Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
/GettyImages-537870655-5a319b5d47c2660036089c34.jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
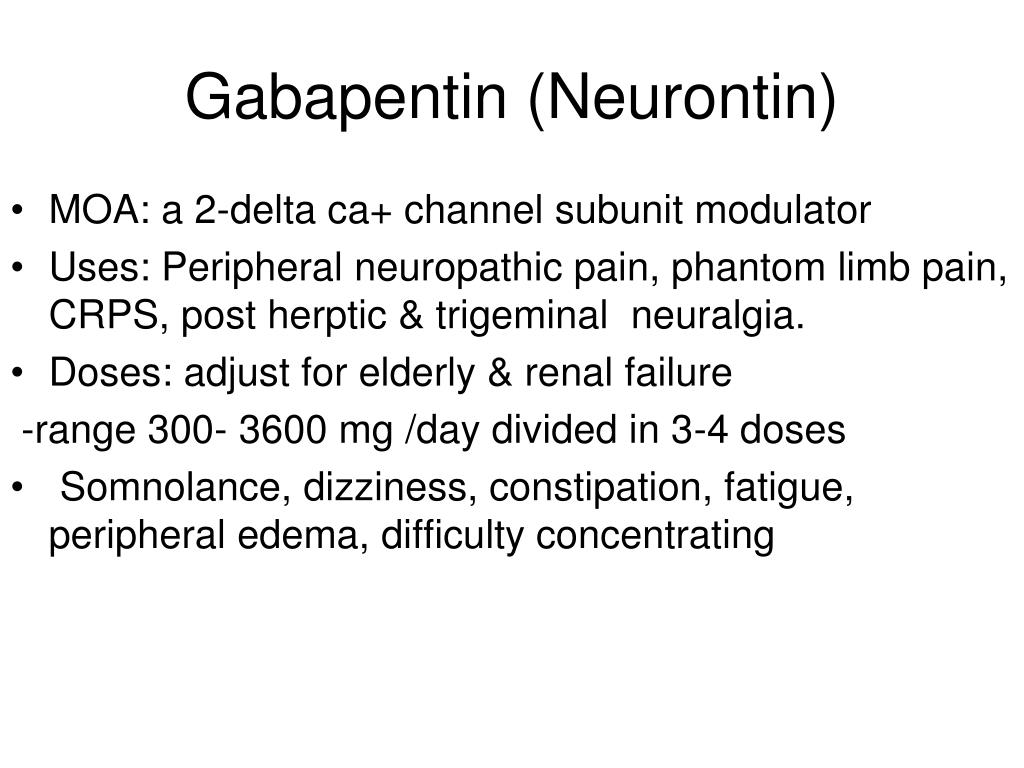
Gabapentin is also used to manage a condition called postherpetic neuralgia, which is pain that occurs after shingles. Gabapentin works in the brain to prevent seizures and relieve pain for certain conditions in the nervous system. It is not used for routine pain caused by minor injuries or arthritis. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant used to treat nerve related back pain, such as sciatica. Learn more about how gabapentin is used in sciatica treatment. Gabapentin for back pain could be a good choice, as it’s the best treatment for neuropathic back pain. However, it should not be taken without consulting a doctor. Let’s explore more. It can take one to two weeks to feel the full effects of Gabapentin for nerve pain. Some people use this medication long-term. Learn how long you should take Gabapentin for nerve pain. Specifically beneficial for those with radiating chronic spine pain, gabapentin and its counterpart, pregabalin, are prescribed to alleviate nerve-related issues. If your back pain is nerve-related, exploring gabapentin with your healthcare provider may pave the way to a more comfortable and active life. How Does Gabapentin Help? Gabapentin, used for treating seizures, effectively addresses back pain through a multifaceted approach, including neurotransmitter modulation and voltage-dependent ion channel effects. In a systematic review and metanalysis, Harsha Shanthanna and colleagues examine the evidence for the benefits and safety of gabapentoids for chronic low back pain. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication prescribed for a variety of conditions. Learn about its uses, side effects, and what you should know if you've been prescribed this medication. Gabapentinoids are not a good substitute for opioids in the management of chronic low back pain that does not include neuropathic pain, study finds. Gabapentin was originally developed as an anti-seizure medication. But healthcare professionals don’t just prescribe it for back pain. It’s also used for nerve pain, postsurgical pain, and occasionally anxiety. Let’s take a closer look at what the research says about gabapentin for back pain, how to take it, and when to consider further care. The use of anticonvulsants like gabapentin (Neurontin) for painful conditions has increased greatly in recent years. This review finds good evidence that these drugs are not an effective treatment Gabapentin is not effective for the treatment of radicular low back pain and is associated with adverse effects. Gabapentin is prescribed for analgesia in chronic low back pain, yet there are no controlled trials supporting this practice. This randomized, two-arm, 12-week, parallel group study compared gabapentin (forced titration up to 3600 mg daily) to inert Background Chronic low back pain (CLBP) is a global health problem, and gabapentin and pregabalin are often used in the treatment of patients without associated radiculopathy or neuropathy. Therefore, determining their efficacy and safety is of Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant with pain-relieving effects that may be used to treat partial-onset seizures or relieve nerve pain. Research has shown gabapentin binds strongly to a specific site (called the alpha2-delta site) on voltage-gated calcium channels and this is thought to be the way gabapentin works to relieve nerve pain and lower Certain medications are safer and more effective than others for treating spine pain in older adults, according to a recent study. Among these are the over-the-counter drugs acetaminophen (Tylenol) and ibuprofen (Advil) and some nerve pain drugs, muscle relaxants, and antidepressants. Back pain is the leading cause of disability in the US (1). With an overwhelming number of available treatments, choosing a medication to treat your back pain can be difficult. If your back pain is nerve-related, then the anticonvulsant drug gabapentin may be a good choice for you. This article will explain how gabapentin works, detail its uses, and go over potential side effects, so that you Gabapentin is an anti-epileptic drug, also called an anticonvulsant. It is used to treat some types of seizures and nerve pain caused by shingles. Back pain can be a potential side effect of Gabapentin. If your back pain is related, it may decrease in severity or go away entirely within 1-3 months, on average. To enhance gabapentin’s effectiveness for back pain relief, consider incorporating low-impact exercises like yoga, walking, or swimming into your routine. Focus on maintaining a healthy weight and practicing good posture to support your back.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
/GettyImages-537870655-5a319b5d47c2660036089c34.jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |