Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
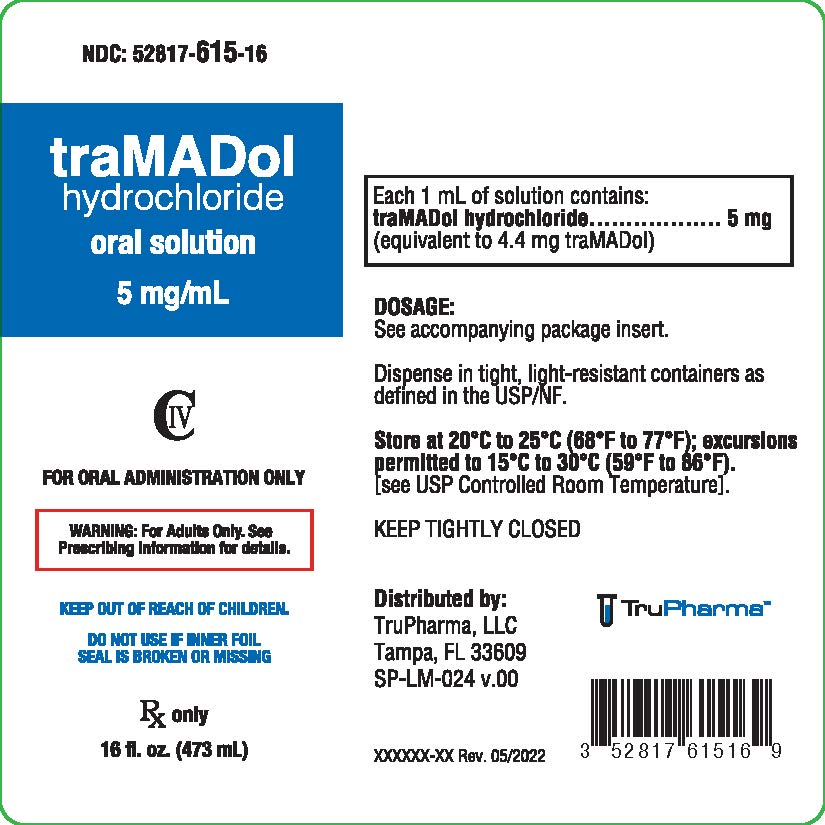
This review is an update of a review of tramadol for neuropathic pain, published in 2006; updating was to bring the review in line with current standards. Neuropathic pain, which is caused by a lesion or disease affecting the somatosensory system, Tramadol is a nontraditional centrally acting analgesic with a dual mechanism of action. It is a weak opioid and also a reuptake inhibitor for serotonin and norepinephrine. Multidisciplinary conservative care and nonopioid medications (tricyclic antidepressants, serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors, gabapentanoids, topicals, and transdermal substances) are recommended as firstline therapy; combination therapy (firstline medications) and tramadol and tapentadol are recommended as secondline; serotonin-specif While Tramadol is commonly used for moderate to severe pain, Gabapentin is more specialized and is often used for nerve pain and some seizure disorders. Here, we’ll break down what each medication does, how they differ, and what to consider if either medication is part of your treatment plan. Tramadol oral tablet is used to treat moderate to severe pain. It comes in immediate-release and extended-release forms. Learn about side effects, warnings, and more. There are several treatment options for nerve pain, including antidepressants, anticonvulsants, opioids, and topicals. Learn about their uses and side effects. Gabapentin vs Tramadol both treat pain but work differently. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant used for nerve pain and seizures, while Tramadol is a weak opioid analgesic that targets pain through the brain's opioid receptors. Tramadol is an opioid medication that may be used to treat moderate to moderately severe chronic pain in adults, including pain after surgery. Tramadol immediate-release tablets and oral solution are used as a short-term treatment to relieve severe pain (pain that begins suddenly, has a specific cause, and is expected to go away when the cause of the pain is healed) in people who are expected to need an opioid pain medication and who cannot be controlled by the use of alternative pain medications. Tramadol extended-release tablets Gabapentin and tramadol are used to treat different types of pain. Gabapentin is an anti-seizure (anticonvulsant) medication also used for nerve pain (neuralgia). Tramadol is an opioid pain reliever (analgesic) used to manage moderate to moderately severe pain. Tramadol - Top 8 Things You Need to Know Medically reviewed by Leigh Ann Anderson, PharmD. Last updated on Oct 22, 2024. Generic Name: tramadol (TRAM a dol) Brand Names: ConZip, Qdolo Maybe you've heard that tramadol is a "safer" pain medication. But is that really true? Is tramadol a narcotic? The facts: tramadol is classified as a centrally-acting, oral analgesic (pain drug) that contains a Gabapentin primarily calms overactive nerves, while tramadol alters pain perception. Combining them can amplify their CNS effects. This synergistic effect can potentially enhance pain relief but also significantly increase the risk of side effects. Both medications can cause drowsiness and dizziness. Gabapentin is an antiepileptic medication used to treat certain seizures and nerve pain, while Tramadol is an opioid used for pain relief when non-opioid medications aren't effective. Gabapentin and tramadol are sometimes prescribed together to treat neuropathic (nerve-related) or chronic pain. However, due to their shared classification as central nervous system depressants, it's generally inadvisable to combine these medications. Detailed Tramadol dosage information for adults, the elderly and children. Includes dosages for Pain and Chronic Pain; plus renal, liver and dialysis adjustments. Find patient medical information for Tramadol on WebMD including its uses, side effects and safety, interactions, pictures, warnings, and user ratings Tramadol, sold under the brand name Tramal among others, [17][1] is an opioid pain medication and a serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) used to treat moderately severe pain. [13][17] When taken by mouth in an immediate-release formulation, the onset of pain relief usually begins within an hour. [13] It is also available by injection. [18] It is available in combination with Gabapentin: Works on the nervous system to calm overactive nerve signals, particularly effective for neuropathic pain. Tramadol: Alters the brain’s pain perception by binding to opioid receptors, making it effective for various types of pain but with a higher risk of dependency. Tramadol is stronger for managing acute or severe pain, while gabapentin is more effective for chronic nerve pain. The choice between these medications depends on the specific condition being treated and the type of pain involved. Tramadol is often preferred by people who need quick relief from pain, while Gabapentin is preferred by people who experience nerve pain. Gabapentin is often taken 2-3 times a day, while Tramadol is also taken 2-3 times a day.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |