Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
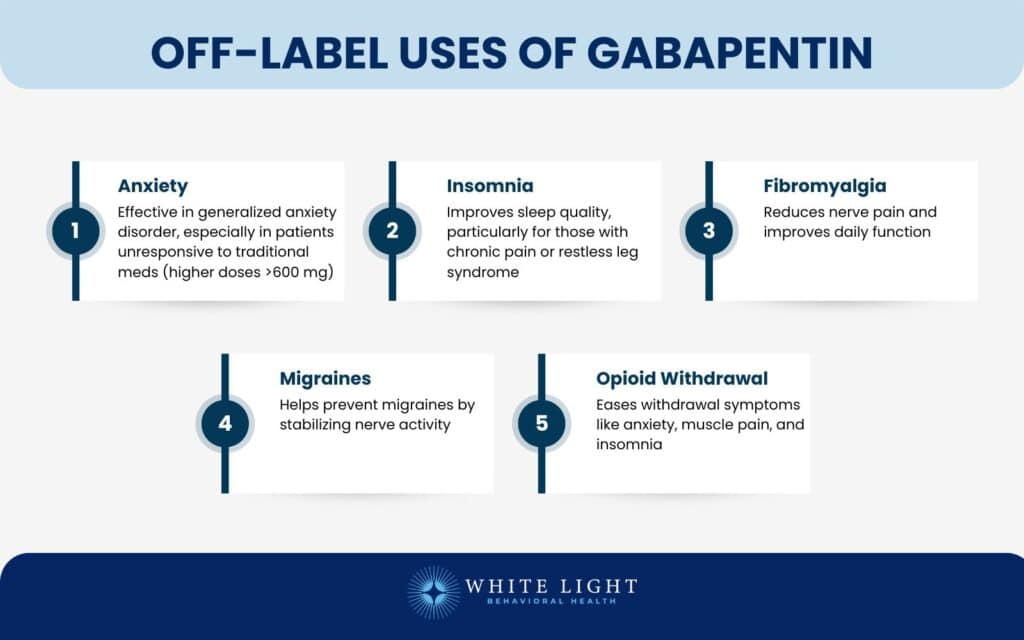 |  |
Gabapentin is a nerve pain medication and anticonvulsant that has proven to be effective for people who have hard-to-treat depression or other mood disorders. Discover the benefits and risks of Gabapentin 100mg, a widely prescribed medication for nerve pain, seizures, and anxiety. Learn about its dosage, uses, and potential side effects, as well as its interactions with other medications. Get informed about this popular treatment and make informed decisions about your health. Gabapentin (Neuraptine, Gralise, and Gralise 30-Day Starter Pack) is an anti-seizure (anticonvulsant) medication used to treat seizure disorders and postherpetic neuralgia (the pain that follows an episode of shingles). Off-label uses (uses not approved by the Food and Drug Administration, or FDA) for gabapentin include alcohol withdrawal, cocaine withdrawal, anxiety, hiccups, restless leg In this article, we’re diving into the various Gabapentin uses, highlighting the unique benefits it offers to those dealing with chronic pain, anxiety, and other neurological conditions. 📈 From its effectiveness in stabilizing electrical activity in the brain to its soothing effects on nerve pain, understanding how Gabapentin works can empower you to make informed decisions about your Gabapentin: Uses and Benefits Gabapentin is a medication that is commonly used for pain management. It works by reducing the sensitivity of the nerves and blocking the transmission of pain signals. This makes it an effective option for individuals who suffer from chronic pain conditions such as neuropathy, fibromyalgia, and postherpetic neuralgia. Aside from pain management, gabapentin is also Second, PubMed/MEDLINE and Embase were used to identify other systematic reviews/meta-analyses and primary literature using search terms “gabapentin” or “Neurontin” along with respective off-label indications. Off-label indications without systematic reviews/meta-analyses were evaluated based on largest body of primary literature available. GoodRx explains in detail how Gabapentin is used to treat anxiety including dosage, side effects, and more. Gabapentin is a strong drug that helps in the treatment of nerve pain. Nerve pain cannot be relieved by normal painkillers, but when gabapentin is combined with other painkillers, it can help in relieving pain. Find patient medical information for Gabapentin (Gralise, Neurontin) on WebMD including its uses, side effects and safety, interactions, pictures, warnings, and user ratings ANSWER: Gabapentin was originally approved as a drug to control epilepsy, but it soon became clear that it was useful for chronic pain, especially the kind that comes from damaged nerves. Frequent use of gabapentin for back pain may raise the risk of dementia by 29% and mild cognitive impairment by 85%, new study finds. People with prior gabapentin use, dementia, epilepsy, stroke, or cancer were excluded from the study. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication prescribed for a variety of conditions. Learn about its uses, side effects, and what you should know if you've been prescribed this medication. Gabapentin Patient Tips Medically reviewed by Carmen Pope, BPharm. Last updated on June 18, 2024. How it works Upsides Downsides Bottom Line Tips Response/effectiveness Interactions FAQ 1. How it works Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant with pain-relieving effects that may be used to treat partial-onset seizures or relieve nerve pain. Research has shown gabapentin binds strongly to a specific Gabapentin capsules, tablets, and oral solution are used along with other medications to help control certain types of seizures in people who have epilepsy. Gabapentin capsules, tablets, and oral solution are also used to relieve the pain of postherpetic neuralgia (PHN; the burning, stabbing pain or aches that may last for months or years after an attack of shingles). Gabapentin extended Discover gabapentin uses for treating epilepsy, nerve pain, and more. Learn about its mechanisms, benefits, and potential side effects. Gabapentin is an anti-epileptic drug, also called an anticonvulsant. It is used to treat some types of seizures and nerve pain caused by shingles. Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Gabapentin is available in both branded and generic forms. Doctors prescribe gabapentin to treat epilepsy, restless legs syndrome, and some types of nerve pain. Learn more the drug's uses, risks, and safety here. Receiving six or more prescriptions of the drug gabapentin for low back pain is associated with significantly increased risks of developing dementia and mild cognitive impairment (MCI)—29% and
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |