Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
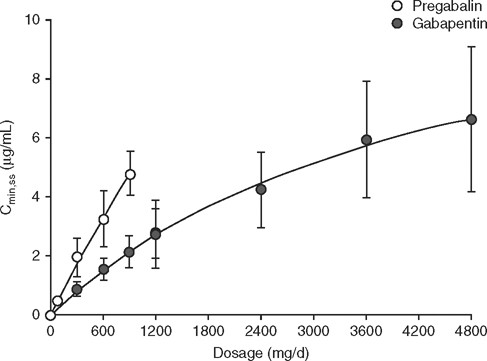 |  |
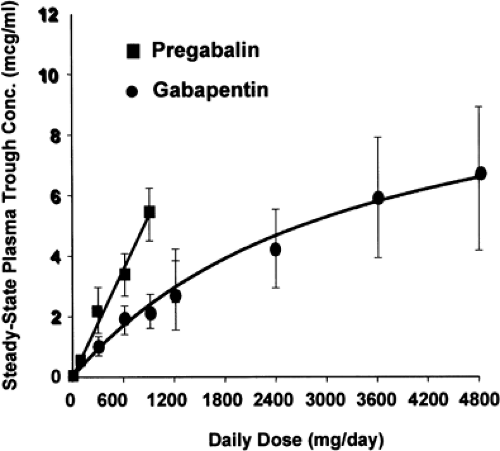
Pregabalin and gabapentin are members of a unique class of compounds characterized by high affinity binding to the alpha-2-delta (α2δ) protein in the CNS. Both have been shown to be effective as adjunctive therapy for partial seizures and neuropathic pain disorders. Clinical pharmacology studies conducted to characterize the pharmacokinetics, bioavailability, and drug-drug interaction Pregabalin is rapidly and completely absorbed as com-pared to gabapentin. Peak plasma concentrations are seen within an hour as compared to 3 hours with gabapentin.12 Oral bioavailability for pregabalin is more than 90% as compared to 30–60% for gabapen-tin. These differences can be explained by the mecha-nism of absorption. First, gabapentin is primarily absorbed in the small intestine, while pregabalin is absorbed at multiple sites, the small intestine and the ascending portion of the colon. 6 Second, gabapentin’s absorption is saturable; meaning that as gabapentin doses increase, the rate of absorption and resulting bioavailability decreases. Pharmacokinetics of Pregabalin and Gabapentin Both pregabalin and gabapentin are antiepileptic medications that bare structural resemblance to gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), though neither agent has activity in GABA’s neuronal systems. Although the exact mechanism of action is somewhat unclear, the drugs’ efficacy in neuropathic pain is linked to their ability to bind to voltage-gated Pregabalin and gabapentin have different pharmacokinetic profiles, which affect their absorption, distribution, metabolism, and elimination. Pregabalin is absorbed more quickly and has a higher bioavailability than gabapentin, with a peak concentration reached within 1 hour compared to 3-4 hours for gabapentin. Neuropathic pain is a prevalent and burdensome condition, and both pregabalin and gabapentin are widely used for its treatment. However, there is a lack of clarity regarding their comparative efficacy and safety. This meta-analysis aims to evaluate Pregabalin and gabapentin share a similar mechanism of action, inhibiting calcium influx and subsequent release of excitatory neurotransmitters; however, the compounds differ in their pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic characteristics. Gabapentin is absorbed slowly after oral administration, with maximum plasma concentrations attained within 3–4 hours. Orally administered gabapentin Pregabalin (Lyrica) and gabapentin (Neurontin) are both approved to treat nerve pain. How are they different, and which one is preferred? Compare both meds here. Figure 55.1. Chemical structure of gabapentin, pregabalin, and gabapentin enacarbil. The mechanism of action of gabapentinoids differs from that of other antiepileptic drugs (AEDs). Contrary to ini Absorption and distribution Pregabalin is rapidly and completely absorbed as compared to gabapentin. Peak plasma concentrations are seen within an hour as compared to 3 hours with gabapentin. 12 Oral bioavailability for pregabalin is more than 90% as compared to 30–60% for gabapentin. These differences can be explained by the mechanism of absorption. Although both gabapentinoids are absorbed Pregabalin offers key advantages over gabapentin, including improved absorption, faster onset / titration, more predictable dose-response relationship, and more convenient dosing. Gabapentin is more likely than Lyrica to cause side effects such as difficulty speaking, fever, an increased risk of viral infections, unusual eye movements, or jerky movements Lyrica is absorbed faster and starts working more quickly than gabapentin. We breakdown dosing, pharmacokinetics, uses, cost, and many other considerations when comparing gabapentin versus pregabalin. Gabapentin (Neurontin) vs. Lyrica (Pregabalin) What's the Difference? Gabapentin (Neurontin) and Lyrica (Pregabalin) are both medications commonly used to treat neuropathic pain, seizures, and certain types of nerve-related conditions. They belong to the same class of drugs called gabapentinoids and work by binding to specific receptors in the brain to reduce the transmission of pain signals Pregabalin and gabapentin share a similar mechanism of action, inhibiting calcium influx and subsequent release of excitatory neurotransmitters; however, the compounds differ in their pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic characteristics. Gabapentin is absorbed slowly after oral administration, with m Comparison of gabapentinoids gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica), differences between gabapentin and pregabalin chart, latest comparative clinical trials, up-to-date drug information. Pregabalin is more rapidly absorbed compared to gabapentin, which has a slower absorption rate. However, the oral bioavailability of gabapentin is more variable than the oral bioavailability of pregabalin. Lyrica vs Gabapentin: Discover their key differences in uses, absorption, side effects, and safety to choose the best option for your needs. Gabapentin is pharmacodynamically close or identical to pregabalin, and is available at low cost in the United States. Gabapentin could theoretically represent a reasonable alternative to pregabalin for the treatment of anxiety disorders, but available evidence does not fully support this hypothesis.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |