Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
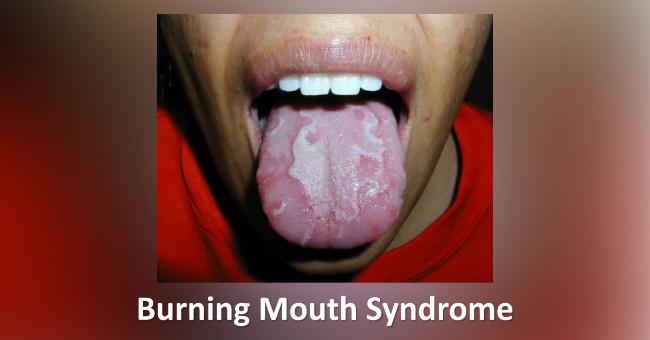
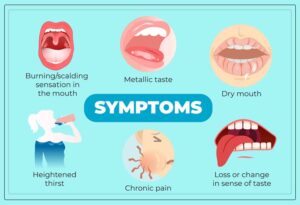
Abstract Objective: The aim of this retrospective study was to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of topical gabapentin solution (250 mg/mL) for the management of burning mouth syndrome (BMS). The aim of this retrospective study was to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of topical gabapentin solution (250 mg/mL) for the management of burning mouth syndrome (BMS). A retrospective chart review was conducted of all patients diagnosed with Abstract Background Burning mouth syndrome is a chronic idiopathic intractable intraoral dysaesthesia that remains a challenge to clinicians due to its poorly understood pathogenesis and inconsistent response to various treatments. Aim This review aimed to study the short- (≤3 months) and long-term (>3 months) effectiveness and sustainable benefit of different burning mouth syndrome Objective The aim of this retrospective study was to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of topical gabapentin solution (250 mg/mL) for the management of burning mouth syndrome (BMS). Study design A retrospective chart review was conducted of all patients diagnosed with BMS and managed with gabapentin 250 mg/mL solution (swish and spit) between January 2021 and October 2022. Patient-reported Abstract Objective The aim of this retrospective study was to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of topical gabapentin solution (250 mg/mL) for the management of burning mouth syndrome (BMS). Burning mouth syndrome is a debilitating disorder involving oral pain that may have at least 4 underlying causes. Although several treatments have been proposed, none seems to be universally A more significant volume in terms of sample size, multi-centres, and multi-arm comparison of therapeutic agents with placebo and longitudinal follow-up studies is recommended to establish a standardised burning mouth syndrome treatment protocol. Further studies are required to assess the analgesic benefits of topical clonazepam and capsaicin, alternative medicines with neurodegenerative Burning mouth syndrome is a poorly understood disease process with no current standard of treatment. The goal of this article is to provide an evidence-based, practical, clinical algorithm as a guideline for the treatment of burning mouth syndrome. Burning mouth syndrome is characterized by a burning sensation in the tongue or other oral sites, usually in the absence of clinical and laboratory findings. Affected patients often present with Treatment of burning mouth syndrome (BMS) is challenging because there is no consensus regarding pharmalogical or nonpharmalogical therapies. The use of anticonvulsants is controversial. We present nine patients BMS who respond to pregabalin. They Chronic orofacial pain is a symptom associated with a wide range of neuropathic, neurovascular, idiopathic, and myofascial conditions that affect a significant proportion of the population. While the collective impact of the subset of the orofacial Burning mouth syndrome (BMS), a burning sensation in the lips, tongue, palate, and other parts of the mouth, can be a side effect of certain medications. Learn more. Reviews and ratings for Gabapentin when used in the treatment of burning mouth syndrome. 13 reviews submitted with a 6.3 average score. What is burning mouth syndrome? Primary burning mouth syndrome (BMS) is a benign condition that presents as a burning sensation in the absence of any obvious findings in the mouth and in the absence of abnormal blood tests. BMS affects around 2% of the population with women being seven times more likely to be diagnosed than men. Female patients are predominately post-menopausal, although men Gabapentin is a drug treatment often tried in the burning mouth syndrome community, where 2,338 members have shared their treatment experiences. It has been reported as tried by 10% of the members with positive effectiveness reports. Ranked #1 most tried and #3 most effective. The present case illustrates the effectiveness of gabapentin as a treatment of burning mouth syndrome. Burning mouth syndrome (BMS) is a debilitating disorder characterized by persistent and painful oral burning sensations. Initial treatments with nortriptyline hydrochloride and sertraline hydrochloride were contraindicated because of adverse effects, but the administration of gabapentin significantly reduced oral burning. The present case illustrates the effectiveness of gabapentin as a treatment of burning mouth syndrome. Burning mouth syndrome (BMS) is a chronic oral pain syndrome that primarily affects peri- and postmenopausal women. It is characterized by oral mucosal burning and may be associated with dysgeusia, paresthesia, dysesthesia, and xerostomia. The etiology of the disease process is unknown, but is thoug Introduction Burning Mouth Syndrome (BMS) is a chronic pain condition characterized by the presence of a burning sensation/pain of the oral cavity without any clinically evident signs of lesions or sys-temic causes [1]. Prevalence rates of BMS in the general population range between 0.7% to 15%, with higher rates seen in older females [2]. ABSTRACT Burning mouth syndrome is a challenging condition in terms of both diagnosis and management. These challenges lead to frustration for patients and difficulties for dental practitioners. Unfortunately, delays are common between initial presentation and definitive diagnosis, and also between diagnosis and appropriate management.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |