Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
+treatment+to+percent+difference+of+glutamate+concentrations+when+compared+to+controls..jpg) | 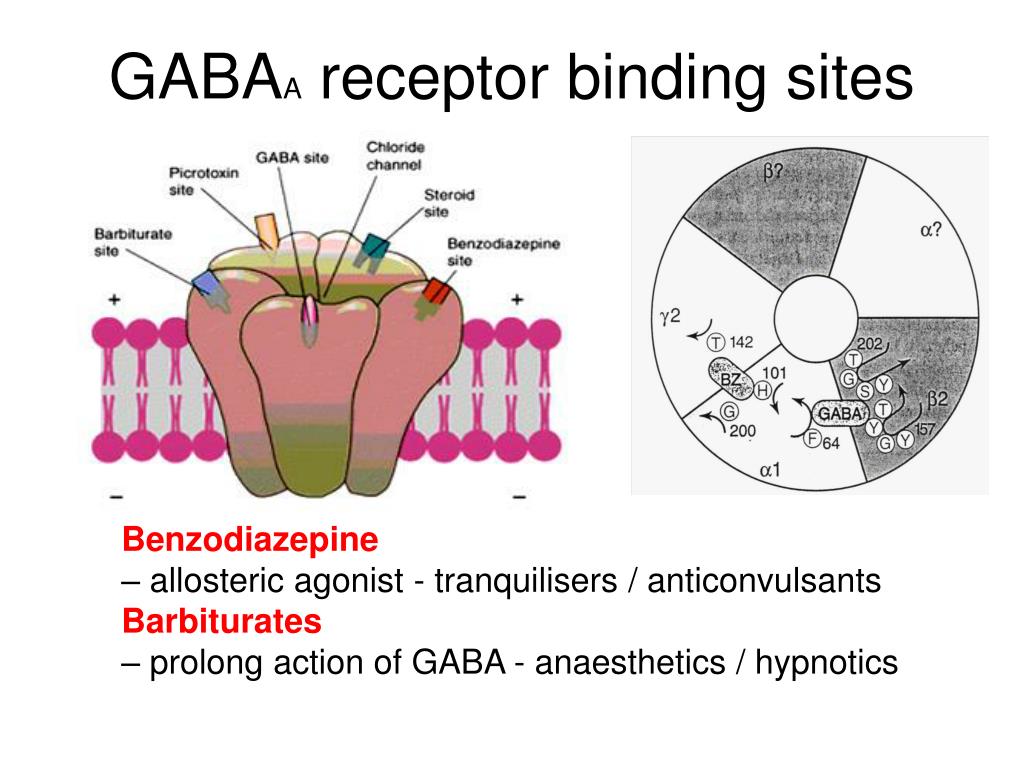 |
 |  |
 |  |
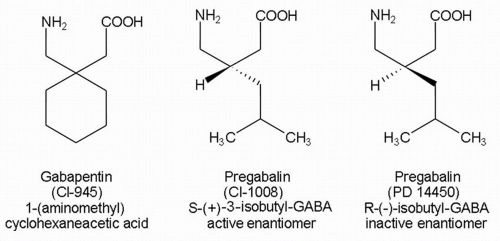
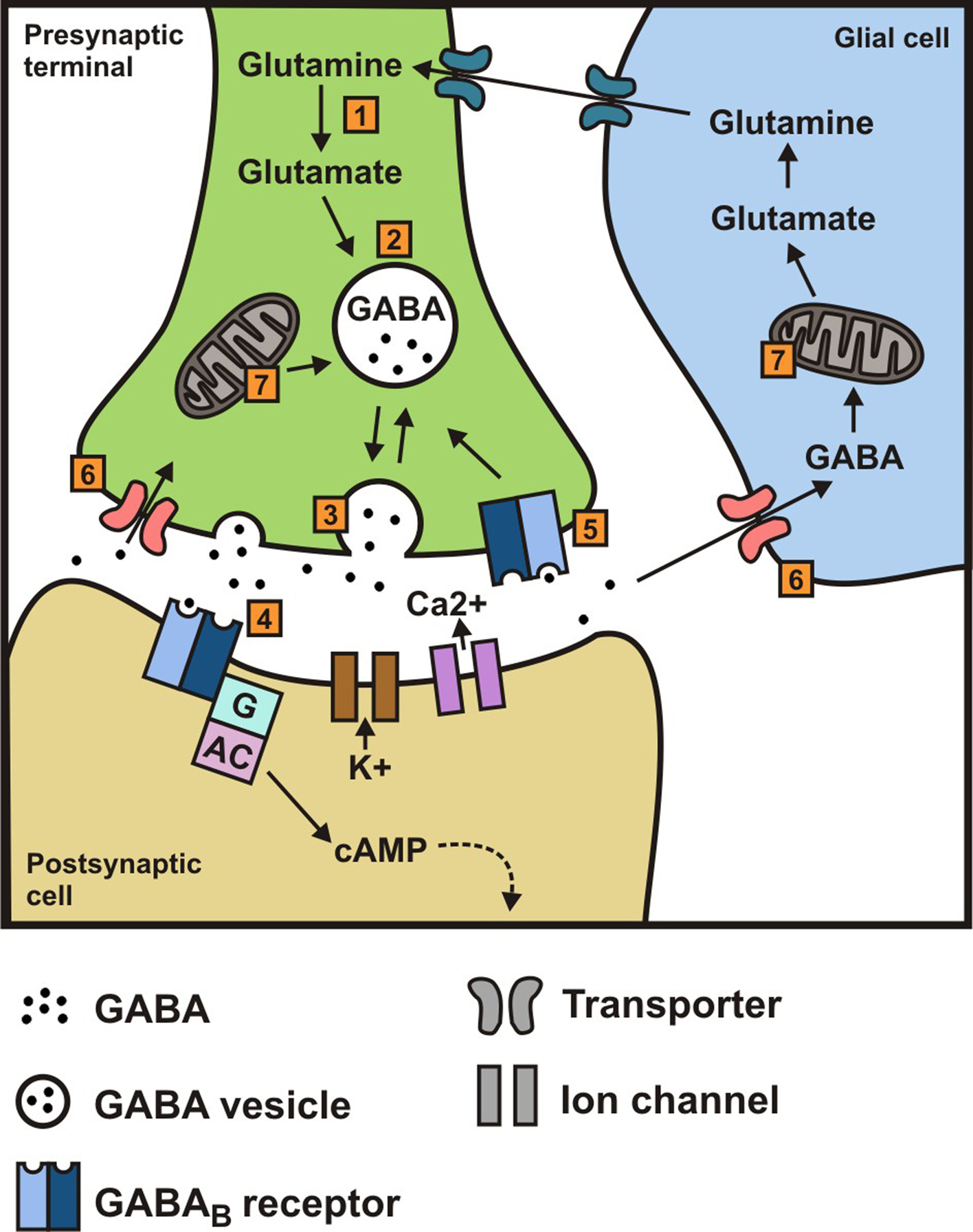
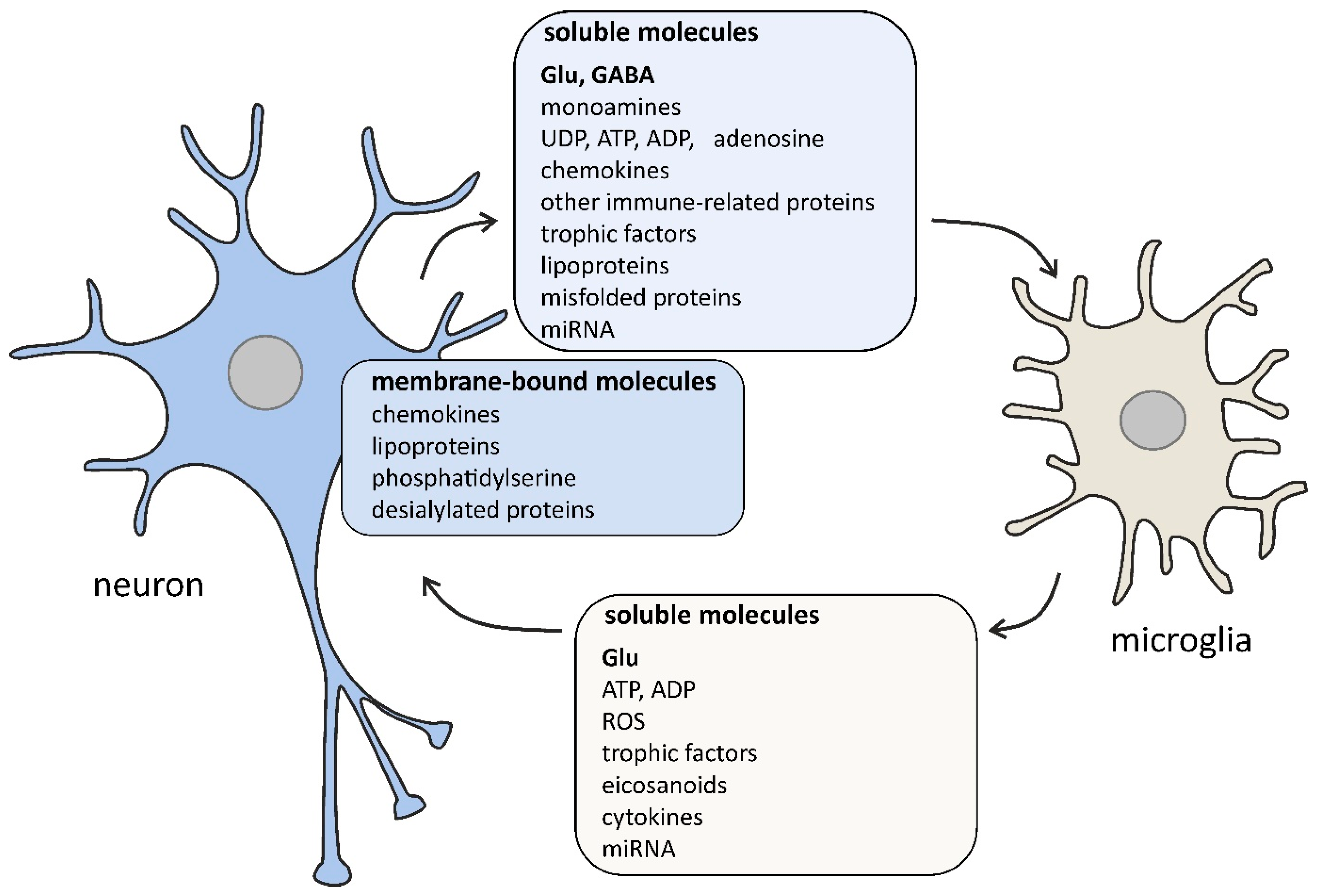
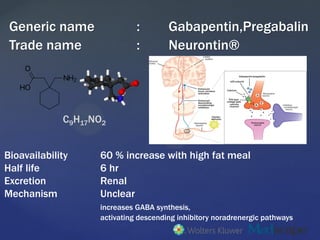
What is gabapentin? Gabapentin is a prescription medication known as a gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogue. GABA reduces the excitability of nerve cells (neurons) in the brain, which play a role in seizures and the transmission of pain signals. Gabapentin mirrors the effects of GABA calming excited neurons. Pregabalin (Lyrica) and gabapentin (Neurontin) are both approved to treat nerve pain. How are they different, and which one is preferred? Compare both meds here. GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter, while gabapentin is a synthetic medication designed to mimic GABA’s effects. GABA is available as a supplement, whereas gabapentin requires a prescription and is used for specific medical conditions like epilepsy and neuropathic pain. The differences between GABA and gabapentin lie in their mechanisms of action in the brain – GABA targets GABA receptors whereas gabapentin interacts with voltage-gated calcium channels. GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) is an amino acid supplement and neurotransmitter; gabapentin is a prescription medication. They are often used interchangeably (as you’ll read below) and should not be! Here are some of the many responses showing how GABA and gabapentin is used interchangeably by a variety of practitioners: We compare the side effects and drug effectiveness of Gaba and Gabapentin. The phase IV clinical study is created by eHealthMe based on reports (from sources including the FDA) of 428,095 people who take Gaba and Gabapentin, and is updated regularly. Gabapentin is a GABA analog, meaning that it looks very similar structurally but it is not completely the same. GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter found in the central nervous system (CNS) that regulates its excitability. Explore the differences between Gamma Aminobutyric Acid (GABA), a neurotransmitter, and Gabapentin, a medication, despite their similar names. GABA and Gabapentin, though distinct entities share a common goal: to promote calmness and regulate neuronal activity. While GABA is a natural neurotransmitter with diverse functions, Gabapentin is a synthetic medication mimicking some of its effects for specific therapeutic purposes. Explore the differences between GABA, a neurotransmitter, and Gabapentin, a medication mimicking GABA's effects, used for neurological conditions. Gabapentin and pregabalin are similar drugs but differ in several distinct ways. The main differences are their indications—specific uses that the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved them to treat—and their dosages. Gabapentin and pregabalin are FDA-approved to treat some of the same GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter in the brain that inhibits or slows down nerve activity, helping to reduce anxiety and promote relaxation. On the other hand, Gabapentin is a medication that is structurally similar to GABA but does not directly bind to GABA receptors. What is the Difference Between GABA and Gabapentin? GABA and gabapentin are chemically close to each other, but they have differences between them. e.g. structural make-up of the chemical compounds, applications, etc. The key difference between GABA and gabapentin is that GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter that can regulate the neuronal excitability in the central nervous system, whereas GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) and gabapentin are different substances with some similarities. GABA is a neurotransmitter in the central nervous system that controls nervous system excitability, while gabapentin is a drug designed as a structural analog of GABA. Here are the key differences between GABA and gabapentin: We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. GABA and gabapentin are often mistakenly used interchangeably, but they are not the same. GABA is an amino acid supplement and neurotransmitter, while gabapentin is a prescription medication. While practitioners may confuse the two, it’s important to understand their differences. Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and glutamate are implicated in numerous neuropsychiatric and substance abuse conditions, but their spectral overlap with other resonances makes them a challenge to quantify in humans. Gabapentin, marketed for the Gabapentin, while structurally similar to GABA, is a medication with distinct effects and applications. This blog post delves into the benefits of GABA, compares it with gabapentin, and discusses their potential side effects and interactions. What is GABA? Gamma Aminobutyric Acid (GABA) and Gabapentin are two compounds often discussed in medical circles, each playing unique roles in neurology and therapy. This article delves into the key differences between GABA and Gabapentin, shedding light on their functions, uses, and impacts on the human body.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
+treatment+to+percent+difference+of+glutamate+concentrations+when+compared+to+controls..jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |