Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 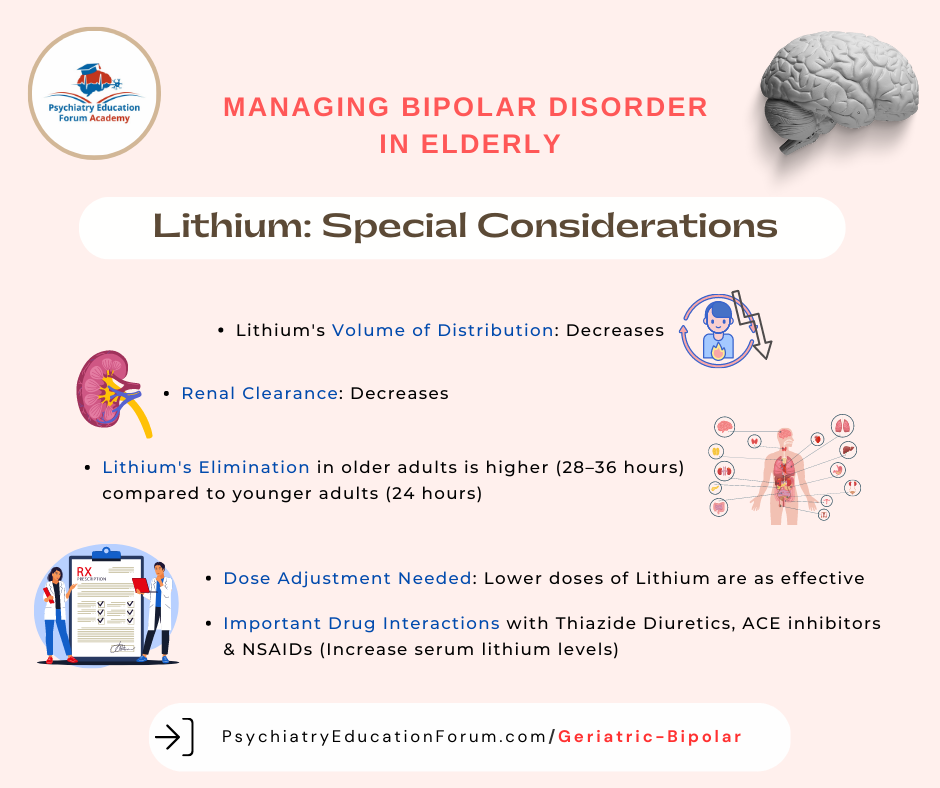 |
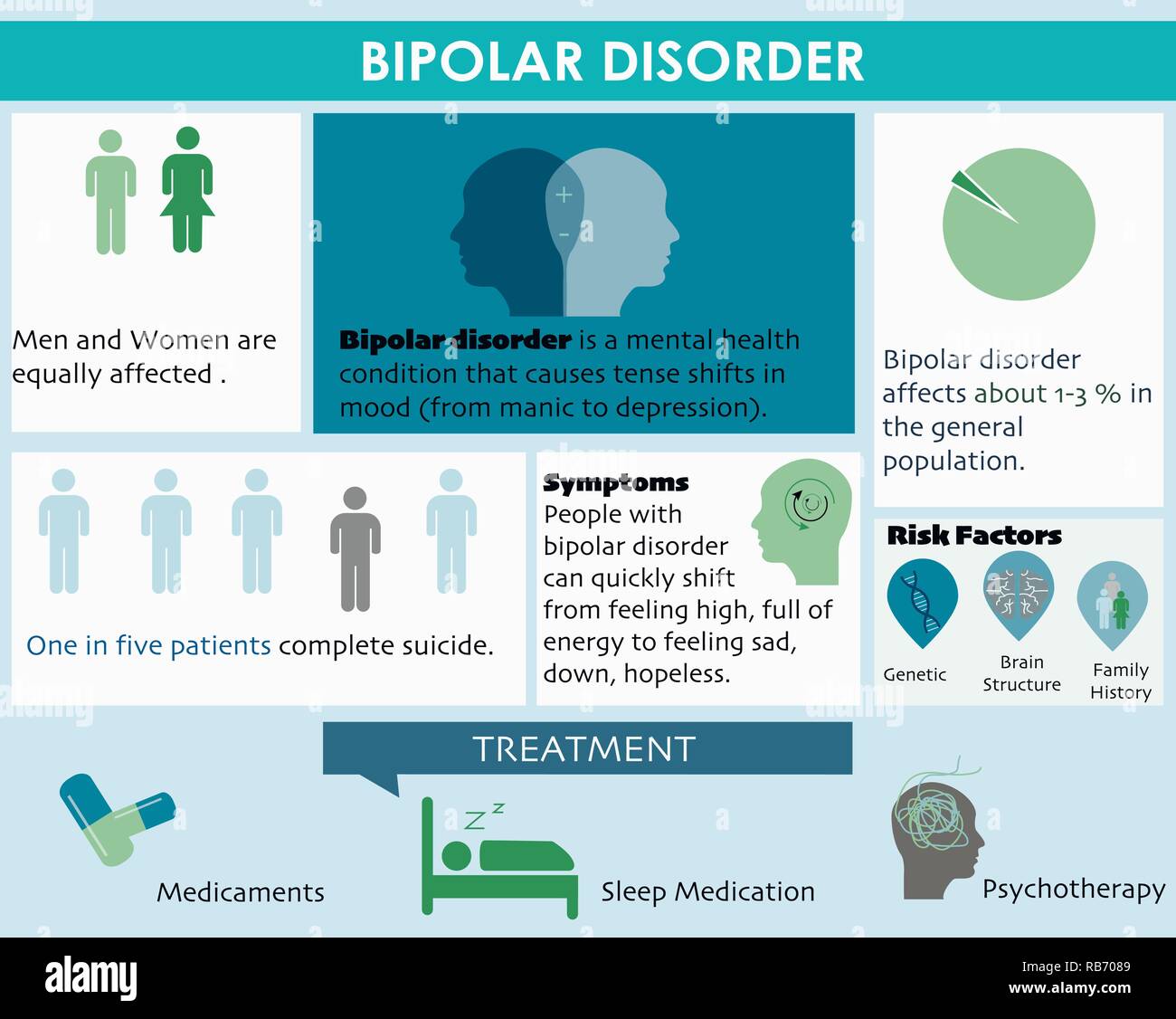
Neurontin is sometimes prescribed off-label for the treatment of the following conditions: Bipolar disorder: Bipolar disorder is a mental condition that causes sudden and extreme changes, in mood, energy levels, and daily functioning. Methods: This was a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of adjunctive gabapentin (dosed flexibly between 900 and 3600 mg/day). Patients with a lifetime diagnosis of bipolar disorder (type I), and who were currently suffering from symptoms of either mania, hypomania or a mixed state despite ongoing therapy with lithium, valproate, or lithium Key takeaways: Gabapentin is a medication that’s used to treat seizures, nerve pain from shingles, and restless leg syndrome. Despite previous marketing claims, there’s no evidence that gabapentin is a good treatment for bipolar disorder. The best treatment for bipolar disorder is therapy and a combination of other medications. These include mood stabilizers, anticonvulsants, and Gabapentin may be a useful drug for the add-on treatment of bipolar patients with poor response to other mood stabilizers. Gabapentin may improve depressive residual symptoms such as irritability, social withdrawal or anxiety. These results should be confirmed in randomized clinical trials. Today, gabapentin is frequently prescribed off-label for various mental health conditions, joining the ranks of other mood-stabilizing medications like lamotrigine, which has shown promise in treating bipolar disorder and depression. Issue: Most patients with a bipolar spectrum disorder are treated with 2 or more drugs in combinations that are sometimes rational and evidence-based and sometimes not. We identified 40 open-label studies on the use of GBP in at least 600 patients with bipolar disorder (BP), manic, depressed, or mixed episodes and unipolar depression and four controlled studies. Results: Gabapentin was moderately to mark-edly effective in 30% (15/50) of patients, with statistically nonsignificant differences between patients with bipolar disorder type I, bipolar dis-order type II and NOS, and unipolar major de-pressive disorder. 70% reported side effects, mainly sedation, with 16% of the total sample discontinuing treatment due to adverse events. Conclusion Gabapentin is a nerve pain medication and anticonvulsant that has proven to be effective for people who have hard-to-treat depression or other mood disorders. Two new anticonvulsants, lamotrigine and gabapentin, have been used increasingly for bipolar disorder in the past several years. Despite this array of options, bipolar disorder remains a difficult disorder to treat. Some subtypes, such as those characterized by rapid cycling or mixed episodes, have been especially resistant to lithium treatment. Abstract Despite its prevalence and disease burden, several chasms still exist with regard to the pharmacotherapy of bipolar disorder (BD). Polypharmacy is commonly encountered as a significant proportion of patients remain symptomatic, and the management of the depressive phase of the illness is a particular challenge. Gabapentin and pregabalin have often been prescribed off-label in spite of Unfortunately, gabapentin does not demonstrate efficacy in randomized trials for bipolar disorder and current treatment guidelines do not emphasize its use. Despite of the lack of evidence, reviews of gabapentin prescribing patterns in the United States show that this medication is still being used with alarming frequency for bipolar disorder. Learn how Neurontin is used to treat bipolar disorder symptoms, its benefits, and potential side effects in this informative medical resource article. Bipolar disorder (BD) Four DB-RCTs investigating the efficacy of gabapentin in BD were identified. 101 patients were randomised to receive gabapentin, 81 to placebo, 30 to lamotrigine and 19 to Abstract Background: Gabapentin, a new anti-epileptic agent, has been anecdotally reported to be effective in the treatment of mania. We systematically assessed the response rate in bipolar patients being treated adjunctively with gabapentin for manic symptoms, depressive symptoms, or rapid cycling not responsive to standard treatments. Conclusion Gabapentin may be a useful drug for the add-on treatment of bipolar patients with poor response to other mood stabilizers. Gabapentin may improve depressive residual symptoms such as irritability, social withdrawal or anxiety. These results should be confirmed in randomized clinical trials. The gabapentinoids, gabapentin, and pregabalin, target the α2δ subunits of voltage-gated calcium channels. Initially licensed for pain and seizures, they have become widely prescribed drugs. Many of these uses are off-label for psychiatric Clinical Points Gabapentin appears to have some benefit for anxiety disorders but failed to show benefit in bipolar disorder trials. In the individual patient with a mixed psychiatric disorder, benefits are most likely due to anxiolytic effects. Gabapentin has modest efficacy for alcohol craving and withdrawal symptoms and may have some benefit in opioid dependence as an adjunct therapy The gabapentinoids, gabapentin, and pregabalin, target the α<sub>2</sub>δ subunits of voltage-gated calcium channels. Initially licensed for pain and seizures, they have become widely prescribed drugs. Many of these uses are off-label for psychiatric indications, and there is increasing concern abou This article reviews evidence-based psychiatric uses of gabapentin, along with associated risks. An extensive literature review was conducted, primarily of articles searchable in PubMed, relating to psychiatric uses, safety, and adverse effects of
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |