Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | /GettyImages-936697886-748e5f0391de4a5b9385547f30c8de72.jpg) |
 |  |
 |
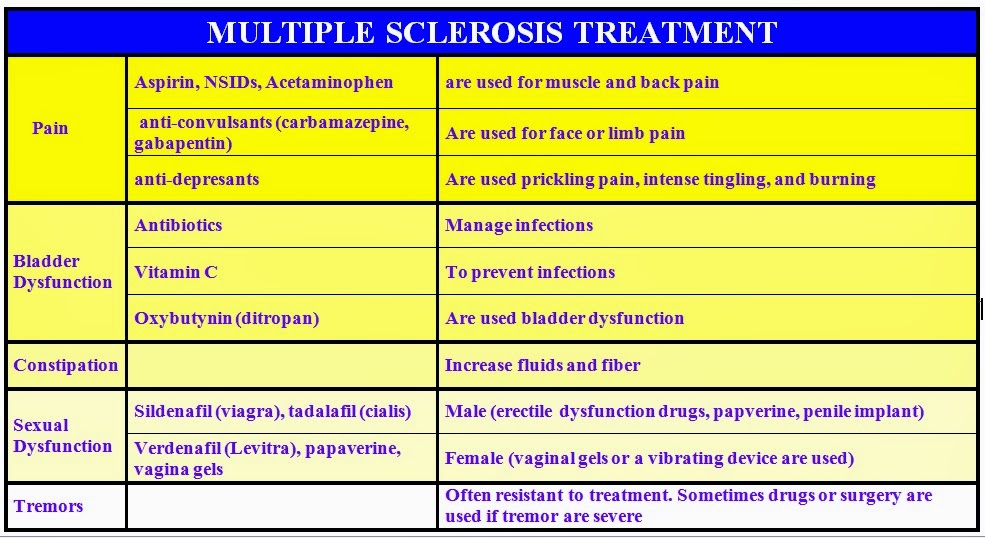
Gabapentin is a medication that has been widely used for the management of multiple sclerosis (MS) symptoms, particularly for the treatment of neuropathic pain, spasticity, and seizures. While it is not a disease-modifying therapy, gabapentin can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals living with MS. Gabapentin, a medication primarily used to treat epilepsy and nerve pain, has been found to have a significant impact on managing symptoms of Multiple Sclerosis (MS). MS is a chronic and often disabling autoimmune disease that affects the central nervous system, causing a wide range of symptoms including pain, fatigue, and difficulty with coordination and balance. The use of gabapentin in MS Treatment for MS pain involves antidepressants and antiseizure medications, but they aren’t the only options. Learn how to manage MS pain. Gabapentin is not approved for use in MS in the U.S., but is often used off-label to manage symptoms such as nerve pain and spasticity. Gabapentinoids, used off-label for MS pain, raise a risk of serious respiratory problems in patients also taking opioids or with lung issues, the FDA warns. Gabapentin is a medication used to treat nerve symptoms in multiple sclerosis such as numbness, muscle twitching, and nerve pain. Originally approved as an anticonvulsant drug for epilepsy, gabapentin is now prescribed off-label to help manage multiple sclerosis symptoms including neuropathic pain and muscle spasms. Abstract Risk of dementia following gabapentin prescription in chronic low back pain patients Introduction Gabapentin is widely used to treat chronic pain, but its association with cognitive decline and dementia remains unclear. This study examined whether gabapentin prescription is associated with dementia in adults with chronic low back pain. Methods We conducted a retrospective cohort study Gabapentin is a drug used in multiple sclerosis to treat neuropathic pain, such as trigeminal neuralgia, or abnormal skin sensations, and spasticity. Find out more about Gabapentin in this A-Z entry. Multiple sclerosis can cause seizures due to brain lesions and chronic inflammation that disrupts connections in the central nervous system. Antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) are used to treat seizures in MS, with doctors often prescribing them for other MS symptoms like spasticity, nerve pain, and the MS hug, and both older and newer AED options are available. If you experience side effects from Gabapentin is a medication that has been widely used to treat various neurological disorders, including multiple sclerosis (MS). MS is a chronic and often disabling disease that affects the central nervous system, causing symptoms such as pain, numbness, and muscle weakness. In this article, we will explore the effectiveness of gabapentin for MS pain management and discuss its benefits and Overview of pain in patient with multiple sclerosis and the Mellen Center’s approach to management. This article provides an overview of gabapentin and MS, addressing its uses in alleviating symptoms such as nerve pain, its potential side effects, and other relevant considerations for individuals considering or currently using this medication, as alternatives to more traditional MS treatments. Gabapentin is a medication that has been widely used to treat various neurological conditions, including epilepsy, nerve pain, and anxiety disorders. In recent years, its potential benefits in managing symptoms associated with multiple sclerosis (MS) have gained significant attention. A big problem in MS practice is the so-called gabapentinoids (gabapentin and pregabalin). These are used for pain management, spasticity, restless leg syndrome, nocturnal spasms, partial seizures, hiccoughs, chronic cough, pruritus & itch, paraesthesia, the MS hug, Lhermitte’s phenomenon, oscilopsia, nystagmus, sedation, anxiety, etc Treatment of Pain Treating pain in patients who have MS should be based on the ABC model. Anti-convulsants: Pregabalin,⁶ gabapentin are often used first-line for most neuropathic pain conditions (no significant drug interaction risk; improved sleep). Topiramate, lamotrigine, and levetiracetam are also used.⁷ Carbamazepine is usually first-line therapy for trigeminal neuralgia, but adverse Gabapentin, an anticonvulsant, is used to treat neuropathic pain caused by multiple sclerosis (MS). It targets ion channels, especially calcium channels, in the central nervous system and spinal cord to reduce pain signals. Clinical trials and systematic reviews support its efficacy in managing pain, disability, and quality of life in MS patients. Introducing Gabapentin – your key to managing MS symptoms. Gabapentin is a medication commonly used to treat nerve pain, and it has shown promising results in managing the symptoms of MS. With its unique mechanism of action, Gabapentin targets the pain signals in the central nervous system, providing relief to those with MS. What is Gabapentin? Gabapentin has active ingredients of gabapentin. It is often used in peripheral neuropathy. eHealthMe is studying from 322,868 Gabapentin users for the drug's side effects, drug interactions, effectiveness and more. Check Gabapentin in the real world. What is Multiple sclerosis? In multiple sclerosis (MS), chronic neuropathic pain is one of the most frequent symptoms that dramatically reduces the quality of life of MS patients. Current treatment strategies include antidepressants, anticonvulsants, and cannabinoid drugs. However, the efficacy of these drugs varies between patients. Neurontin is sometimes prescribed off-label to treat neuropathic pain associated with multiple sclerosis (MS). Neurontin is also referred to by its drug name, gabapentin. Neurontin is an anticonvulsant, or drug that controls seizures. Neurontin is believed to work on certain types of pain by reducing pain signals sent by damaged nerves.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | /GettyImages-936697886-748e5f0391de4a5b9385547f30c8de72.jpg) |
 |  |
 |