Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |
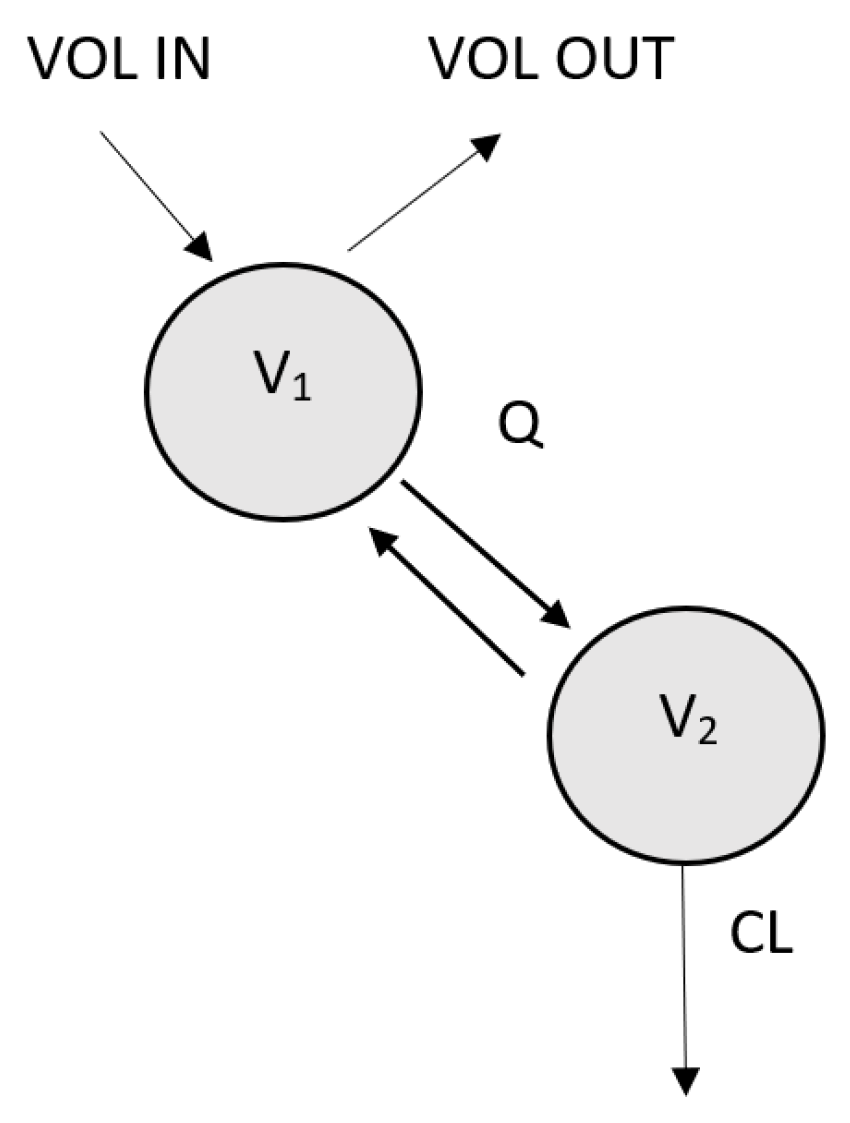
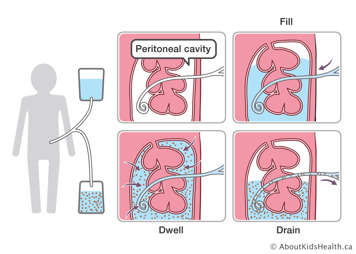
Gabapentin is known to be effectively cleared by hemodialysis, but the efficiency of clearance by peritoneal dialysis (PD) has not been previously described. We report a case of gabapentin toxicity in a patient on long-term PD who was treated with continuous automated cycling PD. We report 2 cases of gabapentin overdose. Patient A, an 85-year-old Caucasian male suffered from chronic kidney disease stage 5 D. He had been treated with peritoneal dialysis for over 2 years due to suspected diabetic nephropathy and nephrosclerosis. The patient was admitted to our tertiary care hospital with repeated syncope and faints. For neuropathic pain, he had been treated with In general, recommendation for drug dosing in peritoneal dialysis patients is to initiate at a low dose, monitoring for adverse drug reaction and toxicity with slow up-titration. Case Report We report 2 cases of gabapentin overdose. Patient A, an 85-year-old Caucasian male suffered from chronic kidney disease stage 5 D. He had been treated with peritoneal dialysis for over 2 years due to suspected diabetic nephropathy and nephrosclerosis. The patient was admitted to our tertiary care hospital with repeated syncope and faints. For neuropathic pain, he had been treated The quantity of drugs removed during peritoneal dialysis is substantially lower than that during hemodialysis, and thus, the supplemental administration of drugs, even when they are efficiently removed during hemodialysis, is not necessary in patients receiving continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialy Give supplemental dose of 125-350mg after each dialysis. Dosage given should be proportional to maintenance dose. Patients receiving at least 300mg/day can be given the higher supplemental dose of 350mg after each dialysis. Other patients should receive a dosage at the lower end of this range. [See above for updated info from the package insert] Pregabalin Has similar efficacy and side effects as gabapentin. May be useful in patients with limited absorption from gabapentin, e.g. not responding despite high doses. Titrate slowly; doses up to 75 mg per day are generally considered safe in dialysis patients. Not covered by Pharmacare Pregabalin’s apparent total clearance is 67–81 mL/min in young healthy subjects and is therefore thought to undergo tubular reabsorption to some extent. 2 Hemodialysis (HD) removes approximately 35% of gabapentin and 50%–60% of pregabalin, where supplemental doses are generally recommended post-HD. 1,2 Therapeutic dosing targets A few small studies have suggested that pain is as common among peritoneal dialysis patients and stage 5 CKD patients who are not on dialysis as among chronic hemodialysis patients [1]. To continue reading this article, you must sign in with your personal, hospital, or group practice subscription. Therapeutic dosing targets of both medications have been established in clinical trials for neuropathic pain (gabapentin 1800–3600 mg/day; pregabalin 150–600 mg/day). The recommended dose of gabapentin in dialysis patients is 100 to 300 mg/per day, but on dialysis day an additional dose is given after the session, due to drug clearance through the dialysis membrane. Gabapentin is almost exclusively cleared by the kidney and thus presents challenges in patients with kidney failure. Gabapentin is known to be effectively cleared by hemodialysis, but the efficiency of clearance by peritoneal dialysis (PD) has not been previously described. We report a case of gabapentin toxicity in a patient on long-term PD who was treated with continuous automated cycling PD Pain control is inadequate Intolerable adverse effects (e.g. sedation, dizziness) at target dose for 2-4 weeks or initial pain ≥5 out of 10 Taper off Gabapentin Background Gabapentin and pregabalin are used to manage neuropathic pain, pruritus, and restless legs syndrome in patients on hemodialysis. These patients may be especially predisposed to complications related to these agents, which are renally Dose Adjustment: 900 - 3600 mg/day TID. How Often to Take: 3 times a day. Notes: Monitor for dizziness or double vision. Notes: Your doctor will decide the best dose for you. Dose Adjustment: 200 - 700 mg/day QD. Notes: Careful monitoring is needed. Timing: After you get your dialysis treatment. The recommended renal dosing for gabapentin is as follows: For patients with creatinine clearance ≥60 mL/min, the total daily dose range is 900-3600 mg/day, with a dose regimen of 300-1200 mg three times a day. In patients with normal renal function, the maximum dose of gabapentin is 3600mg daily in divided doses. However, gabapentin is renally cleared and so the dose needs to be adjusted according to the GFR. For patients on dialysis, the recommended dose is 100-300mg post dialysis on dialysis days only. Dose as in GFR=15–30 mL/min Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugsAntacids: reduce absorption Antidepressants: antagonism of anticonvulsive effect (convulsive threshold lowered) Gabapentin is almost exclusively cleared by the kidney and thus presents challenges in patients with kidney failure. Gabapentin is known to be effectively cleared by hemodialysis, but the efficiency of clearance by peritoneal dialysis (PD) has not been previously described. We report a case of gabapentin toxicity in a patient on long-term PD who was treated with continuous automated cycling PD
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |