Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
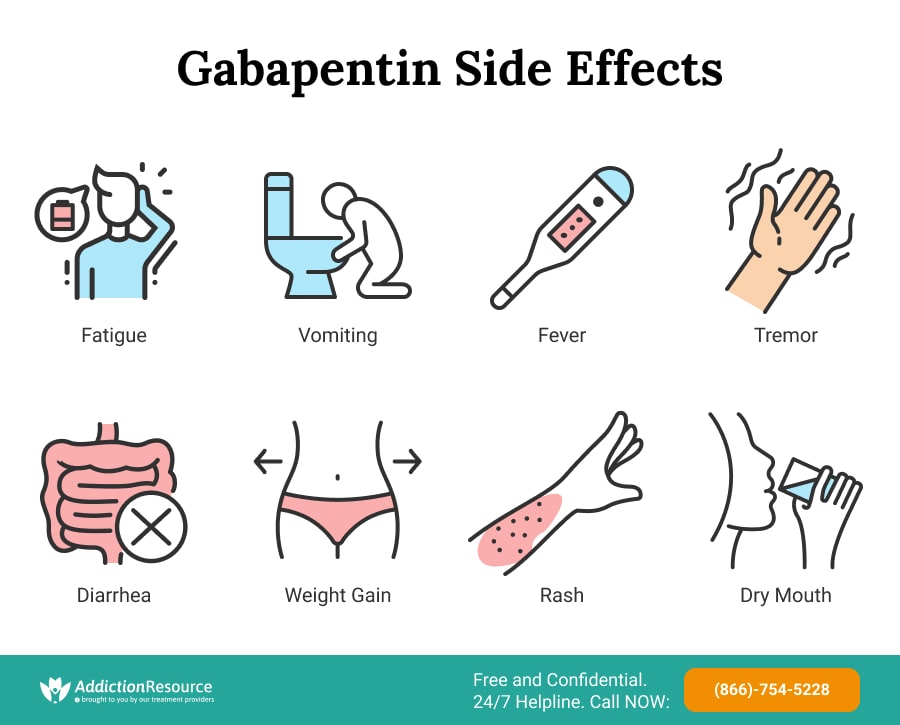
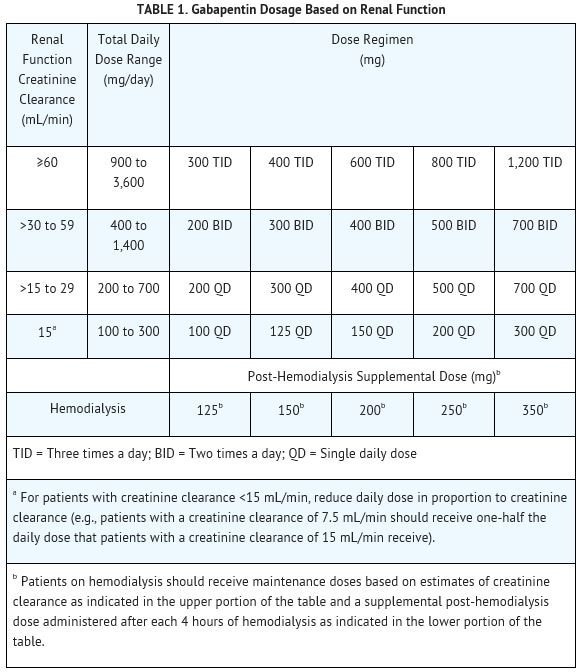
Gabapentin is an effective treatment for chronic neuropathic pain but may cause dizziness, drowsiness, and confusion in some older adults. The goal of this study was to assess the association between gabapentin dosing and adverse outcomes by Conclusion Gabapentin is commonly used for neuropathic pain relief in all stages of life. But how safe is gabapentin for older adults? What are the main gabapentin side effects in the elderly? Older adults have a higher prevalence of side effects due to overlapping health conditions and polypharmacy. Explore the use of gabapentin in elderly patients, including its benefits for neuropathic pain and seizures, potential risks such as dizziness and cognitive effects, and important considerations for safe prescribing in this vulnerable population. The anti-seizure drug gabapentin is used to treat epilepsy, nerve pain after shingles and restless legs syndrome by affecting chemical messengers in the brain and nerves. Common side effects Discover the potential side effects of gabapentin in elderly women, including common reactions, risks specific to older adults, and important considerations for safe use. Learn about common and serious gabapentin side effects in elderly patients. Understand risks, precautions, and when to seek medical help. Key takeaways: Gabapentin (Neurontin) is an antiseizure medication. It’s also used for nerve pain from shingles. Other long-acting forms called Gralise and Horizant are also available. For adults, your gabapentin dosage varies depending on your medical conditions and which form you’re taking. The maximum dosage is 3,600 mg per day. For children, the dosage is based on age and body weight Learn about the common side effects of gabapentin in elderly patients, including dizziness, fatigue, cognitive impairment, and more. Explore the connection between gabapentin and depression, mechanisms behind gabapentin-related depression, and strategies to manage and mitigate side effects. Discover other significant concerns for elderly gabapentin users and the importance of personalized Learn about the side effects of gabapentin, from common to rare, for consumers and healthcare professionals. Gabapentin, widely used for treating various neurological conditions, plays a significant role in the health and well-being of elderly individuals. Although it can effectively manage symptoms of these ailments, recognizing the gabapentin side effects in the elderly is essential for caregivers and family members. These side effects can range from mild to severe, affecting each individual However, elderly patients are more likely to have unwanted effects (eg, problems with balance or walking, swelling in the feet or legs) and age-related kidney problems, which may require caution and an adjustment in the dose for patients receiving gabapentin. Abstract Neuropathic pain due to a lesion or a disease of the somatosensory system often affects older people presenting several comorbidities. Moreover, elderly patients are often poly-medicated, hospitalized and treated in a nursing home with a growing risk of drug interaction and recurrent hospitalization. Neuropathic pain in the elderly has to be managed by a multidimensional approach that Detailed Gabapentin dosage information for adults and children. Includes dosages for Restless Legs Syndrome, Epilepsy and Postherpetic Neuralgia; plus renal, liver and dialysis adjustments. Older adults may also be given a lower dose of gabapentin (Neurontin) depending on the current health state of the patient. Usually, elderly patients have decreased renal function; as such, caution should be taken when determining gabapentin dosage. It is important that you take the medication exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider. Physical side effects of gabapentin in the elderly The biggest concern regarding the physical side effects of gabapentin in seniors involves reactions that pose a heightened risk of falls. Gabapentin and Pregabalin prescribing for neuropathic pain. Prescribing in patients aged 65 years or over. Gabapentin and Pregabalin prescribing for neuropathic pain. Prescribing in patients aged 65 years or over. Key Takeaway While gabapentin can be safe and effective for many elderly patients, it requires careful consideration of individual health factors, potential side effects, and drug interactions to ensure its appropriate use in this population. Gabapentin Side Effects in Elderly: Discover the potential risks and solutions. Ensure senior health with our comprehensive guide on gabapentin side effects in elderly individuals. View gabapentin information, including dose, uses, side-effects, renal impairment, pregnancy, breast feeding, monitoring requirements and important safety information. Cognitive and Neurological Side Effects in Older Adults Gabapentin can cause memory problems, confusion, and difficulty concentrating in older adults, raising concerns about cognitive decline. Dizziness and impaired coordination are also common, increasing the risk of falls and injuries among elderly users.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |