Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
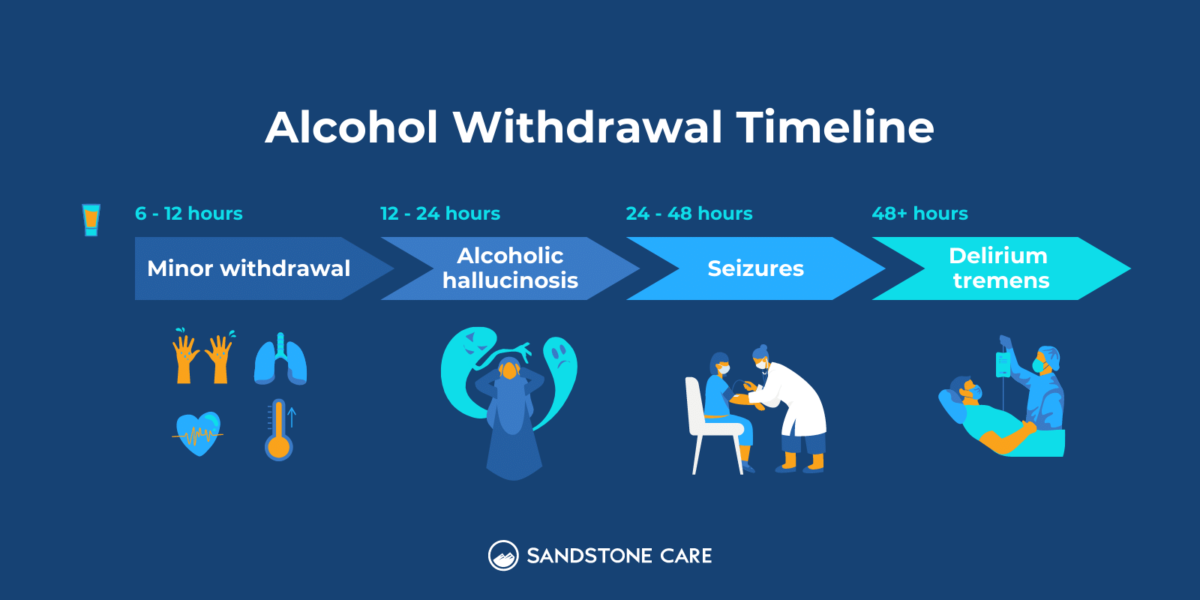
One hundred subjects with DSM-IV diagnosis of alcohol dependence and alcohol withdrawal were randomized to receive gabapentin at one of three different fixed-dose taper regimens (600, 900, or 1200 mg/day starting dose) or lorazepam (6 mg/day starting dose) for 4 days with symptom-triggered rescue doses to treat breakthrough withdrawal. Gabapentin 1800 mg/day used during first 2 days of hospital admission significantly lowered total dose of benzodiazepines. Gabapentin appears to be more beneficial for mild rather than severe alcohol withdrawal. High dose Gabapentin (1800 mg/day) is also associated with decrease in percentage of heavy drinking days. We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Early initiation of high-dose gabapentin was associated with a significant reduction in benzodiazepine exposure, faster stabilization of alcohol withdrawal-related symptoms, and shorter hospital length of stay. Future studies evaluating gabapentin's effect on long-term safety and hospital readmissio Dosage Information The following dosage information may be useful if you are considering taking gabapentin for withdrawal: Since it is a generic drug, dosage amount may vary depending on the brand and different brand name tablets are not interchangeable. 600-1800 mg per day is typically effective to mitigate symptoms. If a small dose of midazolam causes the patient to become sedated, the diagnosis of alcohol withdrawal is less likely (patients with alcohol withdrawal usually exhibit benzodiazepine tolerance). Gabapentin's relatively low abuse potential, side effect profile, and limited hepatic metabolism make it an attractive option compared with benzodiazepines and other anticonvulsants. Several randomized, placebo- and active-controlled trials have evaluated off-label use of gabapentin for the treatment of alcohol detoxification and dependence. Calculate target loading dose with phenobarbital depending on alcohol use severity and comorbid medical illness based on criteria Ideal Body Weight (IBW) x (6 to 15mg/kg) = total mg (of loading dose) Where: IBW for men is: 50 + 2.3kg/inch over 5 feet IBW for women is 45.5 +2.3kg/inch over 5 feet Give loading dose intramuscularly Comprehensive guide on managing moderate and severe alcohol withdrawal syndromes, including symptoms, treatment options, and supportive care strategies. QuestionIs gabapentin efficacious in the treatment of alcohol use disorder in adults with a history of alcohol withdrawal symptoms? FindingsIn this randomized clinical trial, gabapentin compared with placebo significantly increased the number of people with total abstinence and reduced drinking. • Taking medicine for an alcohol use disorder is not substituting one drug for another. How should I take gabapentin? • The recommended dose of gabapentin for the treatment of alcohol use disorder is 300–600 milligrams (mg) three times daily. • Gabapentin can be taken with or without food. Benzodiazepines are the standard pharmacologic treatment for alcohol withdrawal, but they have abuse liability and adverse effects and may increase craving and early relapse. In the first double-blind, dose-response, controlled trial of gabapentin for alcohol withdrawal, investigators randomized 100 treatment-seeking outpatients with alcohol dependence and moderate alcohol-withdrawal symptoms Typically, Gabapentin is prescribed for alcohol withdrawal in doses ranging from 300 to 800 mg, three times daily, with adjustments made based on symptom severity and patient response. The anticonvulsant drug gabapentin is used off-label to treat alcohol-related withdrawal, cravings, anxiety, and insomnia. Although it is well tolerated and has demonstrated efficacy for mild alcohol withdrawal and early abstinence, there is concern about its potential for abuse. Gabapentin should be prescribed only as a second-line alternative to standard therapies, and only after screening To evaluate the efficacy and safety of a fixed-dose gabapentin taper protocol for alcohol withdrawal in hospitalized patients. We retrospectively identified patients admitted to the hospital from January 1, 2016, to April 30, 2018, for alcohol Gabapentin in alcohol withdrawal: For the first time, the DSM-V includes the diagnostic guidelines for alcohol dependency. A variety of severe conditions result from or are influenced by alcohol dependence, including stomach ulcers, liver disorders, increased risk of heart disease, and neuropathy. The primary endpoints included: total dosage of benzodiazepine used (calculated as a chlordiazepoxide dose equivalent); total dosage of gabapentin used; development of delirium or seizures during the withdrawal process after treatment was initiated; initial and maximum CIWA-ar scores; and the time (in hours) until the patient achieved a CIWA-ar The researchers enrolled 96 adults who met the DSM-5 diagnosis for AUD, including alcohol withdrawal symptoms. Following three days of alcohol abstinence, the participants were randomly assigned to receive either gabapentin (starting at 300 mg/day and titrated up to 1,200 mg/day over five days) or placebo pills for 16 weeks. Gabapentin is used off-label in alcohol withdrawal care. This guide covers clinical evidence, side effects, and treatment guidelines.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |