Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
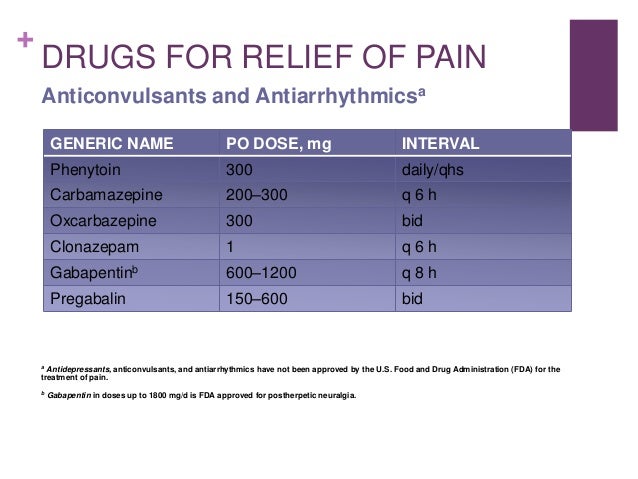 | 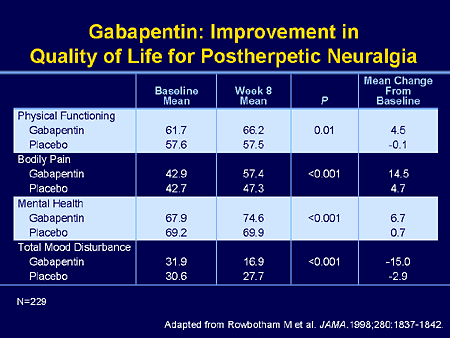 |
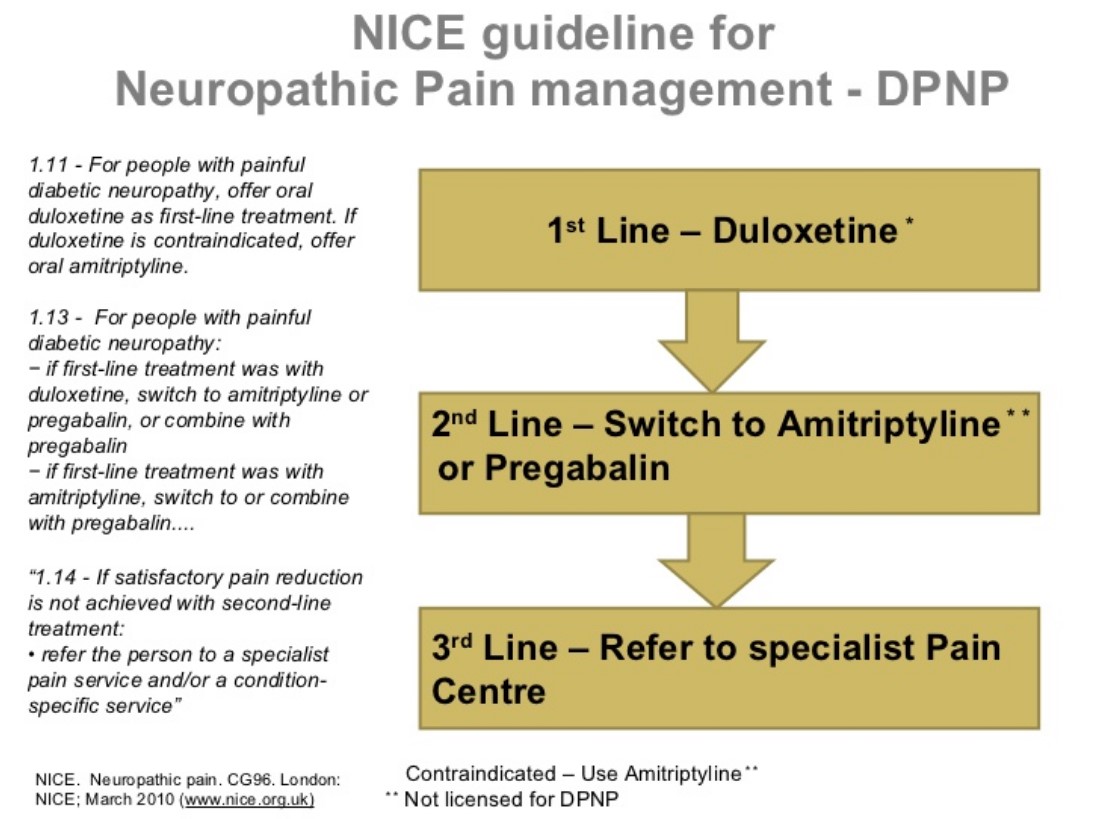
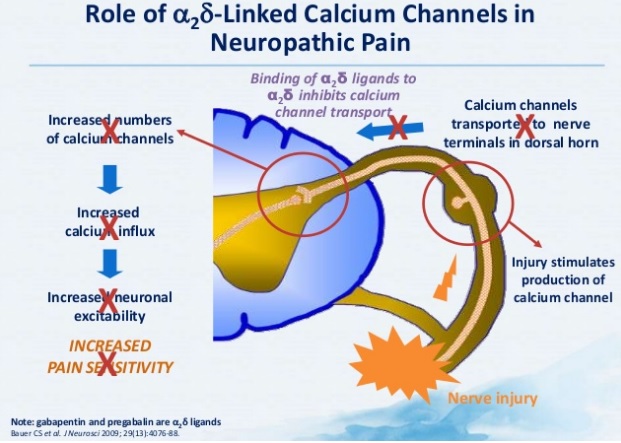
An overview of possible dose equivalences, switching methods and considerations to make before switching between gabapentinoids in adults with neuropathic pain. Pregabalin (Lyrica) and gabapentin (Neurontin) are medications that treat certain types of seizures and nerve pain. Pregabalin has more FDA approved uses. Both are frequently used off-label for a wide range of health conditions. When comparing pregabalin versus gabapentin, they work in similar ways but pregabalin is absorbed more quickly and fully. Gabapentin is contraindicated in individuals who have hypersensitivity to this medication or its components, which can cause fever and other symptoms that could become severe. Pregabalin vs Gabapentin â What is the Difference? Pregabalin and gabapentin can both provide relief from pain and be effective ways to manage seizure disorders. This meta-analysis aims to evaluate and compare the effectiveness and safety of pregabalin vs. gabapentin in managing neuropathic pain. Methods: This study followed PRISMA guidelines and employed the PICOS search strategy. Find out how gabapentin and Lyrica are used for pain control and when they can be used together. Neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury (SCI) has a significant negative impact on the patients’ quality of life. The objective of this systematic review is to examine the safety and efficacy of pregabalin (PGB) and gabapentin (GBP) in the Lyrica may also be used to treat neuropathic (nerve) pain associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy or postherpetic neuralgia, spinal cord injury, and fibromyalgia Gabapentin may also be used to treat nerve pain caused by shingles (herpes zoster) and gabapentin enacarbil, brand name Horizant, is also approved for restless legs syndrome (RLS). Compared with gabapentin, pregabalin was more efficacious and safer for the treatment of neuropathic pain, with significant reductions in pain intensity and duration, opioid use, and adverse events. Pregabalin vs Gabapentin Which is Better Pregabalin and gabapentin are “off-label” medications used for treating perplexing conditions like neuropathic pain, seizures, and anxiety. Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly utilised to relieve nerve-related discomforts. Pregabalin is seen to act quicker and is clinically stronger than gabapentin. I now advocate for deprescribing gabapentin when patients do not achieve adequate pain relief for chronic neuropathic pain at a cumulative daily dose of 1800 mg. Instead, I consider pregabalin as a substitute for gabapentin in patients with inadequate pain control rather than further dose escalations. Researchers compare four treatments for neuropathy Researchers publishing in JAMA Neurology describe the results of a unique trial in which 402 people with idiopathic sensory polyneuropathy were randomly assigned to one of four medications: duloxetine, mexiletine, nortriptyline, or pregabalin. Note that pregabalin is currently approved for treating generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) in Europe, but not in the United States. Continue reading for an in-depth comparison of pregabalin versus gabapentin, including an analysis of their respective uses, proven efficacy, dosing regimens, side effects, and more. Pregabalin and Gabapentin are both anticonvulsants used for nerve pain & anxiety. Pregabalin is generally faster-acting and more potent than Gabapentin. Gabapentin and pregabalin are often considered first line treatment options for various neuropathic pain conditions. The purpose of this retrospective cohort study was to compare clinically meaningful pain reduction and other relevant outcomes among patients prescribed either gabapentin or pregabali The anticonvulsants pregabalin and gabapentin are both indicated for the treatment of peripheral neuropathic pain. The decision on which treatment provides the best alternative, should take into account all aspects of costs and outcomes associated Pregabalin (Lyrica) and gabapentin (Neurontin and others) are drugs used to prevent seizures and to treat nerve pain associated with various conditions (shingles, diabetic neuropathy). Lyrica and gabapentin both cause similar side effects, including tremors, blurred or double vision, memory or concentration problems, dizziness, and drowsiness. Pregabalin vs. gabapentin in the treatment of neuropathic pain: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis of effectiveness and safety Research supports the use of the anticonvulsants gabapentin (Gralise, Neurontin, Horizant) and pregabalin (Lyrica) to help relieve pain caused by damaged nerves. Both gabapentin and pregabalin are particularly effective in the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia, diabetic neuropathy and pain caused by a spinal cord injury. Regarding long-term safety data for the chronic use of pregabalin and gabapentin, in the case of pregabalin for the treatment of anxiety disorders, good tolerability has been observed with effective disease management (12). Comparison of gabapentinoids gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica), differences between gabapentin and pregabalin chart, latest comparative clinical trials, up-to-date drug information.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |