Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
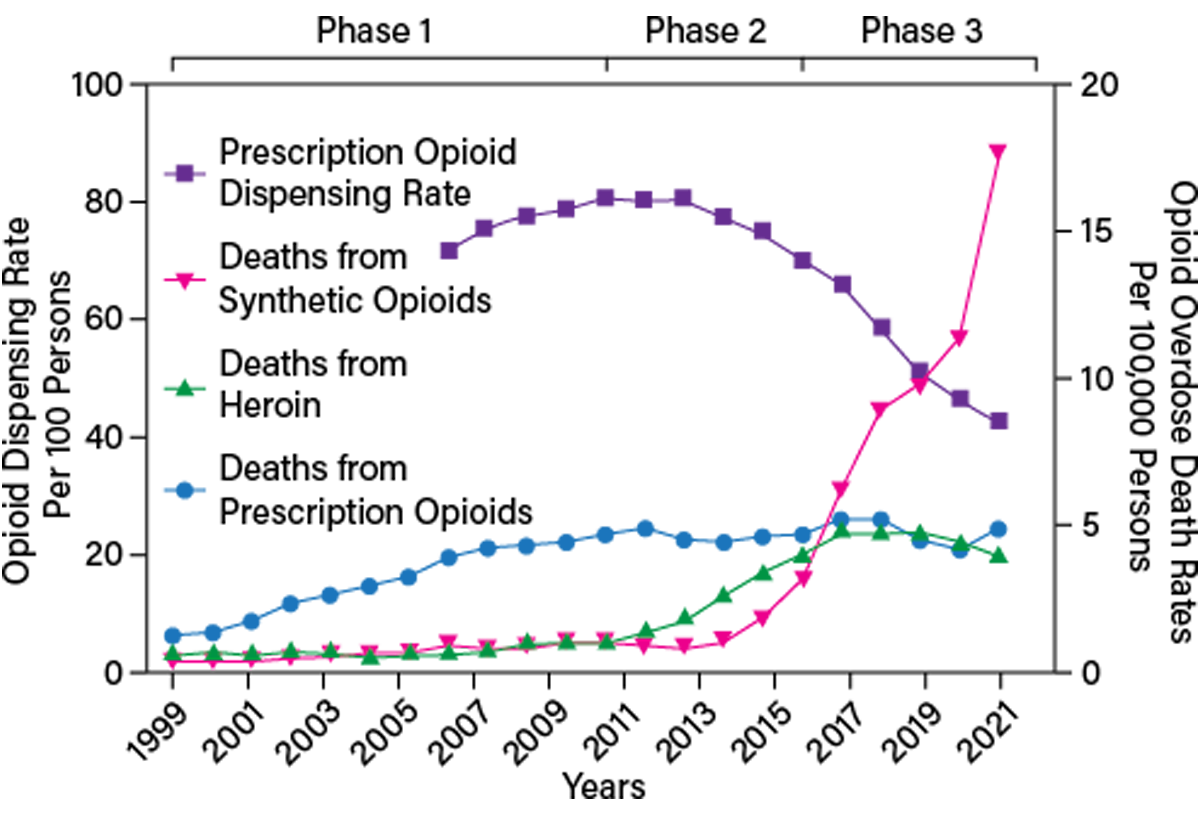 | 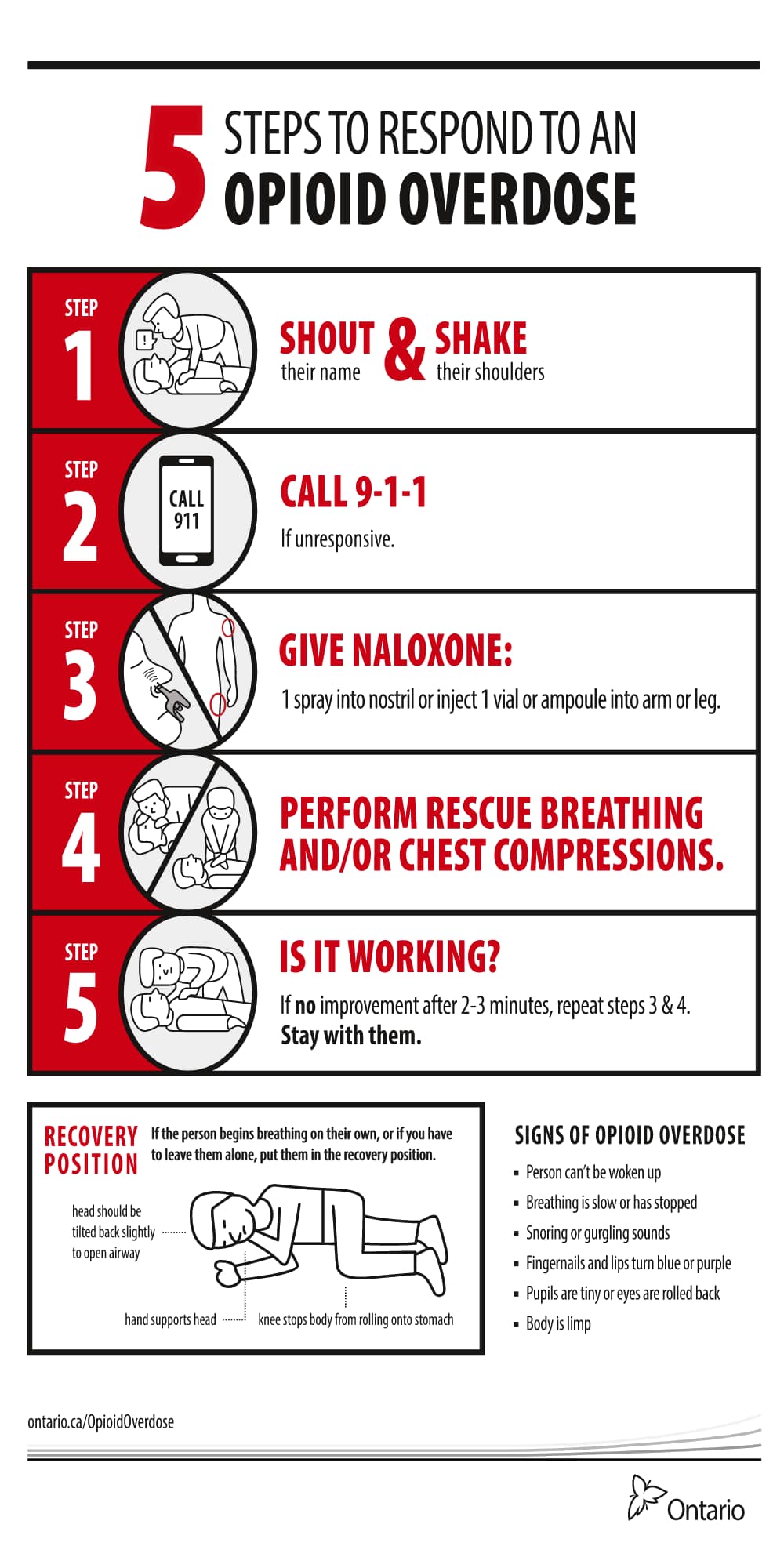 |
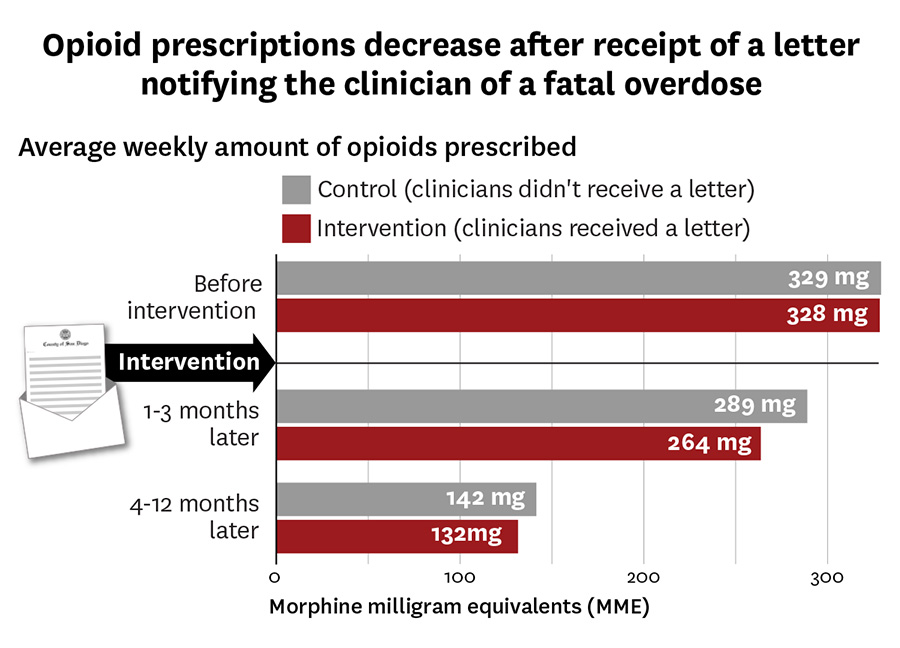
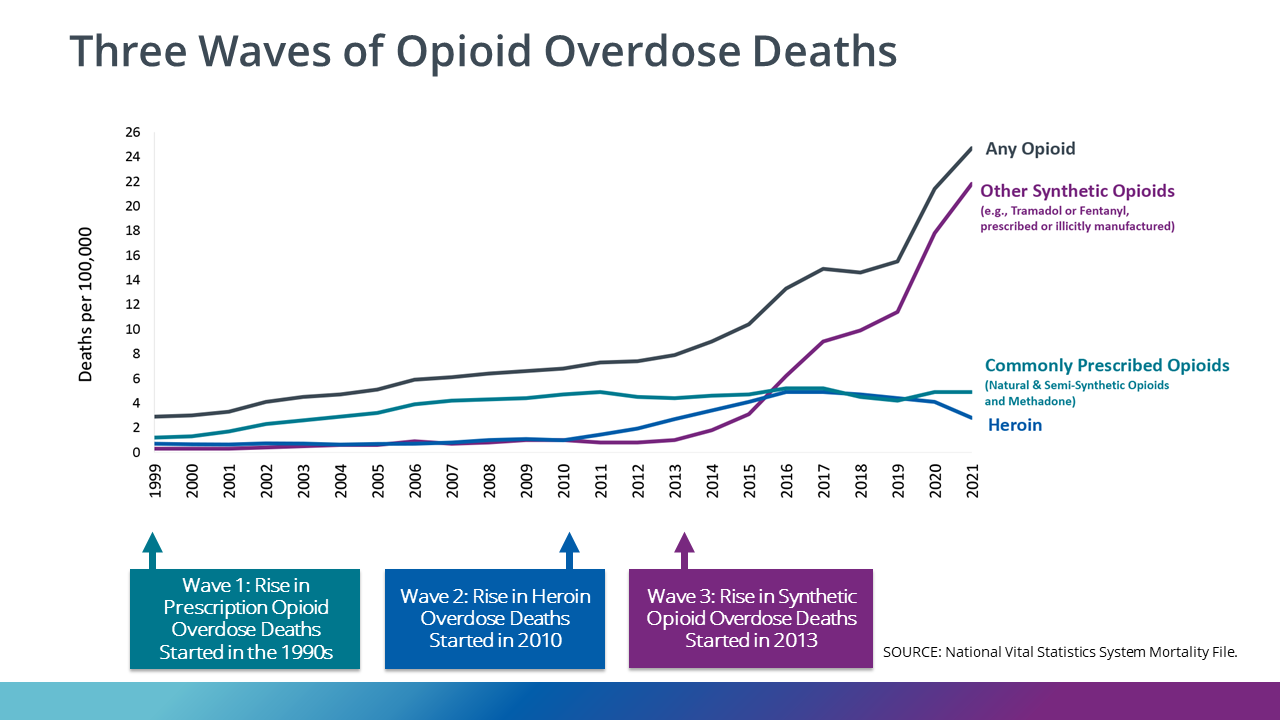
Prescription opioid use is highly associated with risk of opioid-related death, with 1 of every 550 chronic opioid users dying within approximately 2.5 years of their first opioid prescription. Although gabapentin is widely perceived as safe, Gabapentin isn't a narcotic, but it is a controlled substance in some states. Here's what you should know before using it. Opioid medication significantly reduces low back pain, but opioids should not be used in combination with gabapentin (Neurontin) because of their limited effectiveness and potential for abuse, according to the authors of a small new study presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Pain Medicine. The number of opioid-involved deaths has increased substantially since 1999. There have been three distinct waves of increases in opioid overdose deaths over the last 25 years, with each wave driven by different types of opioids. Increasing communities' overdose prevention and response support, capacity, and education may help save lives. What opioid medications do Opioids are a broad group of pain-relieving drugs that work by interacting with opioid receptors in your cells. Opioids can be made from the poppy plant, such as morphine (e.g., Kadian and MS Contin) or synthesized in a laboratory, such as fentanyl (e.g., Actiq and Duragesic). Dr. Carrie Krieger, a clinical [] Gabapentinoid drugs—specifically gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica)—are increasingly being prescribed for pain because physicians and patients seek alternatives to opioids in the Opioids are a broad group of medicines used to relieve pain. Although these medicines are effective, they can lead to addiction. Take them only as directed. Gabapentin (Neurontin) is not a narcotic or federally controlled substance by the DEA as of November 2022, but it is classified as a Schedule V controlled substance in certain states. In general, medications classified as Schedule V (Schedule 5) controlled substances are considered to have the lowest potential for abuse compared to other controlled schedules, but may still pose a risk of A plain language summary of prescription opioids that explains effects on the brain and reported use. The term opioid is sometimes used interchangeably with opiate; the latter, however, refers more narrowly to natural opioids—namely codeine, heroin, morphine, and opium. Opioids and opiates are classified as narcotics, which are any drugs that produce pain relief and narcosis (a state of stupor or sleep) and that can cause addiction. Gabapentin can also lead to sedation, which is a major side effect of opioids. When taken at high doses it is possible to feel high from gabapentin, and again, this is an effect of opioids. Opioids are powerful drugs that relieve pain. Learn their medical uses and side effects, plus factors that may increase opioid use disorder risk. ExposureGabapentinoids (gabapentin or pregabalin) coadministered with opioids starting the day of surgery vs opioid therapy without gabapentinoids. Main Outcomes and MeasuresPrimary outcome was opioid overdose. Secondary outcomes included respiratory complications, unspecified adverse effects of opioid use, and a composite of these 3 outcomes. Opioids are a powerful class of medications meant to be used for a short time after an injury or surgery to manage acute pain and enable activity. Drugs that fall into this class include morphine, oxycodone, hydrocodone, hydromorphone, fentanyl and the illegal drug heroin. The term “opioid” is often used inter- changeably with the term “opiate,” but this isn’t always correct. Opiate Traditionally, gabapentin and other non-opioid-type medications were used for long-term chronic pain conditions, including anxiety, seizures, shingles, and diabetic neuropathy, as opposed to opioids, which were prescribed for short-term pain relief in acute situations, such as post-operative, according to Little. Growing evidence of misuse and overdoses involving gabapentin—often in conjunction with opioids—is drawing attention to substantial off-label prescribing of the anticonvulsant drug. Opioids are a class of natural, semi-synthetic, and synthetic drugs. These include both prescription medications used to treat pain and illegal drugs like heroin. Opioids are addictive. Use of opioids, either by themselves or in combination with other drugs, is a major driver of the drug overdose crisis in the United States. The vast majority of overdose deaths in recent years involved The weak opioid codeine, in low doses and combined with one or more other drugs, is commonly available in prescription medicines and without a prescription to treat mild pain. [32][33][34] Other opioids are usually reserved for the relief of moderate to severe pain. [33] Gabapentin is not an opioid. Understand the differences between gabapentin and opioids, including how they work, their uses, risks, and when each may be appropriate for pain management. Key takeaways: Gabapentin (Neurontin) is FDA approved to treat certain types of seizures and nerve pain. Opioids are approved to treat moderate to severe pain. Gabapentin is sometimes used “off-label” as an alternative to opioid medications to help manage pain. Opioids have a higher potential for dependence and addiction than gabapentin.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |