Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
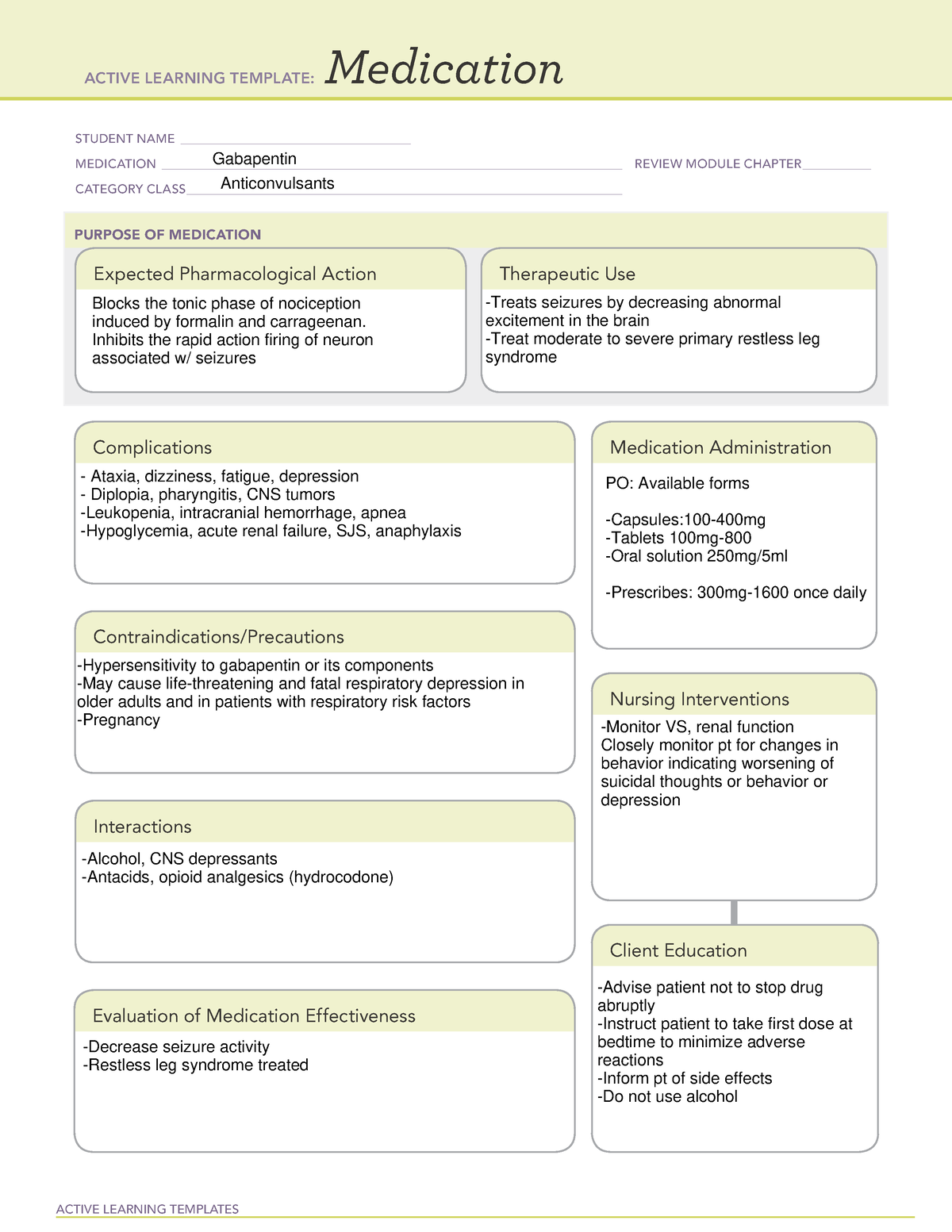
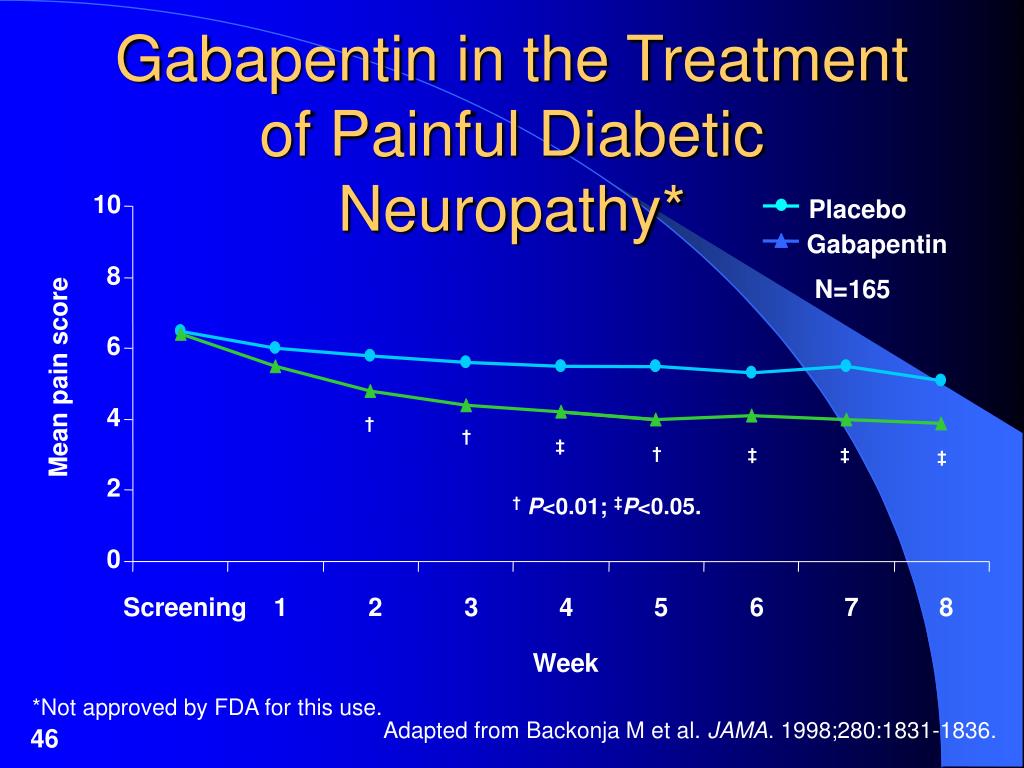
Neurontin (gabapentin): FDA approved for post-herpetic neuralgia, used off-label for fibromyalgia, diabetic neuropathy, and other neuropathic pain Lyrica (pregabalin): FDA approved for post-herpetic neuralgia, diabetic neuropathy, fibromyalgia, pain from spinal cord injury, and central neuropathic pain Anti-seizure medicines. Medicines such as gabapentin (Gralise, Neurontin, Horizant) and pregabalin (Lyrica), developed to treat epilepsy, often improve nerve pain. Side effects can include drowsiness and dizziness. Topical treatments. Lidocaine cream that is available without a prescription can be applied to the skin. A Cochrane review of gabapentin for chronic neuropathic pain in adults confirmed that gabapentin is associated with greater rates of pain relief compared with placebo in post-herpetic neuralgia and diabetic peripheral neuropathy, but it concluded that evidence for other neuropathic pain conditions was weak [60]. Gabapentin is indicated for: Neuropathic pain caused by postherpetic neuralgia Adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial seizures with or without secondary generalization Neuropathic pain caused by diabetic peripheral neuropathy and spinal cord injury Restless leg syndrome (gabapentin enacarbil) Gabapentin is frequently used off-label for: It is also indicated for the treatment of neuropathic pain inclusive of diabetic neuropathy, post-herpetic neuralgia and trigeminal neuralgia in adults ≥18 yrs. Dosage: The recommended dose for Epilepsy: Adults and children >12 yrs: Initially 300 mg tds on day 1 or by titrating dose as: 300 mg once daily on day 1, 300 mg bd on day 2 and 300 Gabapentin (Gralise, Neurontin) also is an option. Side effects can include feeling drowsy or dizzy, and getting swelling in the hands and feet. Antidepressants. Some of these medicines ease nerve pain even if you aren't depressed. Tricyclic antidepressants may help with mild to moderate nerve pain. Gabapentin (GBP) is a Health Canada approved antiepileptic drug. 5 In the UK, GBP is licensed for the treatment of peripheral and central neuropathic pain in adults and in the US it is marketed for post-herpetic neuralgia (PHN). 3 The mechanism of action for GBP relates to its ability to bind with high-affinity to the alpha-2-delta subunit of Pain expert offers clinical guidance to a commonly asked question about the proper, safe, and effective dose of gabapentin when treating neuropathic pain. A gastroretentive gabapentin formulation for the treatment of painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy: efficacy and tolerability in a double-blind, randomized, controlled clinical trial. Our El Paso Podiatrists Can Offer More Effective Treatment Options for Diabetic Neuropathy in the Feet Burning, tingling, and numbness in your feet can make every step a challenge. You've heard about gabapentin for nerve pain, but is it really the miracle cure you've been hoping for? The experienced Diabetic Foot care Podiatrists at The Foot Institute, with multiple locations throughout El Painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy occurs in approximately 25% of patients with diabetes mellitus who are treated in the office setting and significantly affects quality of life. It typically Gabapentin can help relieve nerve pain in some people with postherpetic neuralgia (nerve pain after shingles) and peripheral diabetic neuropathy (nerve pain in the feet in people with diabetes). This review is an update of a review published in 2011, itself a major update of previous reviews published in 2005 and 2000, investigating the effects of gabapentin in chronic neuropathic pain (pain due to nerve damage). Antiepileptic drugs are One, from the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence in the United Kingdom, includes the use of gabapentin as a first-tier treatment for all neuropathic pain. 14 Similarly, the European The Neuropathic Pain Special Interest Group of the International Association for the Study of Pain recently sponsored the development of evidence-based guidelines for the pharmacological treatment of neuropathic pain. Tricyclic antidepressants, dual reuptake inhibitors of serotonin and norepinephrine, calcium channel α2-δ ligands (ie, gabapentin and pregabalin), and topical lidocaine were Gabapentin is commonly used to treat neuropathic pain (pain due to nerve damage). This review updates a review published in 2014, and previous reviews published in 2011, 2005 and 2000. To assess the analgesic efficacy and adverse effects of Gabapentin was effective in the treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, and other neuropathic pain syndromes. It relieved symptoms of allodynia, burning pain, shooting pain, and hyperesthesia. Adverse effects were typically mild to moderate and usually subsided within approximately 10 days from the initiation of treatment. It can take one to two weeks to feel the full effects of Gabapentin for nerve pain. Some people use this medication long-term. Learn how long you should take Gabapentin for nerve pain. Painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy occurs in approximately 25% of patients with diabetes mellitus who are treated in the office setting and significantly affects quality of life. It typically The bottom line Direct comparisons of treatments for idiopathic sensory polyneuropathy — which many simply call neuropathy — are sorely needed, so this trial is important. Yet, the biggest take-home message of this research is that many current treatments aren’t very good.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |