Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |
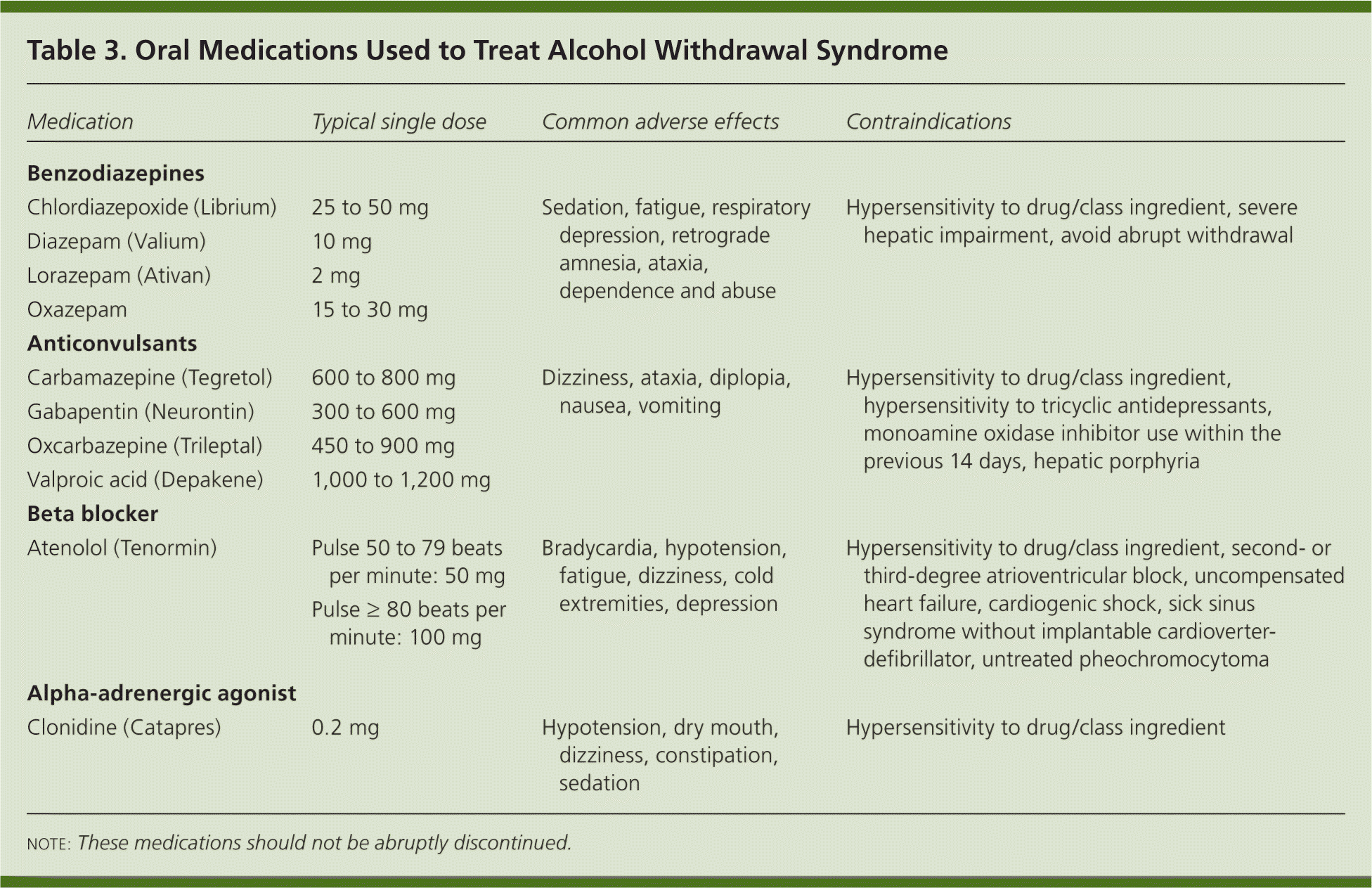
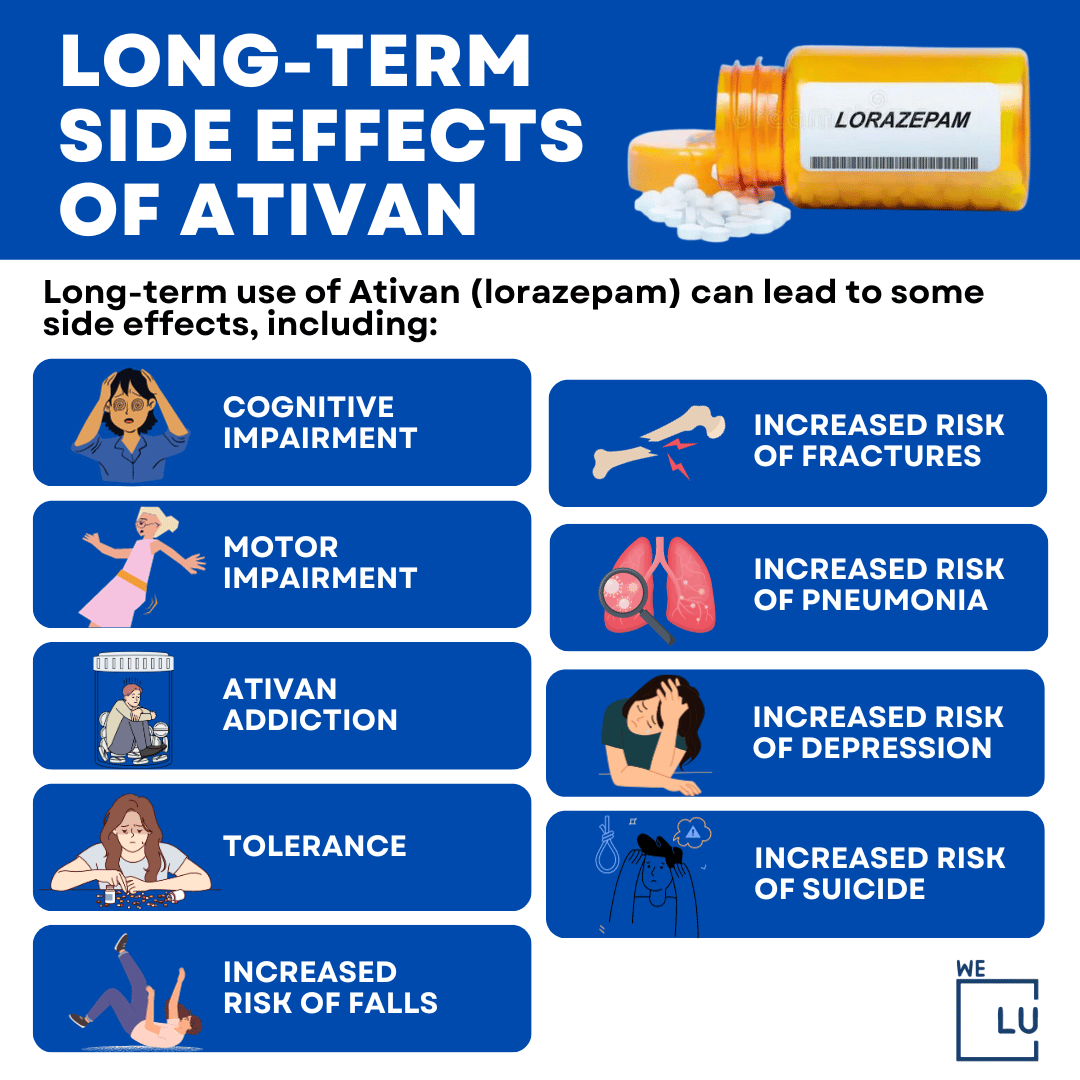
Ativan is a benzodiazepine used to treat anxiety disorders or anxiety associated with depression. Learn about side effects, interactions and indications. A double- blind trial of gabapentin versus lorazepam in the treatment of alcohol withdrawal. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2009 Sep;33 (9):1582-8. Full-text for Emory users. Figure 1. Alcohol withdrawal symptoms: CIWA‐Ar score over time. Comparisons: GBP 900mg versus 1200mg: t=5.83, p=0.019. GBP 900mg versus lorazepam: not significant. Conclusions: Gabapentin was well tolerated and effectively diminished the symptoms of alcohol withdrawal in our population especially at the higher target dose (1200 mg) used in this study. Gabapentin reduced the probability of drinking during alcohol withdrawal and in the immediate postwithdrawal week compared to lorazepam. Gabapentin Use in Acute Alcohol Withdrawal Management Christopher Wilming, PharmD; Mariah Alford, PharmD; and Lynnette Klaus, PharmD, BCPS Gabapentin’s anxiolytic and sedative properties along with its overall safety profile suggest that it may be a viable adjuvant to lorazepam in the management of acute alcohol withdrawal. Gabapentin is used off-label in alcohol withdrawal care. This guide covers clinical evidence, side effects, and treatment guidelines. Lorazepam is in a group of drugs called benzodiazepines and is used to treat anxiety disorders. Learn about side effects, interactions and indications. What Is Ativan? Ativan (lorazepam) is a benzodiazepine used for the management of anxiety disorders, insomnia, panic attacks, and alcohol withdrawal. Ativan is available in generic form. What Are Side Effects of Ativan? Ativan may cause serious side effects including: severe drowsiness, thoughts of suicide or hurting yourself, unusual changes in mood or behavior, confusion, aggression QuestionIs gabapentin efficacious in the treatment of alcohol use disorder in adults with a history of alcohol withdrawal symptoms? FindingsIn this randomized clinical trial, gabapentin compared with placebo significantly increased the number of people with total abstinence and reduced drinking. While gabapentin is not yet an FDA-approved treatment for alcoholism, a number of studies support the its use withdrawal and cravings: In a 12-day study detoxifying with either gabapentin or lorazepam (a benzodiazepine prescribed with the brand name Ativan), the former was less likely to drink – and had less craving, anxiety, and sedation. One hundred subjects with DSM-IV diagnosis of alcohol dependence and alcohol withdrawal were randomized to receive gabapentin at one of three different fixed-dose taper regimens (600, 900, or 1200 mg/day starting dose) or lorazepam (6 mg/day starting dose) for 4 days with symptom-triggered rescue doses to treat breakthrough withdrawal. The current randomized, double-blind dose response trial tested the hypothesis that gabapentin would be superior to the benzodiazepine lorazepam in the outpatient treatment of alcohol withdrawal as measured by the CIWA-Ar scale and drinking outcomes as measured by the TLFB and breath alcohol levels. Ativan (lorazepam) is a prescription medication used for anxiety, insomnia, and seizures. Learn about side effects, dosage, uses, and more. A box of Lorazepam Orion (lorazepam) tablets Lorazepam, sold under the brand name Ativan among others, is a benzodiazepine medication. [14] It is used to treat anxiety (including anxiety disorders), insomnia, severe agitation, active seizures including status epilepticus, alcohol withdrawal, and chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting. [14] It is also used during surgery to interfere with The anticonvulsant drug gabapentin is used off-label to treat alcohol-related withdrawal, cravings, anxiety, and insomnia. Although it is well tolerated and has demonstrated efficacy for mild alcohol withdrawal and early abstinence, there is concern about its potential for abuse. Gabapentin should be prescribed only as a second-line alternative to standard therapies, and only after screening Abstract Background and Objectives: Gabapentin has shown promise as a potential agent for the treatment of alcohol withdrawal syndrome. We aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of gabapentin as a benzodiazepine-sparing agent in patients undergoing alcohol withdrawal treatment in all the hospitals of a large tertiary healthcare system. Materials and Methods: Medical records of patients admitted Researchers say the medication used for nerve pain and partial seizures can help ease symptoms of alcohol withdrawal. Approximately one-half of patients with alcohol use disorder who abruptly stop or reduce their alcohol use will develop signs or symptoms of alcohol withdrawal syndrome. The syndrome is due to This may help prevent a worsening of your condition and reduce the possibility of withdrawal symptoms, including hallucinations, headache, seizures, stomach or muscle cramps, tremors, trouble sleeping, or unusual behavior. This medicine will add to the effects of alcohol and other central nervous system (CNS) depressants. Benzodiazepines are currently the gold standard for treatment of alcohol withdrawal. Gabapentin has growing evidence to support its use in the treatment of alcohol use disorder, however there is limited evidence regarding its role in the treatment The aim of this study was to evaluate alcohol use and symptom reduction of gabapentin when compared with lorazepam in the treatment of alcohol withdrawal in a double-blinded randomized clinical trial.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |