Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
+are+the+best-studied+drugs+for+neuropathic+pain.+Optimal+analgesia+requires+treatment+of+depression..jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
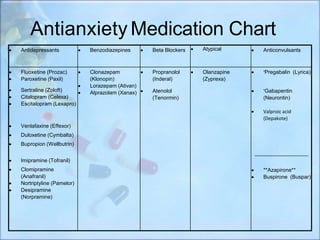
Can gabapentin cause brain fog? Yes, gabapentin can cause brain fog in some individuals. Cognitive issues, such as a decrease in alertness, may occur as side effects, often accompanied by dizziness and drowsiness, affecting about 10% of users. While gabapentin is used to manage conditions like nerve pain and menopause symptoms, its impact on cognitive function is a concern for some patients Antidepressants are a common treatment option for depression and other mental health conditions. This article contains information about frequently prescribed antidepressant medications from the National Institute of Mental Health and MedlinePlus. Read about common SSRIs, SNRIs, and atypical antidepressants including side effects, how they work, and where to find more information and find the Neurontin Drug Usage Information Neurontin is not your traditional anxiety treatment. It was originally created as an anticonvulsant used to treat epilepsy though for some people who anxiety, it may be an effective treatment. Doctors that prescribe Neurontin for anxiety often only do so if the patient has been diagnosed with bipolar disorder. Understanding Gabapentin’s Psychiatric Effects Potential psychiatric side effects of gabapentin Gabapentin, commonly prescribed for seizures and neuropathic pain, has been reported to cause a range of psychiatric side effects. While it is generally considered safe, some users have exhibited significant mood changes, including increases in depression, anxiety, and irritability. Notably Gabapentin, a prescription drug, is an anticonvulsant medication used to treat seizures and also helps treat nerve pain for people with conditions such as shingles or restless leg syndrome. In recent years, some doctors have begun prescribing gabapentin to also treat depression, but is this the best course of treatment? Antidepressants balance brain chemicals called neurotransmitters to ease depression symptoms, with several classes available, including SSRIs, SNRIs, and MAOIs. Side effects vary among Medicine options to treat depression include SSRIs, SNRIs, atypical antidepressants, tricyclic antidepressants, MAOIs and other drugs. Gabapentin is a nerve pain medication and anticonvulsant that has proven to be effective for people who have hard-to-treat depression or other mood disorders. Antidepressants are common prescription medications that can help treat depression and other conditions like anxiety and obsessive-compulsive disorder. There are several types of antidepressants. You and your healthcare provider will work together to find the best one for you. The UK National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE)'s 2022 guidelines indicate that antidepressants should not be routinely used for the initial treatment of mild depression, "unless that is the person's preference". [29] The guidelines recommended that antidepressant treatment be considered: For people with a history of moderate or severe depression. For people with mild The top 5 antidepressants to treat depression include SSRIs, SNRIs, atypical antidepressants, serotonin modulators, and cyclic antidepressants. This article reviews evidence-based psychiatric uses of gabapentin, along with associated risks. An extensive literature review was conducted, primarily of articles searchable in PubMed, relating to psychiatric uses, safety, and adverse effects of Conclusion Gabapentin is a medication that can provide relief for various medical conditions, including epilepsy, neuropathic pain, and restless leg syndrome. While concerns have been raised about the potential link between gabapentin use and depression, research on this topic is still ongoing. Antidepressants help to relieve symptoms of depression such as low mood, irritability, feelings of worthlessness, restlessness, anxiety, and difficulty sleeping. Antidepressants are classified into types depending on their structure and their effect on the body. There are at least seven categories of antidepressants. Explore gabapentin's role in mental health treatment, including its uses, benefits, and potential risks. Learn about dosage, effectiveness, and side effects. Although Gabapentin has been used to treat seizures, there is evidence to suggest it may be a method for treating anxiety and depression. Learn more! Outpatient prescription of gabapentin for FDA-approved indications (i.e., partial-onset seizures and postherpetic neuralgia) was less than 1%, and depression and anxiety disorders were the most frequent psychiatric diagnoses among off-label users. Exploring Depression Medications: Understanding Antidepressants for Effective Depression Treatment available in the U.S. Find out about the different types of antidepressants, how they work, adverse effects, when a person can take them, and available alternatives. Bipolar disorder Depression The off-label use of gabapentin warrants careful consideration, particularly regarding the efficacy and safety profiles relative to established antidepressants. As we move forward in this article, understanding these connections will allow for a nuanced discussion on the relationship between gabapentin and depression.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
+are+the+best-studied+drugs+for+neuropathic+pain.+Optimal+analgesia+requires+treatment+of+depression..jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |