Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
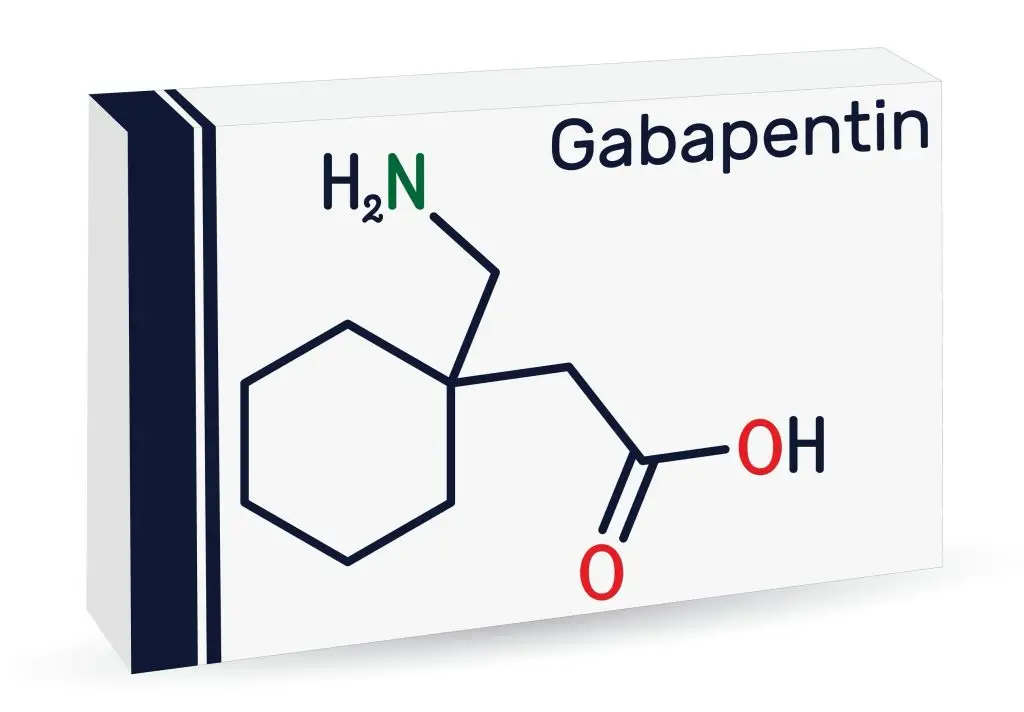
Gabapentin is a structural analog of the inhibitory neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Its anticonvulsant, analgesic and anxiolytic properties suggest that it increases GABAergic inhibition; however, the molecular basis for these effects is unknown as gabapentin does not directly modify GABA type A (GABA A) receptor function, nor does it modify synaptic inhibition. Here, we What is Gabapentin? Gabapentin is a prescription medication commonly used for the treatment of seizures and nerve pain. It belongs to a class of medications known as anticonvulsants. Gabapentin works by mimicking the effects of GABA, a neurotransmitter that helps to reduce neuronal excitability in the brain. This mechanism of action makes it effective in controlling seizures and reducing nerve Gabapentin is a structural analog of the inhibitory neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Its anticonvulsant, analgesic and anxiolytic properties suggest that it increases GABAergic inhibition; however, the molecular basis for these effects Abstract Purpose: Gabapentin (GBP) was introduced as an antiepileptic drug (AED) and has been used in the management of neuropathic pain. We reported that daily dosing increased brain gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in patients with epilepsy. This study was designed to determine how rapidly brain GABA and the GABA metabolites, homocarnosine and pyrrolidinone, increase in response to the first Gabapentin has been successfully used to treat some of the effects of brain damage. However, prolonged use can cause serious side effects. This article will summarize the use of gabapentin for brain damage and discuss which symptoms it can help relieve. What Is Gabapentin Used For? Gabapentin is most commonly prescribed for nerve pain such [] What's the Difference? GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) and Gabapentin are both substances that affect the central nervous system, but they have different mechanisms of action and uses. GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter in the brain that inhibits or slows down nerve activity, helping to reduce anxiety and promote relaxation. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication prescribed for a variety of conditions. Learn about its uses, side effects, and what you should know if you've been prescribed this medication. GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter in the brain, primarily responsible for inhibiting nerve transmission, which helps to reduce neuronal excitability. In contrast, gabapentin is a medication designed to mimic the effects of GABA, used primarily to treat conditions like epilepsy and neuropathic pain. Understanding the differences between these two can help in making informed Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and glutamate are implicated in numerous neuropsychiatric and substance abuse conditions, but their spectral overlap with other resonances makes them a challenge to quantify in humans. Gabapentin, marketed for the treatment of seizures and neuropathic pain, has been sh Learn about the side effects of gabapentin, from common to rare, for consumers and healthcare professionals. Gabapentin (Neurontin®) is a second-generation antiepileptic drug widely used for treatment of neuropathic pain. It is also used to treat anxiety, insomnia, bipolar disorder, and restless leg syndrome. Although first introduced as an adjunct therapy for epilepsy, gabapentin became a blockbuster drug for the management of chronic pain from many nerve conditions [8]. Side effects are usually Gabapentin is an anti-epileptic drug, also called an anticonvulsant. It is used to treat some types of seizures and nerve pain caused by shingles. Gabapentin, marketed for the treatment of seizures and neuropathic pain, has been shown to increase in vivo GABA concentration in the brain of both rodents and humans. Though gabapentin has many potential uses, it can cause side effects. Read more about 13 gabapentin side effects here. Research regarding gabapentin's effects on GABA and glutamate synthetic and metabolizing enzymes reveals a complex pattern of activity and provides an incomplete explanation for its anticonvulsant effects. Find patient medical information for Gabapentin (Gralise, Neurontin) on WebMD including its uses, side effects and safety, interactions, pictures, warnings, and user ratings Gabapentin may cause certain adverse effects, which are listed below. Severe reactions: The severe adverse reactions include suicidality, depression, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, anaphylaxis, angioedema, erythema multiforme, rhabdomyolysis, and withdrawal seizure or withdrawal symptoms if the drug is discontinued abruptly. Both GABA and gabapentin are similar to each other but they have their differences. The first point of difference is their structural make-up. Gabapentin is a GABA analog, meaning that it looks very similar structurally but it is not completely the same. GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter found in the central nervous system (CNS) that GABA may be able to help those with insomnia. Learn how best to try this supplement and how much to take. Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Gabapentin is available in both branded and generic forms.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |