Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
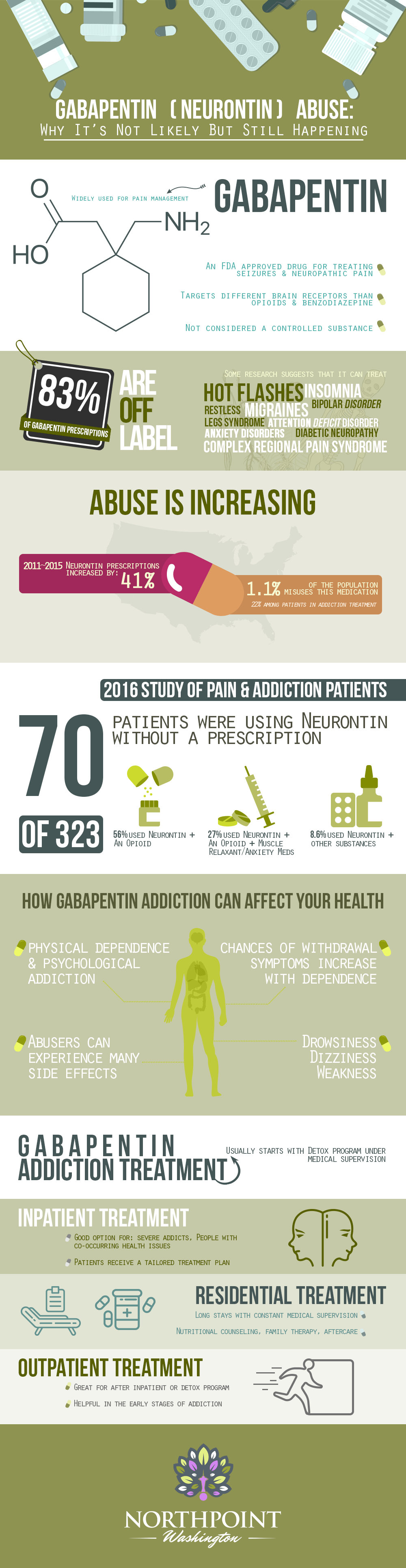 |  |
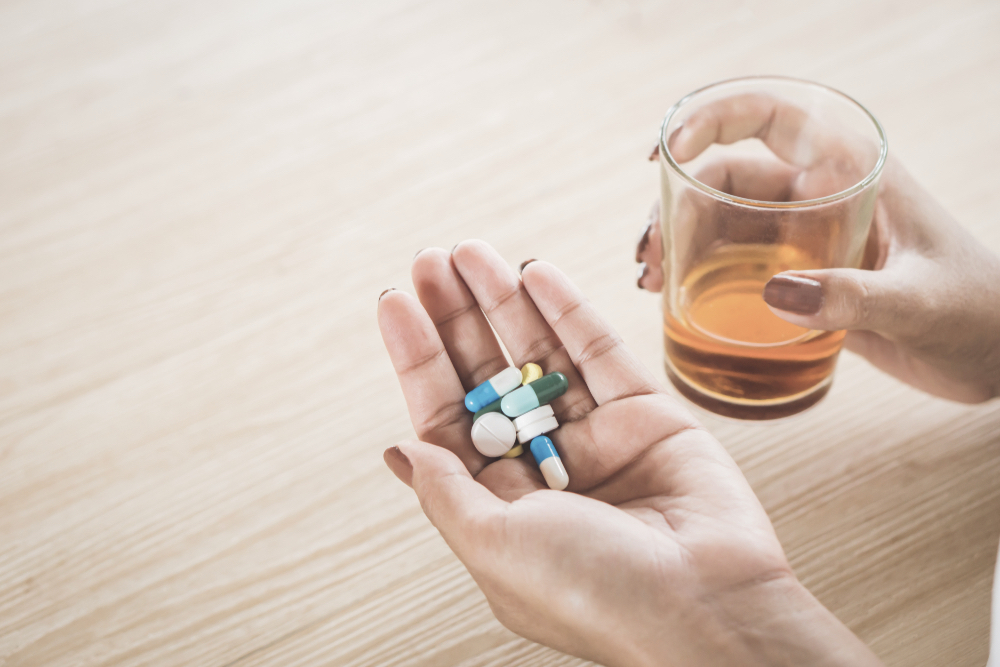
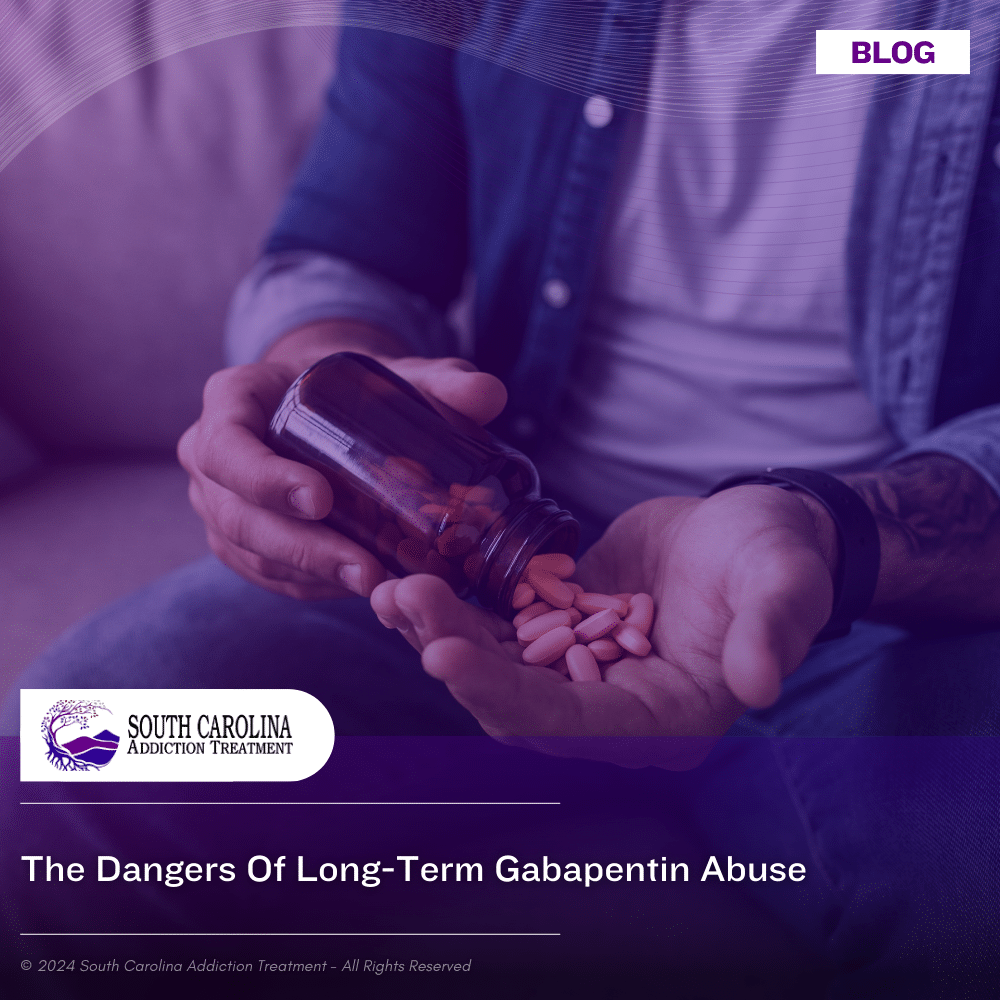
The anticonvulsant drug gabapentin is used off-label to treat alcohol-related withdrawal, cravings, anxiety, and insomnia. Although it is well tolerated and has demonstrated efficacy for mild alcohol withdrawal and early abstinence, there is concern about its potential for abuse. Gabapentin should be prescribed only as a second-line alternative to standard therapies, and only after screening Expert opinion Alcohol use disorder represents a challenge and large, unmet medical need. Evidence from single-site studies lend support to the safety and efficacy of gabapentin as a novel treatment for alcohol use disorder, with unique benefits for alcohol-related insomnia and negative affect, relative to available treatments. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant and pain-relieving medication that has several off-label uses, including the treatment of alcohol withdrawal syndrome. Learn more here. Learn about the dangers of mixing gabapentin with alcohol and find out what to do if you or a loved one is struggling with addiction. Gabapentin has been used for years in hospitals to treat patients with acute alcohol withdrawal, which is characterized by symptoms such as sweating, tremors, anxiety, and irritability. Anytime alcohol and gabapentin are combined, there is a chance that the user will experience one of the many negative side-effects. Gabapentin and alcohol interaction, withdrawal, and side effects. Learn more about Gabapentin and alcohol use disorder, and abuse of this medication here. Alcohol and gabapentin both depress the central nervous system and may lead to dangerous side effects when combined. Treatment for polydrug abuse can help individuals manage substance abuse and avoid overdose and other potential side effects, such as addiction. Since its market release, gabapentin has been presumed to have no abuse potential and subsequently has been prescribed widely off-label, despite increasing reports of gabapentin misuse. This review estimates and describes the prevalence and effects According to the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, these medications can reduce drinking days by 30-50% when combined with counseling. Role Of Gabapentin In Alcohol Withdrawal Management Gabapentin specifically has been shown to decrease rates of relapse in patients with a history of alcohol withdrawal symptoms. Why should hepatologists be involved in treating alcohol use disorder? The burden of alcohol-related liver disease is increasing. Abstract Alcohol misuse is the fifth leading risk factor for premature death and disability worldwide. Fewer than 10% of afflicted Americans receive pharmacological treatment for alcohol use disorder. Gabapentin is a calcium channel GABAergic modulator that is widely used for pain. Studies showing reduced drinking and decreased craving and alcohol-related disturbances in sleep and affect in Find out what you need to know about gabapentin for alcohol withdrawal and discover the pros, cons, risks, and benefits, and how it may affect health. Gabapentin use may become compulsory, and an individual may not be able to stop taking the drug without help. Treating Gabapentin Abuse Gabapentin is not a drug that should be stopped suddenly, and medical detox is often the first line of treatment. What happens if you drink alcohol while on gabapentin? Gabapentin and alcohol each individually cause central nervous system (CNS) depression and respiratory depression. Combining alcohol and gabapentin can worsen either or both effects. CNS depressants slow brain activity and cause drowsiness and dizziness. Combining alcohol and gabapentin, two CNS depressants, can worsen these effects Even though gabapentin is sometimes considered as a treatment option for alcohol and substance abuse, it is important to monitor for drug-seeking behaviors. A history of alcohol or substance abuse appears to be an important part of a patient's medical history when evaluating their risk for addiction and dependence behaviors. This randomized clinical trial examines the efficacy of gabapentin as pharmacotherapy for alchohol use disorder in adults with a history of alcohol withdrawal. Available evidence also suggests that abuse and misuse are more frequent in users of pregabalin compared with users of gabapentin. Health professionals and prescribers should be aware of the risk for misuse of pregabalin and gabapentin, which eventually could lead to abuse, substance dependence, and intoxications. Explore pharmacologic management strategies for alcohol use disorder, including treatment options and outcomes, on this comprehensive resource. Clinical question Is gabapentin an effective treatment for alcohol use disorder (AUD)? Bottom line Gabapentin treatment avoided more heavy drinking days (> 5 standard drinks/day) than placebo (27% vs 9%). Gabapentin can be a second-line, off-label option to treat AUD. However, there is mixed evidence and concerns about abuse-misuse, and drug-related harms. Evidence Results are statistically
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |