Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 | 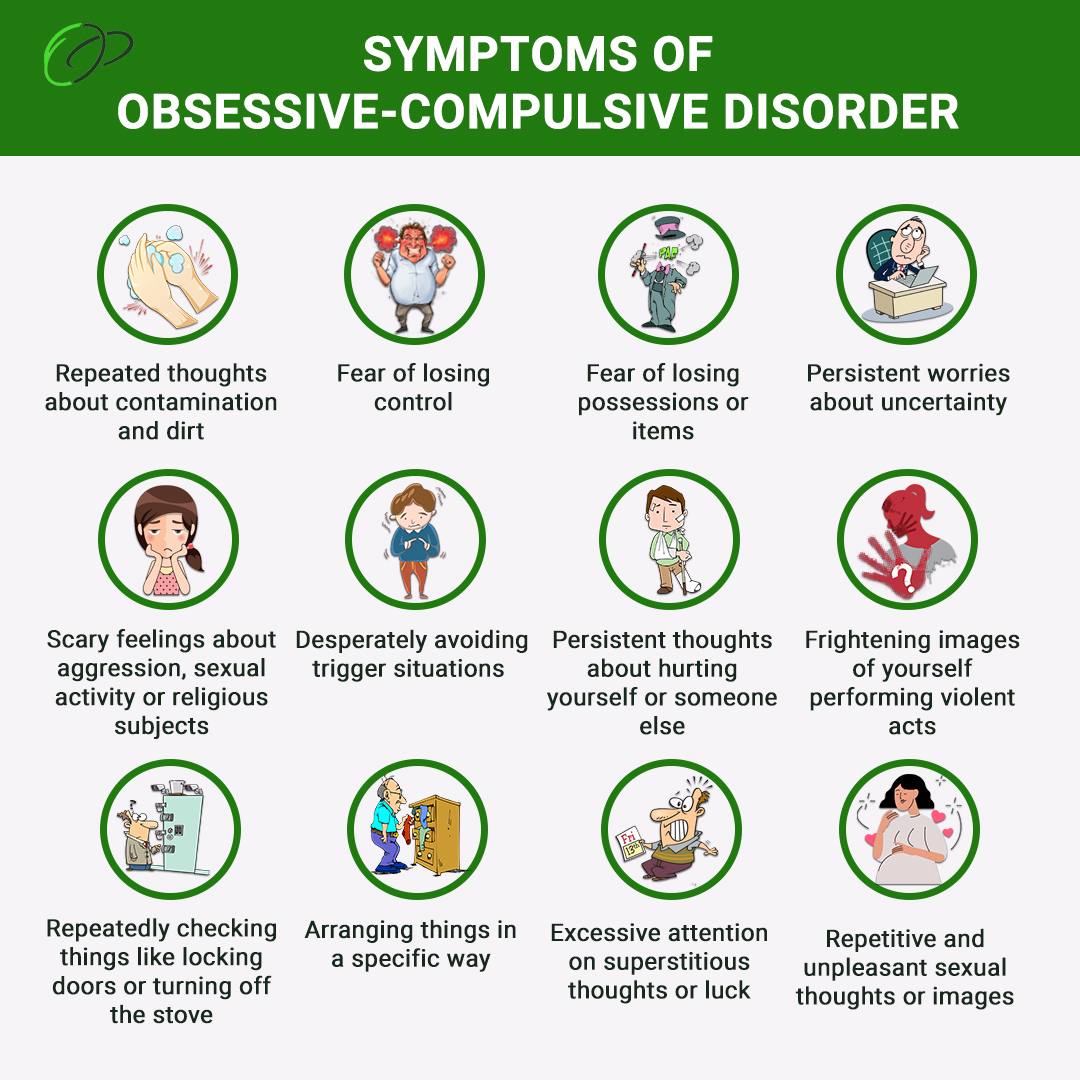 |
Abstract Objective This article reviews evidence-based psychiatric uses of gabapentin, along with associated risks. Method of Research An extensive literature review was conducted, primarily of articles searchable in PubMed, relating to psychiatric uses, safety, and adverse effects of gabapentin. Results Evidence supports gabapentin as a treatment for alcohol withdrawal and alcohol use Gabapentin, commonly referred to by the brand names: Neurontin, Gralise, or Horizant, is an anticonvulsant FDA-approved to treat mini seizures, treatment-resistant partial epilepsy, neuropathy or nerve pain from shingles, or restless leg syndrome (RLS). It is also used “ off-label ” to treat other conditions, such as migraines, fibromyalgia, addiction, hiccups, hyperhidrosis, alcohol or Explore gabapentin's role in mental health treatment, including its uses, benefits, and potential risks. Learn about dosage, effectiveness, and side effects. Adding gabapentin to fluoxetine in the treatment of OCD seems to shorten the time to onset of fluoxetine's anti-obsessive effect without a significant increase in adverse effects. In order to accelerate the clinical response, co-administration of fluoxetine and gabapentin may be a preferable strateg This systematic review and meta-analysis evaluates the association of glutamatergic medications with symptoms of obsessive-compulsive and related disorders as monotherapy or as augmentation to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is a disabling illness affecting approximately 2–3% individuals worldwide that is marked by recurrent, distressing intrusive thoughts (obsessions) and repetitive behaviors (compulsions). 1, 2 The underlying pathophysiology is incompletely understood, but OCD symptoms are thought to emerge partly from Gabapentin is widely prescribed off label in medical practice, including psychiatry. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) warned of risks associated with gabapentin combined with central nervous system depressant (CNS-D) drugs, which are commonly prescribed in psychiatric treatment. This study examined off-label outpatient gabapentin use for psychiatric indications and concomitant CNS-D An exciting new chapter in the treatment of OCD involves interventional and neuromodulation approaches. Collectively, they can be seen to target the hyperactive cortico-striato-thalamo-cortical “loop" implicated in OCD. We reviewed the extant literature to evaluate the current evidence regarding the efficacy and safety of anticonvulsants in the treatment of obsessive–compulsive and related disorders. Relevant litera Featured Buspirone (BuSpar) is an anti-anxiety drug that is sometimes used to treat chronic anxiety and is helpful for panic, as well as OCD. Abstract Objective: This article reviews evidence-based psychiatric uses of gabapentin, along with associated risks. Method of Research: An extensive literature review was conducted, primarily of articles searchable in PubMed, relating to psychiatric uses, safety, and adverse effects of gabapentin. Results: Evidence supports gabapentin as a treatment for alcohol withdrawal and alcohol use Objective The aim of this study was to compare efficacy of fluoxetine alone and co-administration of gabapentin and fluoxetine in patients with obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD). Methods Forty outpatients with a DSM-IV diagnosis of OCD were randomized to open label treatment, 20 of whom were treated with fluoxetine alone and the remaining 20 with fluoxetine plus gabapentin during 8 weeks What does gabapentin do for OCD? Adding gabapentin to fluoxetine in the treatment of OCD seems to shorten the time to onset of fluoxetine’s anti-obsessive effect without a significant increase in adverse effects. In order to accelerate the clinical response, co-administration of fluoxetine and gabapentin may be a preferable strategy. Gabapentin is commonly used off-label in the treatment of psychiatric disorders with success, failure, and controversy. A systematic review of the literature was performed to elucidate the evidence for clinical benefit of gabapentin in psychiatric Gabapentin is commonly used off-label in the treatment of psychiatric disorders with success, failure, and controversy. A systematic review of the literature was performed to elucidate the evidence for clinical benefit of gabapentin in psychiatric disorders. Learn about gabapentin for anxiety: its uses, side effects, and how it can be combined with other treatments. Objective: This article reviews evidence-based psychiatric uses of gabapentin, along with associated risks. Method of Research: An extensive literature review was conducted, primarily of articles searchable in PubMed, relating to psychiatric uses, safety, and adverse effects of gabapentin. Results: Evidence supports gabapentin as a treatment for alcohol withdrawal and alcohol use disorder The present pattern of results suggests that glutamatergic medications such as gabapentin and memantine adjuvant to a standard treatment with an SSRI have no additional positive impact on patients with OCD, as measured with the Y-BOCS. Additionally, side-effects were reported. Future studies should Explore gabapentin's potential benefits and risks for OCD treatment, including research, side effects, and considerations for use. Objective: Gabapentin (GBP) is an anticonvulsant medication that is also used to treat restless legs syndrome (RLS) and posttherapeutic neuralgia. GBP is commonly prescribed off-label for psychiatric disorders despite the lack of strong evidence. However, there is growing evidence that GBP may be effective and clinically beneficial in both psychiatric disorders and substance use disorders
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |