Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |
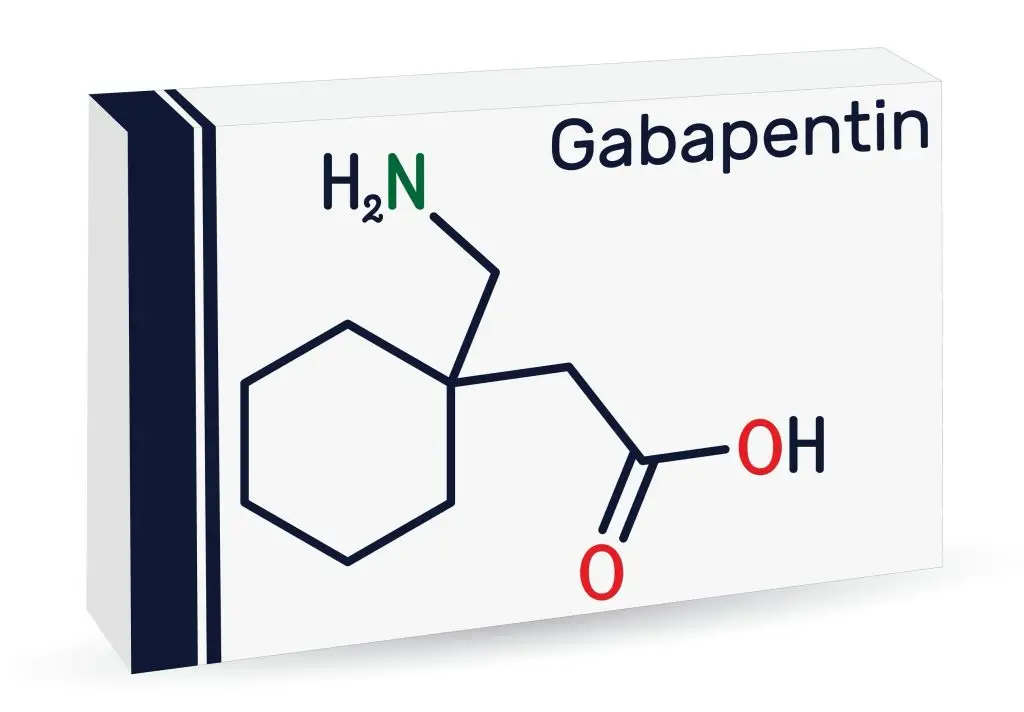
Explore gabapentin's potential psychological side effects, factors influencing mental health impacts, and strategies for managing risks in this comprehensive guide. This article presents the negative side effects of gabapentin such as psychotic and depressive symptoms, which occur shortly after its use. Conclusion: Gabapentin could be used successfully as an adjunct to novel antipsychotics in partially responsive schizophrenia. However, large controlled studies are needed to examine the effectiveness of gabapentin in psychotic disorders. Keywords: schizophrenia, refractory, adjunctive treatment, gabapentin, risperidone, olanzapine Gabapentin is commonly used off-label in the treatment of psychiatric disorders with success, failure, and controversy. A systematic review of the literature was performed to elucidate the evidence for clinical benefit of gabapentin in psychiatric Cyclohexanecarboxylic Acids / therapeutic use* Drug Administration Schedule Drug Resistance Drug Therapy, Combination Gabapentin Haloperidol / therapeutic use Humans Male Schizophrenia / drug therapy* Schizophrenic Psychology Treatment Outcome Violence / prevention & control Violence / psychology gamma-Aminobutyric Acid / therapeutic use* This article presents the negative side effects of gabapentin such as psychotic and depressive symptoms, which occur shortly after its use. The use of gabapentin in mood disorders is discussed through these side effects. Request PDF | On Jan 1, 2003, Karin Jablonowski and others published Gabapentin-induced paradoxical exacerbation of psychosis in a patient with schizophrenia [6] | Find, read and cite all the Gabapentin is widely prescribed off label in medical practice, including psychiatry. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) warned of risks associated with gabapentin combined with central nervous system depressant (CNS-D) drugs, which are commonly prescribed in psychiatric treatment. This study examined off-label outpatient gabapentin use for psychiatric indications and concomitant CNS-D This article examines the role of gabapentin in antipsychotic treatment, discussing its effectiveness, potential side effects, and how it can be used in conjunction with other medications to manage symptoms of schizophrenia and other psychiatric disorders. The combination of gabapentin and opioids has been associated with increased rates of hospitalization and even death. Finally, while the rate of gabapentin abuse in the general population appears to be low, there is a much higher risk for abuse of gabapentin in patients with a history of a substance use disorder, especially opioid use disorder. This article presents the negative side effects of gabapentin such as psychotic and depressive symptoms, which occur shortly after its use. The use of gabapentin in mood disorders is discussed through these side effects. Abstract Background There is a great need in the treatment of schizophrenia for a drug, or drug combinations, to improve clinical response with fewer serious side effects. The objective of this study was to explore the therapeutic effects and tolerability of the anticonvulsant gabapentin as an adjunctive in the treatment of patients with partially responsive schizophrenia. Methods Ten Gabapentin is commonly used off-label in the treatment of psychiatric disorders with success, failure, and controversy. A systematic review of the literature was performed to elucidate the evidence for clinical benefit of gabapentin in psychiatric disorders. This article reviews evidence-based psychiatric uses of gabapentin, along with associated risks. An extensive literature review was conducted, primarily of articles searchable in PubMed, relating to psychiatric uses, safety, and adverse effects of These reports illustrate the breadth of GABA-related abnormalities in schizophrenia, with alterations identified in multiple brain regions using a variety of techniques. Thus, it appears timely to comment on certain aspects of what we currently know, and do not know, about GABA neurotransmission in the disease process of schizophrenia. Psychotic symptoms including persecutory delusion occurred and about 12 hours after the onset of symptoms the patient discontinued gabapentin for 24 hours. Explore gabapentin's role in mental health treatment, including its uses, benefits, and potential risks. Learn about dosage, effectiveness, and side effects. FROM THE EDITOR To keep up-to-date with the voluminous psychiatric literature, I scan many psychiatric and neuroscience publications in search of articles that pull me in for a deeper look. Recently, I skimmed the titles of a weekly email newsletter I receive and was immediately drawn to the first article: “Before You Prescribe Gabapentin, Consider These Risks.” 1 The first sentence of the Gabapentin and Acute psychosis - a phase IV clinical study of FDA data Summary: Acute psychosis is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are male, 50-59 old, have been taking the drug for < 1 month also take Budesonide, and have Muscle spasms. Gabapentin-Induced Paradoxical Exacerbation of Psychosis in a Patient With Schizophrenia Dear Editor: Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant that is in-creasingly prescribed to patients with schizophrenia (1). Uses of anticonvul-sants in this population have traditionally included antipsychotic augmentation and control of aggression and impulsivity (1).
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |