Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
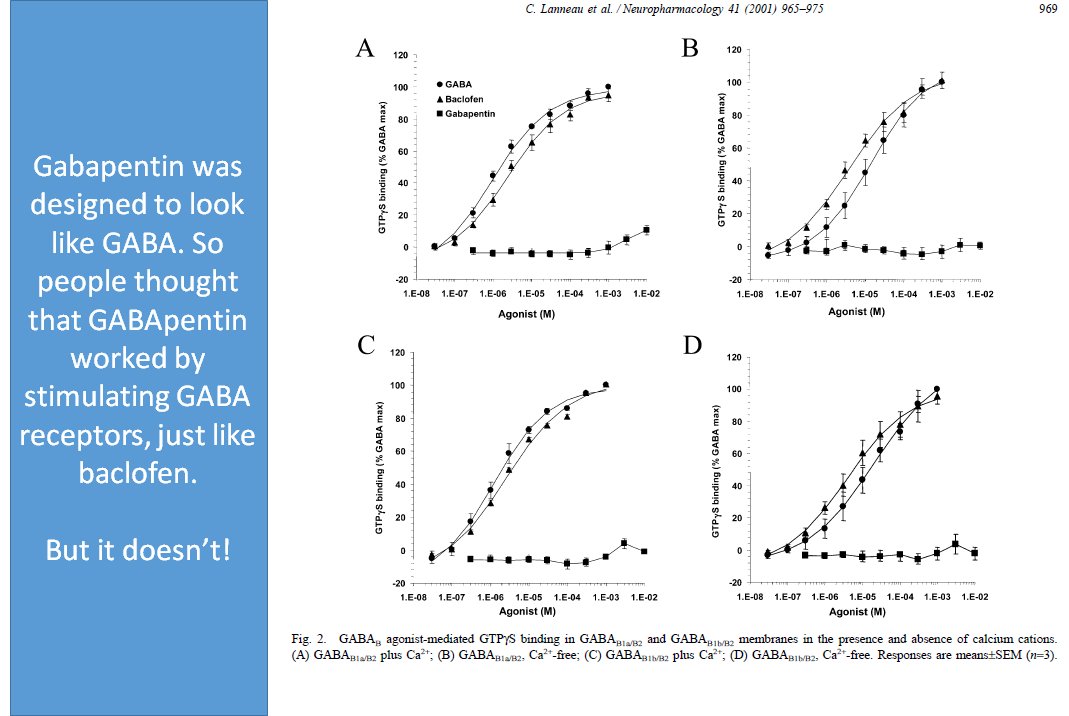
Gabapentin (US brand name Neurontin® and generic) is an analgesic and antiepileptic drug structurally related to gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), the key inhibitory neurotransmitter in the cerebral cortex. Here is basic information about this medication. Mechanism of action The mechanism of action of gabapentin is complex and not clearly known. It does not act on GABA receptors or affect the Wellbutrin works on two neurotransmitters in the brain. These are the chemicals that carry the information from one brain cell to another. Wellbutrin affects the reuptake of dopamine and norepinephrine inbetween brain cells, thereby allowing them to work "longer". How does gabapentin work in the brain? Gabapentin works by imitating the neurotransmitter GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid). GABA is the brain’s major inhibitory neurotransmitter, meaning it reduces neuronal excitability and activity. Specifically, gabapentin binds to a subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels in the brain called α2δ. Investigation of acute and chronic effects of gabapentin on both GABA and glutamate, particularly in brain regions typically implicated in seizure disorders, would be required to further examine gabapentin's anti-seizure effects in human subjects. Gabapentin is a medication used in the treatment of various conditions such as epilepsy, post-herpetic neuralgia, neuropathic pain, and spasticity. It works by affecting calcium channels, leading to a decrease in excitatory neurotransmitters. AI generated definition based on: Brain Research, 2016 Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid, or GABA, is an amino acid that slows down the brain by blocking specific nerve signals. Here’s how GABA receptors work and more. In this episode of I CARE FOR YOUR BRAIN with Dr. Sullivan, board certified neuropsychologist, Dr. Karen D. Sullivan provides some of the latest research on the drug, gabapentin, and its uses and Explore gabapentin's effects on mental function, memory, and cognition. Learn about managing side effects and balancing therapeutic benefits with potential risks. The Basics of Gabapentin Gabapentin, originally developed for treating epilepsy, has carved out a significant role in managing neuropathic pain and anxiety disorders. It's fascinating how a medication designed to control seizures has transformed into a versatile tool in various therapeutic areas. The drug's mechanism of action is intriguing; it primarily binds to the alpha-2-delta subunit of Explore the effectiveness of gabapentin for PTSD, its uses, benefits, side effects, and future research directions. GABA vs. Gabapentin What's the Difference? GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) and Gabapentin are both substances that affect the central nervous system, but they have different mechanisms of action and uses. GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter in the brain that inhibits or slows down nerve activity, helping to reduce anxiety and promote relaxation. On the other hand, Gabapentin is a However, gabapentin was shown to increase expression of δGABAA receptors, inhibitory tone in the cerebellum, and brain GABA concentration in patients, 3,4 while pregabalin enabled a larger neuronal calcium influx for facilitating neurotransmission. 2 These findings substantiate a GABAergic effect of gabapentin and pregabalin. Gabapentin works by changing brain electrical activity and the functioning of neurotransmitters, which send messages between nerve cells. The medication is available in pill, tablet, and liquid form. Brand names for gabapentin include Horizant, Gralise, and Neurontin. Seizures: Gabapentin reduces excessive neural activity in the brain, which can help prevent seizures. Nerve Pain: By reducing the release of certain neurotransmitters, gabapentin can lessen the sensation of pain, especially in cases of nerve-related pain (neuropathy), which can be persistent and hard to treat with typical pain relievers. Sir: Gabapentin is a newer anticonvulsant approved for use as an adjunct agent in the treatment of partial seizures with or without secondary generalization. 1 Recent publications indicate that gabapentin has been useful in a wide array of psychiatric conditions including anxiety disorders, 2 alcohol withdrawal, 3 bipolar disorder, 4 behavioral disorders, 5,6 and even antidepressant-induced Although gabapentin is not considered highly addictive, it does cross the blood-brain barrier and has a risk for physical dependence. Treating Brain Damage with Gabapentin Gabapentin can be an effective treatment for brain damage symptoms such as neuropathy, seizures, and autonomic dysfunction. However, it is not without side effects or risks. How does gabapentin act on the brain? Gabapentin appears to work by altering electrical activity in the brain and influencing the activity of chemicals called neurotransmitters, which send messages between nerve cells. Results with human and rat brain NMR spectroscopy indicate that gabapentin increases GABA synthesis. Gabapentin increases non-synaptic GABA responses from neuronal tissues in vitro. In vitro, gabapentin reduces the release of several mono-amine neurotransmitters. The new work also pinpoints, for the first time, the biochemical mechanism by which the widely prescribed drug gabapentin (also marketed under the trade name Neurontin) works. "We have solved the longstanding mystery of how this blockbuster drug acts," said Ben Barres, MD, PhD, professor and chair of neurobiology. The study shows that gabapentin halts the formation of new synapses, possibly
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |