that affects approximately 1% of the US population. Goals of migraine prophylaxis include reduction in headache severity and frequency, improved Neurontin is a drug used to treat seizures in children and adults. Here's what you should know before taking Neurontin, including its uses and side effects. Gabapentin (GBP), originally an antiepileptic drug, is more commonly used in the treatment of pain, including headache disorders. Off-label GBP is used in headache disorders with some success, some failure, and much debate. Due to this ambiguity, a clinical evidence literature review was performed investigating GBP's efficacy in headache disorders. Therefore, while gabapentin does not directly interact with GABA receptors, it exerts its effects by influencing GABA synthesis and release, which is relevant to its therapeutic use in conditions such as epilepsy and neuropathic pain [4]. The usefulness of gabapentin in vestibular migraine has not been demonstrated but deserves consideration. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication prescribed for a variety of conditions. Learn about its uses, side effects, and what you should know if you've been prescribed this medication. Gabapentin is an anti-seizure drug that is sometimes prescribed to help prevent migraines. However, there is conflicting research on whether it's effective for this use.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/gabapentin-withdrawal-symptoms-timeline-and-treatment-4176217-FINAL-updated-61b1abea5c98489fa075d8fdce211c50.jpg) |
 |  |