Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
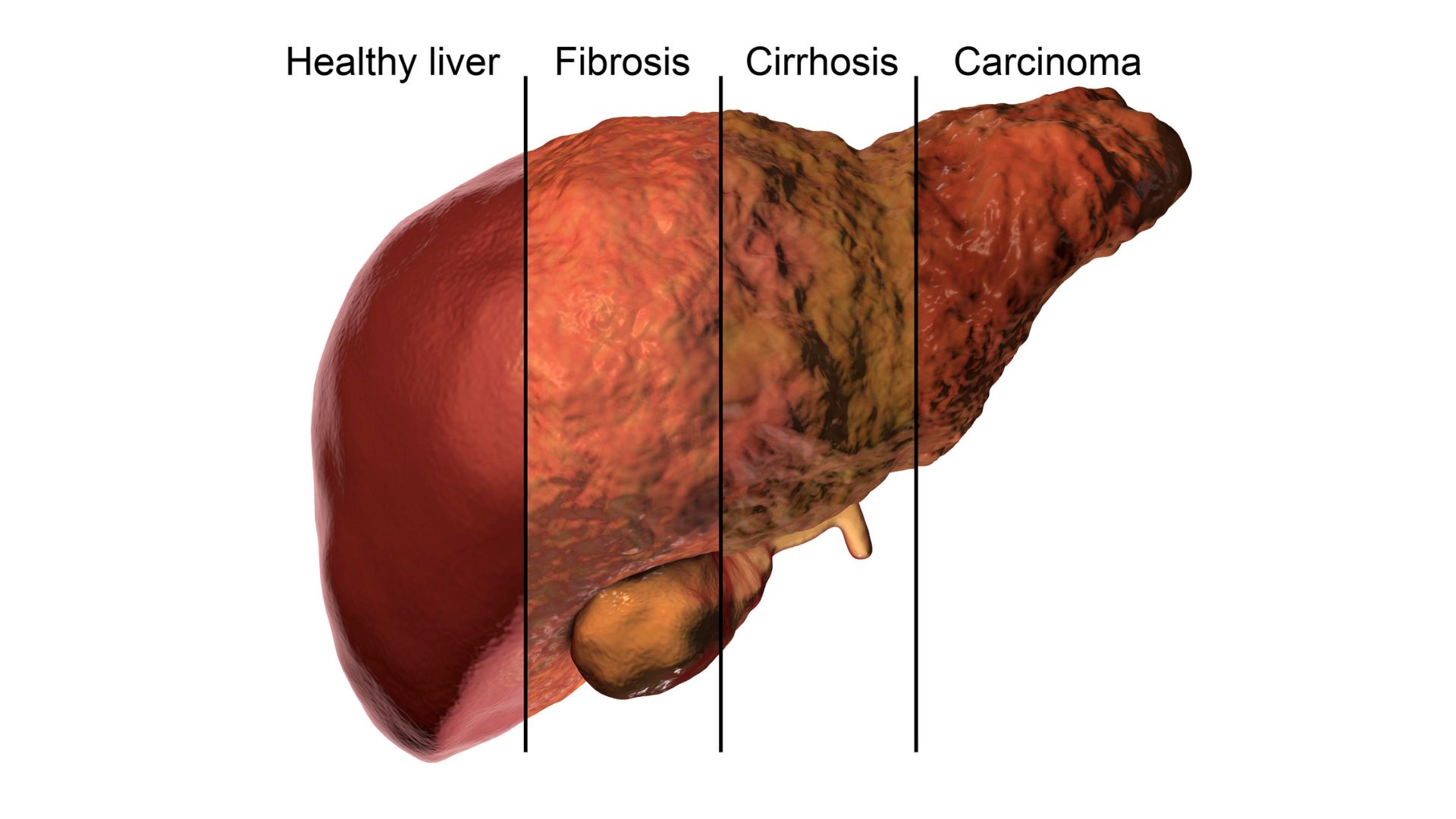
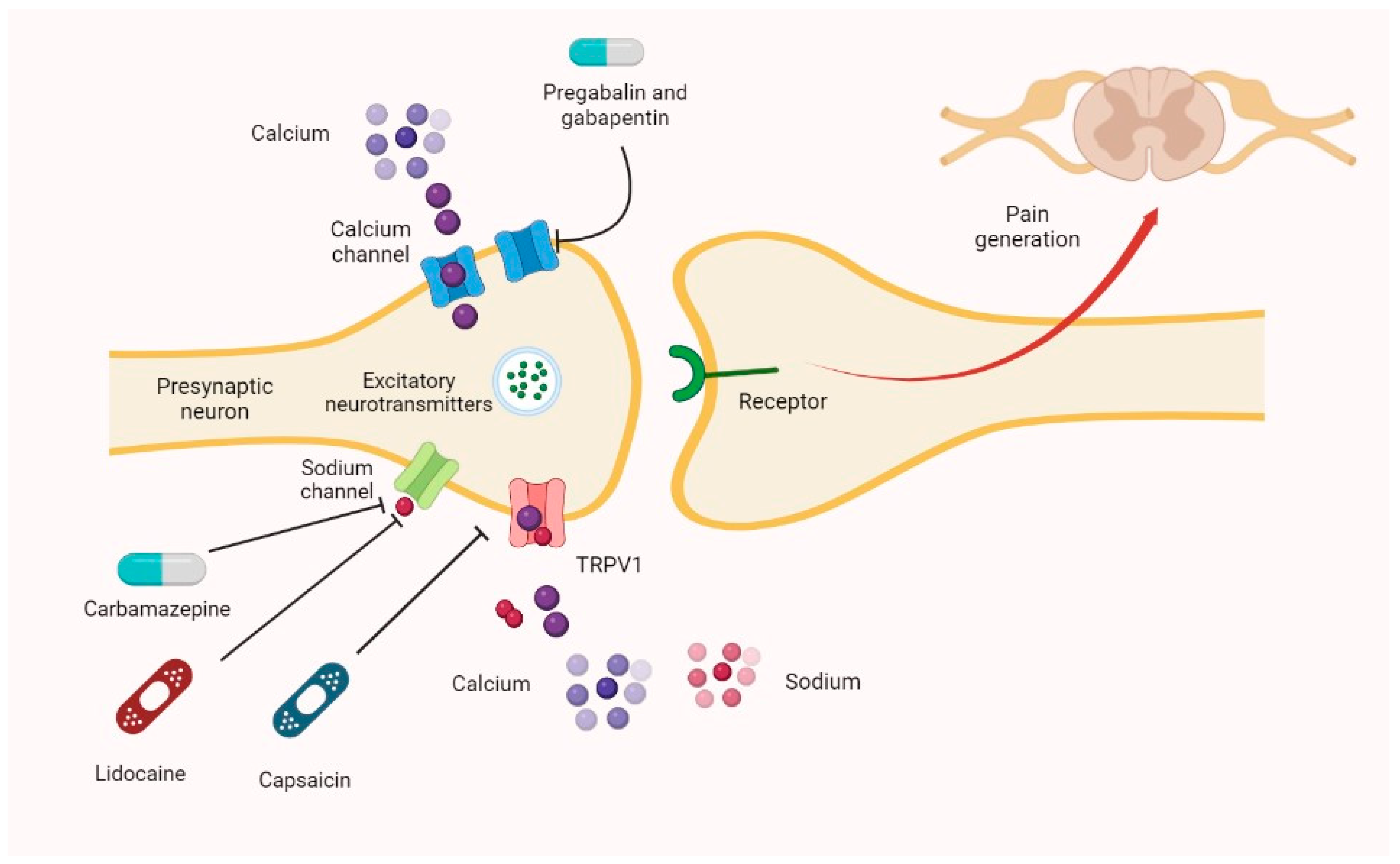
Introduction: Gabapentin is an anti-convulsant that is also used off-label to treat neuropathic pain. It is not metabolized by the liver, and there have been few reports of hepatotoxity associated with it. We present a rare case of gabapentin-induced hepatotoxicity occurring in a young male. Case Description/Methods: A 41-year-old male with an extensive past medical history including type 1 Gabapentin (Neurontin) usually isn’t bad for your liver or kidneys. In most cases, it has little effect on these organs. In rare instances, gabapentin can cause DRESS (drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms) syndrome. This is a severe allergic reaction that can cause damage to major organs, including the liver and kidneys. Pain management in patients with cirrhosis is a difficult clinical challenge for health care professionals, and few prospective studies have offered an evidence-based approach. In patients with end-stage liver disease, adverse events from analgesics Gabapentin is eliminated through the kidneys and, therefore, doesn’t typically cause liver injury. Learn safe dosage recommendations for people with liver disease. Introduction: We are reporting a case of drug induced liver injury (DILI) secondary to gabapentin therapy with risk factors for underlying non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Case Description/Methods: A 56-year-old male with hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes with neuropathy, obesity, and chronic kidney disease stage 3 presented as an outside hospital (OSH) transfer for evaluation Gabapentin is generally considered safe for the liver, but rare cases of liver damage have been reported. Gabapentin, a medication primarily used to treat nerve pain and seizures, has gained popularity for its effectiveness and relatively mild side effects. Gabapentin, a water-soluble amino acid, is eliminated unchanged by the kidneys and there is no appreciable metabolism by the liver. This class, which includes gabapentin and pregabalin, is not metabolized by the liver. Therefore, risks in patients with advanced liver disease are not greatly increased. However, there are case reports of pregabalin‐induced hepatoxicity. 4 Gabapentin and pregabalin are renally excreted, so dosages need to be adjusted for renal failure. 5 Answers - Posted in: gabapentin, liver, liver disease - Answer: Drug companies that do studies on their own products are bias and should Learn about the potential effects of Gabapentin on your liver and kidneys. Find out if it is safe to use and how to protect your organs while taking this medication. Therefore, an understanding of liver enzyme levels, often measured via tools such as liver function tests (LFTs), is crucial for patients on gabapentin. The question of whether is gabapentin bad for your liver requires careful evaluation, particularly for individuals with pre-existing hepatic conditions. Gabapentin is a unique anticonvulsant that is used as adjunctive therapy in management of epilepsy and for neuropathic pain syndromes. Therapy with gabapentin is not associated with serum aminotransferase elevations, but several cases of clinically apparent liver injury from gabapentin have been reported. Gabapentin enacarbil is a long acting form of gabapentin that is used for restless leg syndrome and for painful postherpetic neuropathy. Gabapentin enacarbil and gabapentin are associated with a low rate of transient serum enzyme elevations during treatment and with rare instances of clinically apparent liver injury. A new study suggests that gabapentin could provide greater benefit than FDA-approved drugs for patients with alcohol-associated liver disease. In rare instances, gabapentin can cause DRESS (drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms) syndrome. This is a severe allergic reaction that can cause damage to major organs, including the liver and kidneys. If you have existing kidney problems, you may need a lower dose of gabapentin. MeSH terms Anticonvulsants / therapeutic use Cyclohexanecarboxylic Acids* / adverse effects Drug-Related Side Effects and Adverse Reactions* Gabapentin / adverse effects Hepatitis* Humans gamma-Aminobutyric Acid / adverse effects Liver and renal functions were impaired by gabapentin; where hepatotoxicity was associated by an imbalance in the redox status. However, magnesium only elevated blood urea nitrogen (BUN). Acute, symptomatic seizures or epilepsy may complicate the course of hepatic disease. Choosing the most appropriate antiepileptic drug in this setting represents a difficult challenge, as most medications are metabolized by the liver. This article focuses on the acute and chronic treatment of seizur Gapentin is not metabolized by the liver, and its effects on the liver and kidneys are similar to previous studies. In rare cases, gabapentin can cause DRESS (drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms). The removal of gabapentin and the administration of steroids resulted in the normalization of liver test abnormalities. Another case reported a 26-year-old patient taking 1500 mg of gabapentin with associated hepatocellular injury [4].
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |