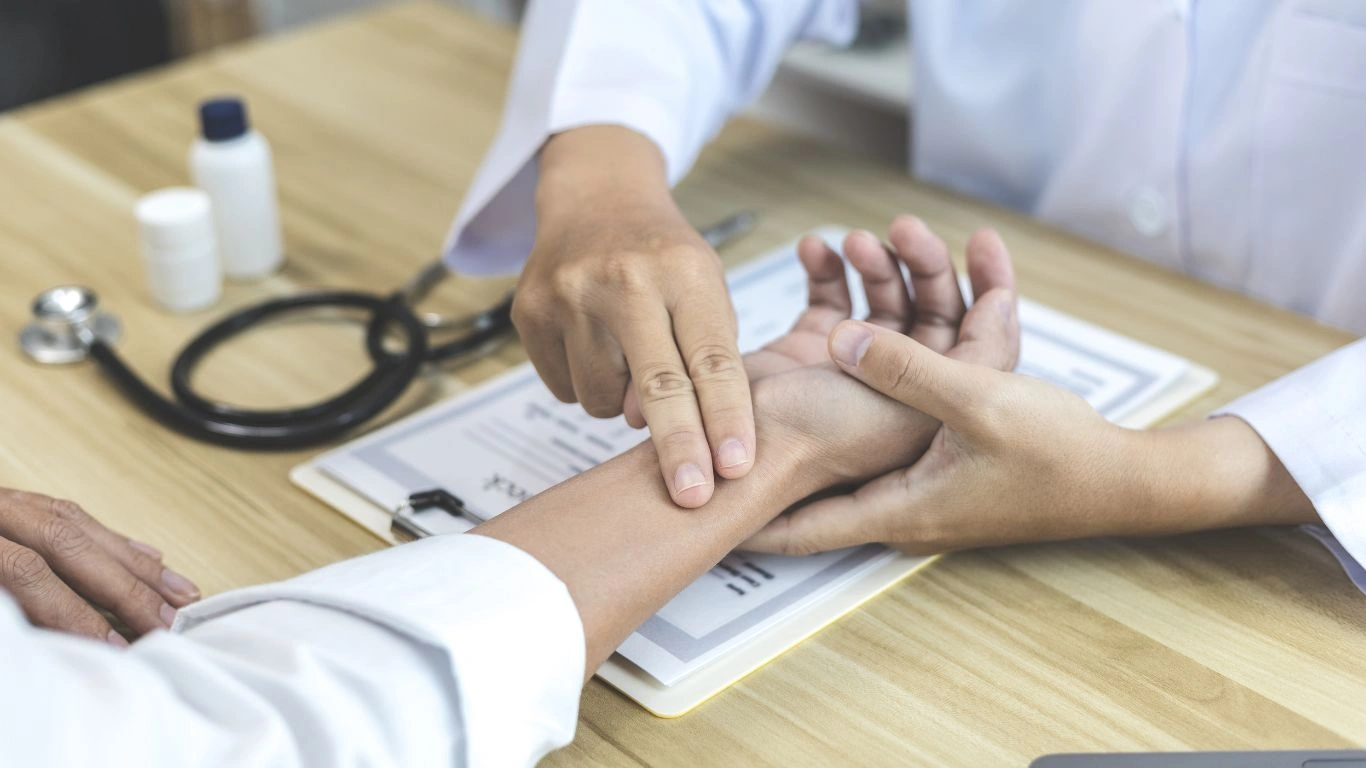
Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 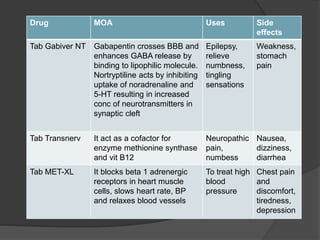 |
Discover how gabapentin affects blood pressure. Learn if it can lower, raise, or have no effect on high blood pressure and its interactions with other medications. Though gabapentin has many potential uses, it can cause side effects. Read more about 13 gabapentin side effects here. However, their effect on blood pressure (BP) is unclear. In this study, we investigated the hemodynamic response to acute and chronic administration of gabapentin, a ligand of auxiliary α 2 δ subunit of VDCCs, in adult SHR with established neurogenic hypertension. Gabapentin is not primarily used to lower blood pressure, but some studies suggest it may have a mild effect on blood pressure regulation. To review the blood pressure (BP) effects of pain and analgesic medications and to help interpret BP changes in people suffering from acute or chronic pain. Acute pain evokes a stress response which prompts a transient BP increase. Chronic pain is Importantly, oral, high-dose (1200 mg/kg daily) gabapentin had no effect on blood pressure over a 10-day period. Routine use of gabapentin or pregabalin is unlikely to compromise the hemodynamics of most patients. ObjectivesThe aim of the present study was to assess the effect of gabapentin on blood pressure (BP) in cats with and without chronic kidney disease (CKD).MethodsA randomized, blinded, placebo-cont Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication prescribed for a variety of conditions. Learn about its uses, side effects, and what you should know if you've been prescribed this medication. Yes, it can cause High Blood Pressure (hypertension) Cardiovascular side effects including hypertension have been reported to occur in more than one percent of patients taking gabapentin. Learn about the potential effects of gabapentin on blood pressure and how Statcare can help you manage your medication concerns. Summary: High blood pressure is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 60+ old, have been taking the drug for < 1 month also take Tylenol, and have Rheumatoid arthritis. The phase IV clinical study analyzes which people have High blood pressure when taking Gabapentin. It is created by eHealthMe based on reports of 313,421 The relationship between gabapentin and blood pressure is complex, as the drug may exert both hypertensive and hypotensive effects depending on the patient’s clinical context and individual response. Doctors prescribe gabapentin to treat epilepsy, restless legs syndrome, and some types of nerve pain. Learn more the drug's uses, risks, and safety here. Well, gabapentin has several side effects, and high blood pressure isn’t directly one of them. But that doesn’t mean one can suffer high blood pressure when taking gabapentin. Studies have shown mixed results regarding the effects of gabapentin on blood pressure, with some indicating an increase and others showing no significant change. Factors such as dosage, duration of use, and individual health conditions can influence how gabapentin affects blood pressure. We observed that unilateral microinjection of gabapentin into the NTS whether to change dose-related BP and HR. Then, unilateral microinjection of gabapentin into the NTS before and after N (ω)-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME) treatment whether to change blood pressure and heart rate. Background Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly prescribed medications to treat pain in patients with diabetic neuropathy. Gabapentin and pregabalin can cause fluid retention, which is hypothesized to be associated with cardiovascular diseases. However, whether long-term use of gabapentin and pregabalin is associated with adverse cardiovascular diseases remains unknown. This study aims to Abstract Background Oral and intravenous gabapentin can markedly attenuate blood pressure (BP) in hypertensive rats. The nucleus tractus solitarii (NTS) is the primary integrative center for cardiovascular control and other autonomic functions in the central nervous system. However, the signaling mechanisms involved in gabapentin-mediated cardiovascular effects in the NTS remain unclear. We Abstract Gabapentin (GBP), a GABA analogue, is primarily used as an anticonvulsant for the treatment of partial seizures and neuropathic pain. Whereas a majority of the side effects are associated with the nervous system, emerging evidence suggests there is a high risk of heart diseases in patients taking GBP. In the present study, we first used a preclinical model of rats to investigate
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |