Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | +Labeling+of+rib+cage.+(B)+Inflammation+of+coastal+cartilages..jpg) |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
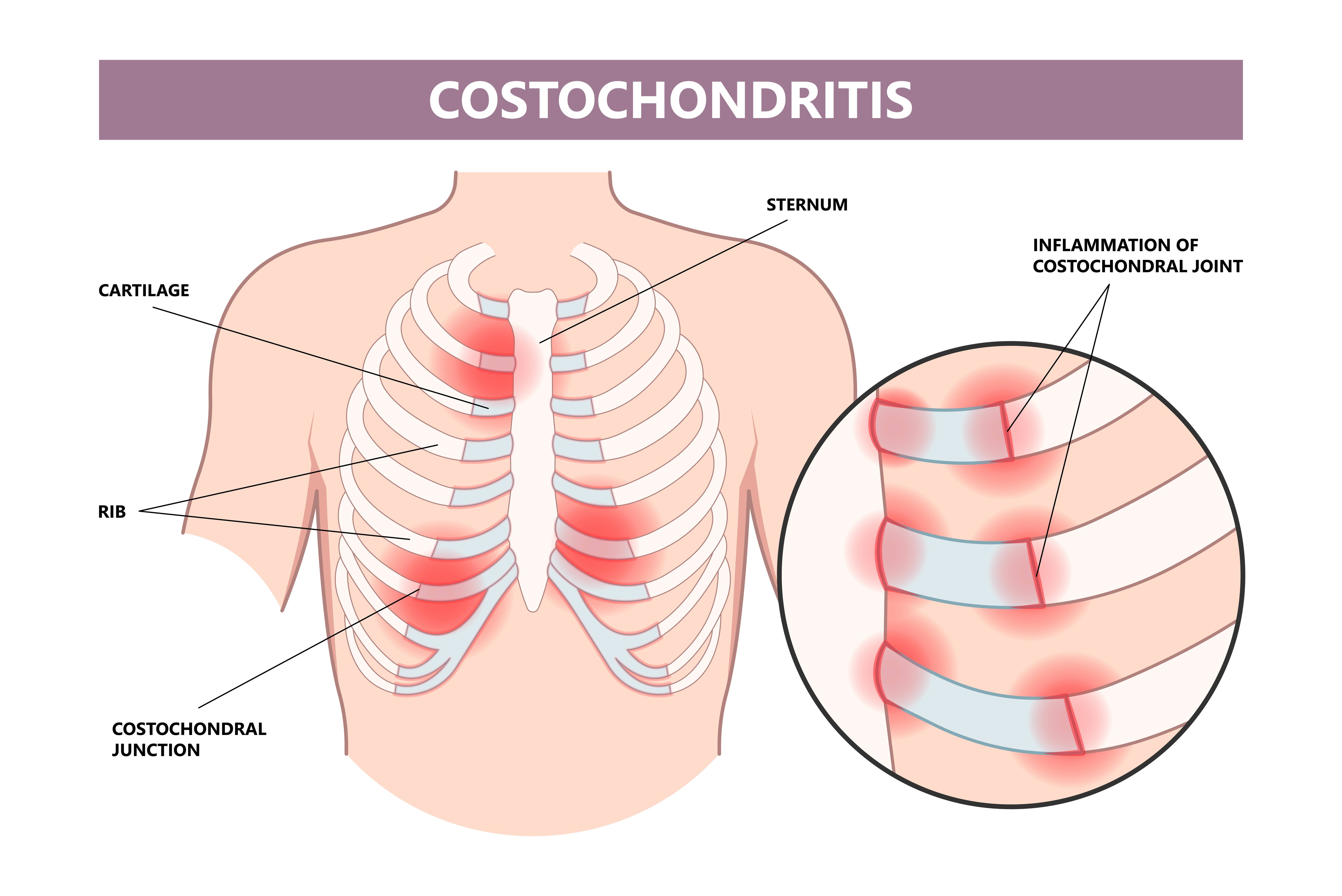
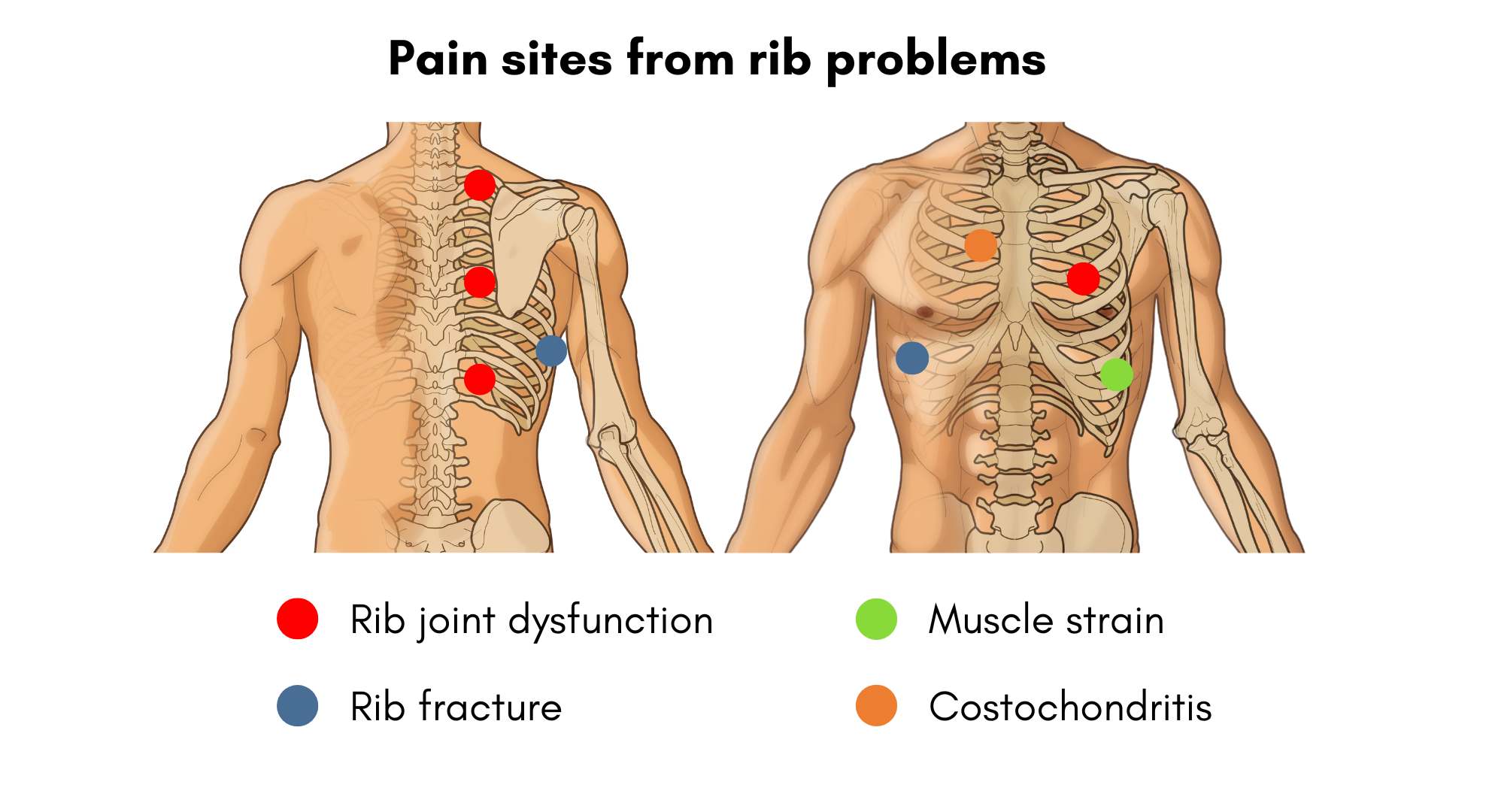
Costochondritis usually goes away on its own, although it might last for several weeks or longer. Treatment focuses on pain relief. Costochondritis is an agonizing inflammation in the chest, often mistaken for a heart attack. WebMD explores its origins, signs, diagnosis, and remedies. Costochondritis is an inflammation condition of the cartilage that connects the rib to the breastbone (sternum). The areas where the upper ribs join the cartilage that holds the breastbone are called costochondral junctions. The pain due to costochondritis can often be mistaken for a heart attack and other chest ailments. However, chest pain due to costochondral may not require treatment Overview Costochondritis (kos-toe-kon-DRY-tis) is an inflammation of the cartilage that connects a rib to the breastbone (sternum). Pain caused by costochondritis might mimic that of a heart attack or other heart conditions. Costochondritis is sometimes known as chest wall pain, costosternal syndrome or costosternal chondrodynia. Sometimes, swelling accompanies the pain (Tietze syndrome Costochondritis (kos-toe-kon-DRY-tis) is an inflammation of the cartilage that connects a rib to the breastbone (sternum). Pain caused by costochondritis might mimic that of a heart attack or other heart conditions. Costochondritis is sometimes known as chest wall pain syndrome, costosternal syndrome or costosternal chondrodynia. Sometimes, swelling accompanies the pain (Tietze syndrome). What Antiseizure drugs: Epilepsy medications such as gabapentin (Neurontin) have been effective in controlling the chronic pain associated with costochondritis. Antibiotics for infections: Antibiotics can be used to combat underlying bacterial or fungal infections contributing to the condition. Narcotics can be habit-forming. Antidepressants. Tricyclic antidepressants, such as amitriptyline, are often used to control chronic pain — especially if it's keeping you awake at night. Anti-seizure drugs. The epilepsy medication gabapentin (Neurontin) also has proved successful in controlling chronic pain. Costochondritis is a common cause of chest pain. It most commonly occurs in adults between 40 and 50 years of age, with a slight predominance in women. Although musculoskeletal and other chest A common cause of chest wall pain is costochondritis, a condition in which the cartilage that attaches the ribs to the breastbone (sternum) becomes inflamed. Costochondritis is not a life-threatening condition but can sometimes cause significant discomfort and distress to patients. Gabapentin: A Detailed Review of Effectiveness, Side Effects, and Comparisons for Treating Costochondritis. In summary, gabapentin is an off-label option for costochondritis, primarily used for nerve pain and seizures. Gabapentin (also known as Neurontin, an anti-epileptic / anticonvulsant drug) – can help relieve nerve pain, often used to treat chronic pain Prednisone – oral steroids are often prescribed for costochondritis to reduce inflammation Antibiotics (IV or oral) may be prescribed if your costochondritis is the result of a bacterial or fungal What is the treatment for costochondritis? There are different treatment options for costochondritis, dependent upon the severity of the condition. These include: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications narcotic pain medications tricyclic antidepressants, which may decrease pain gabapentin, another medication that may decrease pain Compare risks and benefits of common medications used for Costochondritis. Find the most popular drugs, view ratings and user reviews. A group for those who are suffering from costochondritis and Tietze syndrome (/r/TietzeSyndrome). Feel free to ask questions, and share what helps you manage the pain and hasten the recovery process. MembersOnline • mrnorris1966 ADMIN MOD Both gabapentin and diclofenac are effective in the treatment of chronic PCPP, without obvious side effects. However, gabapentin is found to be superior to diclofenac and its effects sustain longer. The results show that there may be some evidence in PCPP as a kind of neuropathic pain. Costochondritis is sometimes known as chest wall pain syndrome, costosternal syndrome or costosternal chondrodynia. Sometimes, swelling accompanies the pain (Tietze syndrome). What causes costochondritis is unclear. Treatment focuses on easing the pain while waiting for the condition to improve on its own, which can take several weeks or more. Antidepressants: There are some prescription antidepressants that help provide pain relief for persistent costochondritis. If your costochondritis is causing constant pain, tricyclic antidepressants (i.e. amitriptyline) might help. Anti-seizure drugs: Gabapentin (Neurontin), an epilepsy medication, can also be helpful in reducing persistent pain. Do you take Gabapentin and are concerned about Costochondritis? eHealthMe's data-driven phase IV clinical trials have been referenced on 800+ peer-reviewed medical publications including The Lancet, Mayo Clinic Proceedings, and Nature. Check whether Costochondritis is associated with a drug or a condition. What is costochondritis treatment? The most common costochondritis treatment is resting your chest and ribcage. Giving your irritated costochondral joints time to heal is the best thing to do for costochondritis. Over-the-counter (OTC) medications like NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) or acetaminophen can relieve your pain. Chest wall pain or costochondritis, also called Tietze’s syndrome, is an inflammation which occurs between the tissues that connect the rib to the sternum.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | +Labeling+of+rib+cage.+(B)+Inflammation+of+coastal+cartilages..jpg) |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |