Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
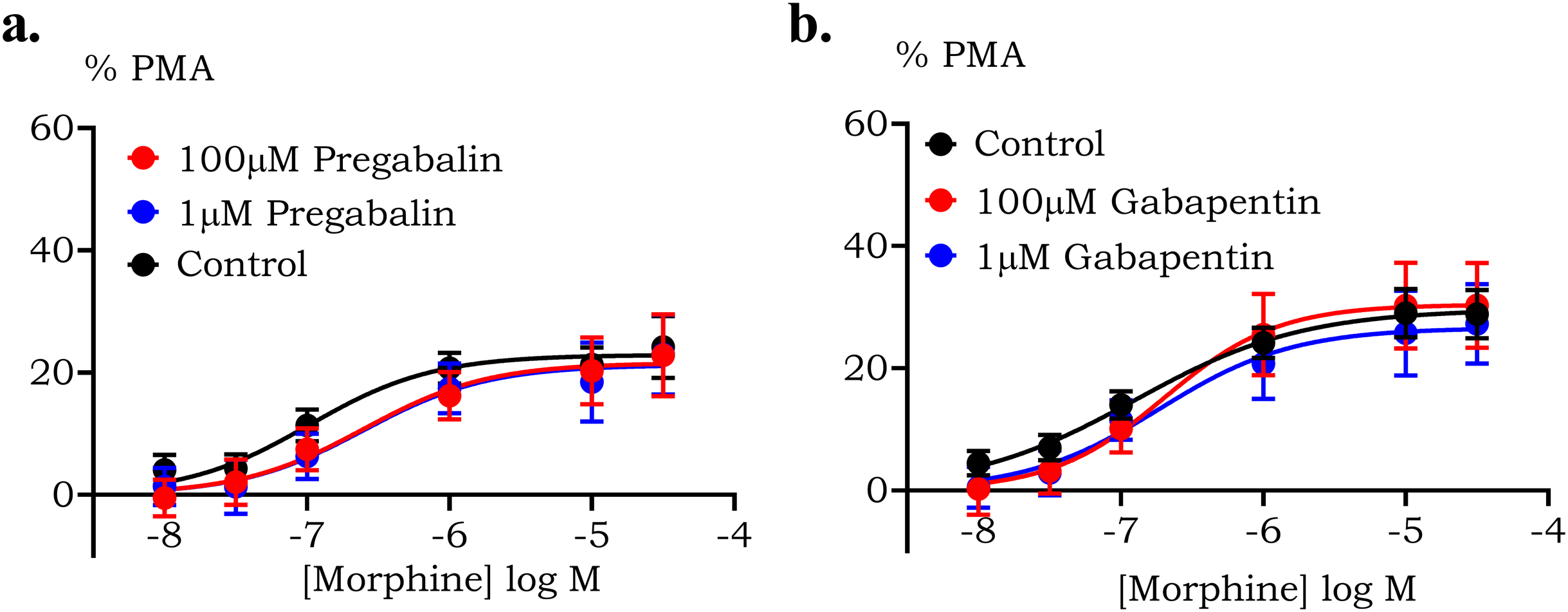
Use of gabapentinoids (gabapentin, pregabalin) by people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) was associated with a 39% increased risk for severe disease exacerbation, according to investigators from McGill University and Lady Davis Institute for Medial Research in Montreal, Canada. Findings from the population cohort study, published in the Annals of Internal Medicine, are the PURPOSE: Recent evidence suggests an association between the use of gabapentinoids (gabapentin and pregabalin) and more frequent and clinically severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) exacerbations. 1 Hence, we aim to investigate a potential association of commonly prescribed muscle relaxants, including cyclobenzaprine and methocarbamol, with COPD exacerbation. A Canadian cohort study found that gabapentin and pregabalin use was associated with an increased risk of severe exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease . The risk was comparable for all gabapentinoid indications including epilepsy, neuropathic pain and other chronic pain. To assess whether gabapentinoid use is associated with severe exacerbation in COPD, researchers culled health insurance databases from the Régie de l'assurance maladie du Québec in Canada to create a base cohort of patients with COPD. Primary outcome was severe COPD exacerbation requiring hospitalization. The authors found that compared with nonuse, gabapentinoid use was associated with an increased risk for severe COPD exacerbation among users taking these drugs for epilepsy, neuropathic pain, and chronic pain and peak increase in risk for severe COPD exacerbation occurred after approximately 6 months of continuous use. “In patients with COPD, gabapentinoid use was associated with increased risk for severe exacerbation,” they concluded. “These findings support the warnings from regulatory agencies and highlight the importance of considering this potential risk when prescribing gabapentin and pregabalin to patients with COPD.” Gabapentin did not differ from pregabalin in risk for severe COPD exacerbations. Comment: Although this study has typical limitations of a retrospective cohort design, it affirms reported cases of respiratory problems related to these medications and parallels anaesthesia-setting cohort studies that have suggested respiratory depression “In patients with COPD, gabapentinoid use was associated with increased risk for severe exacerbation,” the authors wrote. “This study supports the warnings from regulatory agencies and highlights the importance of considering this potential risk when prescribing gabapentin and pregabalin to patients with COPD.” Gabapentinoids are associated with an increased risk of severe exacerbation in people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), a study of more than 10 000 people has reported.1 Researchers from McGill University and Lady Davis Institute for Medical Research studied Canadian insurance data and found that the highest risk for severe COPD exacerbation occurred after around six months of In 2019, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration issued a warning related to nearly 50 case reports of breathing difficulties following use of gabapentinoids (i.e., gabapentin and pregabalin) that were reported between 2012 and 2017; however, such warnings are not reflected in current pain management guidelines. In patients with COPD, gabapentinoid use was associated with increased risk for severe exacerbation. These findings support the warnings from regulatory agencies and highlight the importance of considering this potential risk when prescribing gabapentin and pregabalin to patients with COPD. In patients with COPD, gabapentinoid use was associated with increased risk for severe exacerbation. These findings support the warnings from regulatory agencies and highlight the importance of Synopsis: This study examined 13,504 patients aged at least 55 years with COPD who initiated gabapentin or pregabalin for epilepsy, neuropathic pain, or other chronic pain, matched 1:1 with nonusers. Gabapentinoid use was associated with an increased risk of severe COPD exacerbations (hazard ratio, 1.39; 95% CI, 1.29-1.50) across all indications. A population-based cohort study of more than 10,000 persons using gabapentinoids found that their use was associated with an increased risk of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) exacerbation. This study, published in Annals of Internal Medicine, supports the warnings from regulatory agencies and highlights the importance of considering this potential risk when prescribing gabapentin Gabapentinoids, including gabapentin and pregabalin are medications used to treat seizures, anxiety and pain caused by nerve damage. Recently, their prescription has increased in North America and Europe, partly due to use for unapproved indications. However, these medications are ineffective for many unapproved uses and can cause serious adverse effects, including sleepiness and respiratory Previous research has prompted warnings from North American and European health agencies of severe exacerbations associated with gabapentinoid use by patients with COPD. The researchers compared Gabapentinoid use, namely gabapentin and pregabalin, was associated with increased risk for severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) exacerbation in patients with epilepsy, neuropathic Conclusion: In patients with COPD, gabapentinoid use was associated with increased risk for severe exacerbation. This study supports the warnings from regulatory agencies and highlights the importance of considering this potential risk when prescribing gabapentin and pregabalin to patients with COPD. Conclusion: In patients with COPD, gabapentinoid use was associated with increased risk for severe exacerbation. This study supports the warnings from regulatory agencies and highlights the importance of considering this potential risk when prescribing gabapentin and pregabalin to patients with COPD. A population-based cohort study of more than 10,000 persons using gabapentinoids found that their use was associated with an increased risk of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) exacerbation. This study supports the warnings from regulatory agencies and highlights the importance of considering this potential risk when prescribing gabapentin and pregabalin to patients with COPD. The
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |