Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
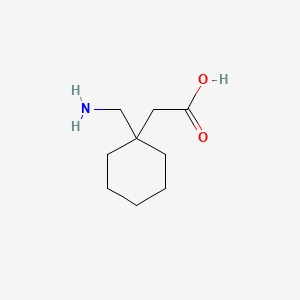 |
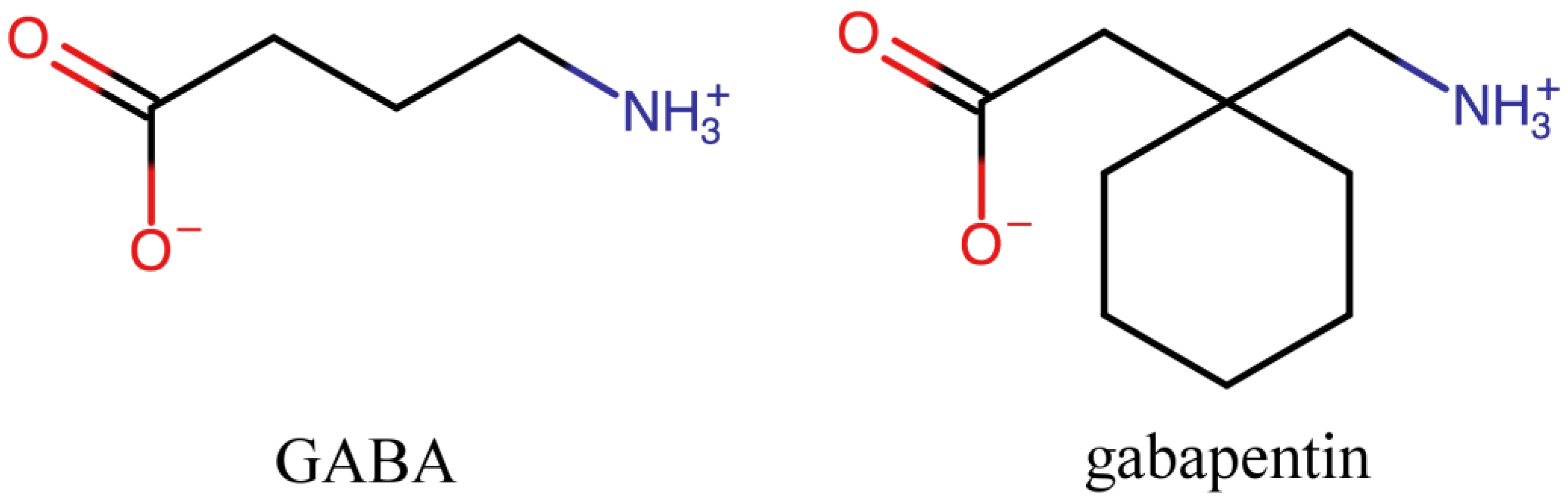
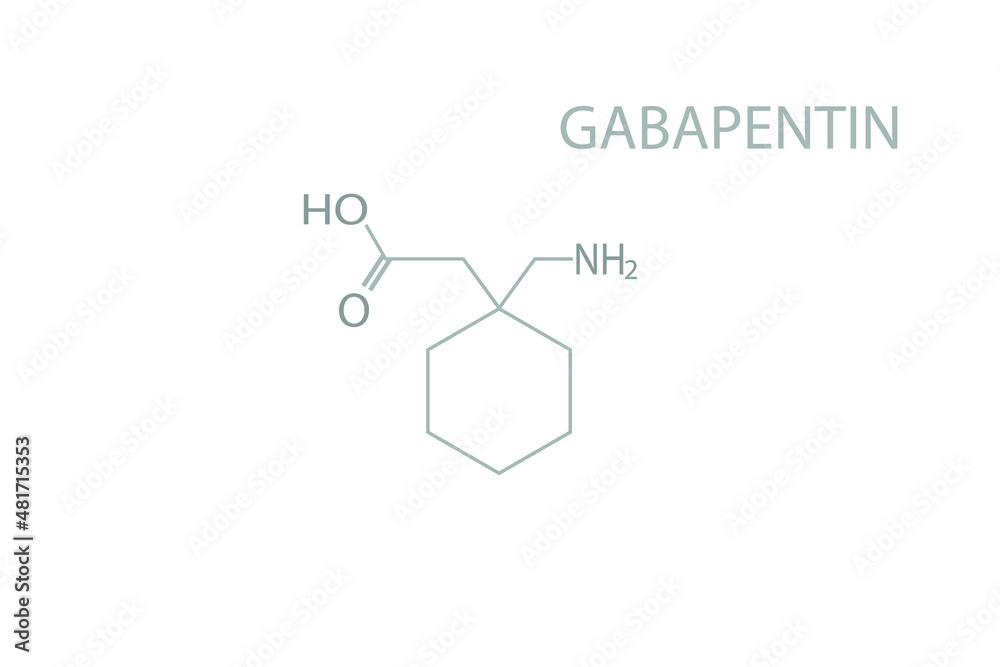
Gabapentin hydrochloride | C9H18ClNO2 | CID 6453919 - structure, chemical names, physical and chemical properties, classification, patents, literature, biological Gabapentin tablet contains gabapentin, a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogue, as the active pharmaceutical ingredient. Gabapentin's chemical name is 1- (aminomethyl)cyclohexaneacetic acid In animals, gabapentin readily enters the brain and shows efficacy in some, but not all, seizure models. These animal models included genetic models of seizures, and seizures induced by maximal electroshock, from chemical convulsants including inhibitors of GABA synthesis. The chemical structure of gabapentin is derived from the addition of a lipophilic cyclohexyl group to the backbone of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Gabapentin is a crystalline substance and freely soluble in water, alkaline and acidic solutions. Gabapentin readily enters the brain and prevents seizures in a number of animal models of epilepsy. Gabapentin binds with high affinity to the α2δ (alpha-2-delta) subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels and it is proposed that binding to the α2δ subunit may be involved in gabapentin's anti-seizure effects in animals. ChemSpider record containing structure, synonyms, properties, vendors and database links for Gabapentin, 60142-96-3, UGJMXCAKCUNAIE-UHFFFAOYSA-N Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication used in the management of peripheral neuropathic pains, postherpetic neuralgia, and partial-onset seizures. The active ingredient in NEURONTIN capsules, tablets, and oral solution is gabapentin,which has the chemical name 1- (aminomethyl)cyclohexaneacetic acid. The molecular formula of gabapentin is C9H17NO2 and the molecular weight is 171.24. Gabapentin is a white to off-white crystalline solid with a pKa1 of 3.7 and a pKa2 of 10.7. Gabapentin (CAS 60142-96-3) information, including chemical properties, structure, melting point, boiling point, density, formula, molecular weight, uses, prices Gabapentin is a new chemical compound designed as a structural analog of GABA that is effective in the treatment of partial seizures. In contrast to GABA, gabapentin readily penetrates the blood–brain barrier. In man, gabapentin has been demonstrated to increase GABA concentrations [126]. Most probably the mechanism of action is related to events modulated through its interaction with a Gabapentin, USP is a white to off-white powder with a pKa1 of 3.7 and a pKa2 of 10.7. It is freely soluble in water, 0.1 N hydrochloric acid, 0.1 N sodium hydroxide and glacial acetic acid; slightly soluble in methanol, very slightly soluble in ethanol, 2-propanol; insoluble in toluene. The log of the partition coefficient (n-octanol/0.05M phosphate buffer) at pH 7.4 is –1.25. Know about technical details of Gabapentin like: chemical name, chemistry structure, formulation, uses, toxicity, action, side effects and more at Pharmacompass.com. Gabapentin is an antiepileptic drug that is considered a first-line treatment for the management of neuropathic pain. GBP is also approved for the treatment of focal seizures. However, it is ineffective in treating generalized epilepsy [4, 6, 7]. Aside from neuropathic pain, off-label use in primary care is very common. These include the treatment of a wide range of conditions such as bipolar Gabapentin, sold under the brand name Neurontin among others, is an anticonvulsant medication primarily used to treat neuropathic pain and also for partial seizures [10][7] of epilepsy. It is a commonly used medication for the treatment of neuropathic pain caused by diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, and central pain. [11] It is moderately effective: about 30–40% of those given Gabapentin is a structural analogue of the inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid ( [GABA]) that was first approved for use in the United States in 1993. It was originally developed as a novel anti-epileptic for the treatment of certain types of seizures - today it is also widely used to treat neuropathic pain. Gabapentin has some stark advantages as compared with other anti DESCRIPTION Neurontin® (gabapentin) Capsules, Neurontin (gabapentin) Tablets, and Neurontin (gabapentin) Oral Solution are supplied as imprinted hard shell capsules containing 100 mg, 300 mg, and 400 mg of gabapentin, elliptical film-coated tablets containing 600 mg and 800 mg of gabapentin or an oral solution containing 250 mg/5 mL of gabapentin. DESCRIPTION Neurontin® (gabapentin) Capsules, Neurontin (gabapentin) Tablets, and Neurontin (gabapentin) Oral Solution are supplied as imprinted hard shell capsules containing 100 mg, 300 mg, and 400 mg of gabapentin, elliptical film-coated tablets containing 600 mg and 800 mg of gabapentin or an oral solution containing 250 mg/5 mL of gabapentin. Patients taking gabapentin should not drive until they have gained sufficient experience to assess whether gabapentin impairs their ability to drive. Driving performance studies conducted with a prodrug of gabapentin (gabapentin enacarbil tablet, extended-release) indicate that gabapentin may cause significant driving impairment. Gabapentin, a medication widely used for treating nerve pain and certain types of seizures, has gained considerable attention in both medical and non-medical contexts. Understanding what goes into this drug can provide insights into its effectiveness, potential side effects, and overall safety. The composition of gabapentin is essential for both healthcare providers and patients to know, as it Gabapentin is a nonprotein amino acid and a synthetic neurotransmitter that is related to γ-aminobutyric acid1 (GABA). It was first described in 1976 West German patent DE2460891 on cyclic amino acids to Gerhard Satzinger and co-inventors at Goedecke AG (Freiburg). The corresponding US Patent is 4,024,175 (1977).
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |