Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
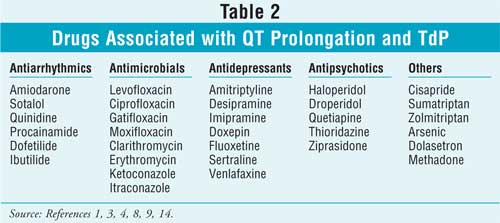
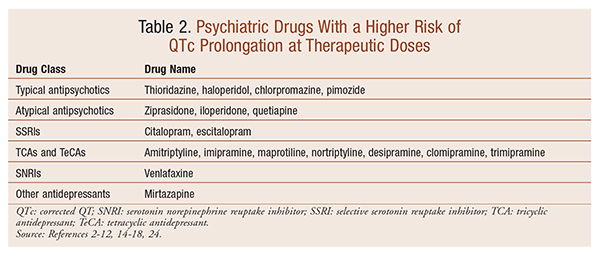
Do you take Gabapentin and are concerned about Long qt syndrome? eHealthMe's data-driven phase IV clinical trials have been referenced on 800+ peer-reviewed medical publications including The Lancet, Mayo Clinic Proceedings, and Nature. Check whether Long qt syndrome is associated with a drug or a condition. Mood stabilizers Among the mood stabilizers, lithium [22] has a moderate risk of QTc prolongation while the antiepileptics used for this purpose such as carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, topiramate, valproate, [26] pregabalin, gabapentin, [27] and lamotrigine [28] are reported to be safe with a low risk of QTc prolongation. Anxiolytic drugs and A definitive QT/QTc study of healthy human subjects showed no effect on QTc interval after either a single low dose (1200 mg) or high dose (6000 mg) of oral gabapentin enacarbil (Fig. 1) [17 ••]. Case reports suggest the potential for these drugs to enhance QTc prolongation in patients receiving one or more known QTc–prolonging medications. in the past decade, the single most common cause of the with- drawal or restriction of the use of drugs that have already been marketed has been the prolongation of the QT interval associated with INTRODUCTION Long QT syndrome (LQTS) is a disorder of myocardial repolarization characterized by a prolonged QT interval on the electrocardiogram (ECG) (waveform 1). This syndrome is associated with an increased risk of polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (VT) and a characteristic life-threatening cardiac arrhythmia also known as torsades de pointes (TdP) (waveform 2A-B). LQTS may be either A comprehensive list of conditions and drugs that may prolong the QT interval, and cause torsade de pointes (TdP) and long QT syndrome (LQTS) is presented below. With regards to drugs, the risk of QT prolongation and TdP varies markedly across the list but tends to be rather similar within a drug class. Drugs associated with QT Prolongation, QTc prolongation including Antipsychotics, antiarrhythmics, antidepressants, and antihistamines Prolongation of the QT interval above 470 ms for men and 480 ms for women should be regarded as abnormal [4]. Several risk factors for QT prolongation have been identified, including female sex, advanced age, drug-drug interactions, genetic predisposition, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, heart failure, and bradycardia [5, 6]. The unexpected and catastrophic cardiovascular effects of psychotropic drugs are well described albeit uncommon. The list of drugs which have been associated with prolonging QT interval and hence potentially causing Torsades de pointes is In this population of healthy adults, gabapentin enacarbil at doses of 1200 and 6000 mg was not associated with QT prolongation and was generally well-tolerated. Medications to be avoided, or requiring special caution, in people with Long QT syndrome This list includes medications which prolong the QT interval and is meant as a guide for people with Long QT syndrome, or acquired long QT interval from heart muscle disease, and their parents or guardians. It should not be seen as all inclusive. The heart has an electrical system that allows it to contract in a rhythm. A vital aspect of this electrical system is depolarization and repolarization. The focus of this activity is on the QT interval. It is measured from the Q wave until the T wave, and the QT interval clinically represents the repolarization of the ventricles. Many commonly used medications exhibit QT-prolonging effects Definitions for QT prolongation vary in the literature, but for men QTc >440 msec and for women QTc >470 msec are commonly used. The risk of TdP increases with increasing QTc, for every 10 msec increase, there is a ~5-7% increase in the risk of arrhythmic events. When QTc is greater than 500 msec for both men and women and/or an increase of >60 msec from baseline, risks are higher, and urgent While the preponderance of clinical data would suggest that use of most antiepileptic drugs does not pose excessive additional risk of QT prolongation, available data also do not provide sufficient evidence that these drugs are entirely free of risk in all patients. However, a patient's risk of a fatal ventricular arrhythmia may be reduced with the pharmacist's awareness of nonpharmacologic risk factors, drugs known to cause QT prolongation, and specific drug interactions. QT Interval The QT interval is the length of time required for the heart to repolarize following the onset of depolarization. For people with LQTS there are specific medications that can have a serious effect by further prolonging the QT interval. We give a list of these medicines below. This list includes drugs that can stimulate and irritate the heart by causing adrenaline-like effects. Keywords: Long QT Syndrome, Torsades de pointes, Anesthesia, QT-prolongation, Anesthetic drugs Core tip: Long QT syndrome is a cardiac conduction disorder characterized by prolongation and increased dispersion of ventricular repolarization, manifested by lengthening of the QT interval on the surface electrocardiography. Gabapentin exposure was reported to have been proportional to the dose of gabapentin enacarbil administered, with no prolongation of QT interval observed at any of the dose levels. The length of the QT interval represents the time required for ventricular depolarization and repolarization. Prolongation of ventricular repolarization can result in fatal ventricular arrhythmias [3]. Faster heart rates can shorten the QT interval [4], so it is often adjusted for rate and reported as the heart rate corrected (QTc) interval. Electrocardiogram qt corrected interval prolonged is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 40-49 old, also take Mirtazapine, and have High blood pressure.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |