Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
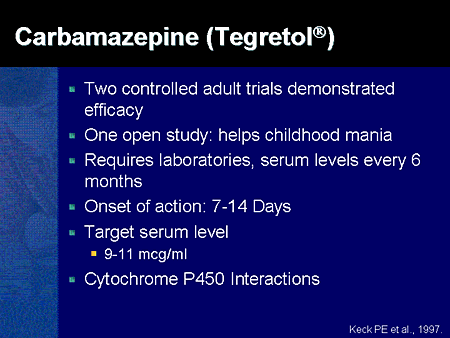
Explore gabapentin's role in mental health treatment, including its uses, benefits, and potential risks. Learn about dosage, effectiveness, and side effects. Experts agree that gabapentin doesn’t work for bipolar disorder. Learn more about gabapentin and bipolar as well as what conditions it’s FDA approved to treat. Quantitative analysis was not performed due to clinical and methodological heterogeneity. Table 1 Double-blind randomised controlled trials of gabapentin in bipolar disorder (BD). Gabapentin What is gabapentin treatment for bipolar disorder? Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant used primarily in the treatment of seizure disorders such as epilepsy. Anticonvulsant medications influence the actions of neurotransmitters leading to a decrease in brain cell (neuron) excitability. A systematic search strategy employing different combinations of the keywords (bipolar, mania, hypomania, gabapentin, neurontin, gralise, gabarone, fanatrex, pregabalin, lyrica) was developed and performed in five databases namely OVID Medline, PubMed, ProQuest, PsychInfo and ScienceDirect from database inception to 7 June 2021. The gabapentinoids, gabapentin, and pregabalin, target the α<sub>2</sub>δ subunits of voltage-gated calcium channels. Initially licensed for pain and seizures, they have become widely prescribed drugs. Many of these uses are off-label for psychiatric indications, and there is increasing concern abou This article reviews evidence-based psychiatric uses of gabapentin, along with associated risks. An extensive literature review was conducted, primarily of articles searchable in PubMed, relating to psychiatric uses, safety, and adverse effects of The drugs gabapentin and pregabalin are sometimes prescribed for people with bipolar disorder or insomnia. Research found little evidence that they are effective. The drugs have side effects and can be addictive; the team calls for further trials. Gabapentin and pregabalin (collectively known as gabapentinoids) are licensed in the UK to treat pain and seizures. Two new anticonvulsants, lamotrigine and gabapentin, have been used increasingly for bipolar disorder in the past several years. Despite this array of options, bipolar disorder remains a difficult disorder to treat. Some subtypes, such as those characterized by rapid cycling or mixed episodes, have been especially resistant to lithium treatment. Unfortunately, gabapentin does not demonstrate efficacy in randomized trials for bipolar disorder and current treatment guidelines do not emphasize its use. Despite of the lack of evidence, reviews of gabapentin prescribing patterns in the United States show that this medication is still being used with alarming frequency for bipolar disorder. Key takeaways Gabapentin is not FDA approved for bipolar disorder, and studies show limited evidence of its effectiveness for this purpose. While it may help with symptoms like anxiety and insomnia, gabapentin’s benefits for bipolar disorder are inconclusive. Gabapentin can cause side effects such as drowsiness and dizziness and may interact with other medications. Gabapentin dosages for The gabapentinoids, gabapentin, and pregabalin, target the α2δ subunits of voltage-gated calcium channels. Initially licensed for pain and seizures, they have become widely prescribed drugs. Many of these uses are off-label for psychiatric Reviews and ratings for Gabapentin when used in the treatment of bipolar disorder. 144 reviews submitted with a 8.5 average score. As for Neurontin itself, the results are fairly mixed. It is used for such a specific purpose (reducing anxiety in bipolar patients) that it can be hard to differentiate between the anxiety reduction qualities of other medication concurrently prescribed to treat bipolar and the anxiety reduction qualities of Neurontin. Learn how Neurontin is used to treat bipolar disorder symptoms, its benefits, and potential side effects in this informative medical resource article. Gabapentin is commonly used off-label in the treatment of psychiatric disorders with success, failure, and controversy. A systematic review of the literature was performed to elucidate the evidence for clinical benefit of gabapentin in psychiatric Abstract Background: Gabapentin, a new anti-epileptic agent, has been anecdotally reported to be effective in the treatment of mania. We systematically assessed the response rate in bipolar patients being treated adjunctively with gabapentin for manic symptoms, depressive symptoms, or rapid cycling not responsive to standard treatments. Gabapentin is a nerve pain medication and anticonvulsant that has proven to be effective for people who have hard-to-treat depression or other mood disorders. The use of gabapentin in bipolar disorder (BPD) treatment provides an informative case of off-label uptake and abandonment of a new medication. Gabapentin was patented by Warner-Lambert in 1977 and FDA-approved in December1993 for the adjunctive treatment of epilepsy and in 2002 for postherpetic neuralgia (see Appendix 1 for timeline).
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |