Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
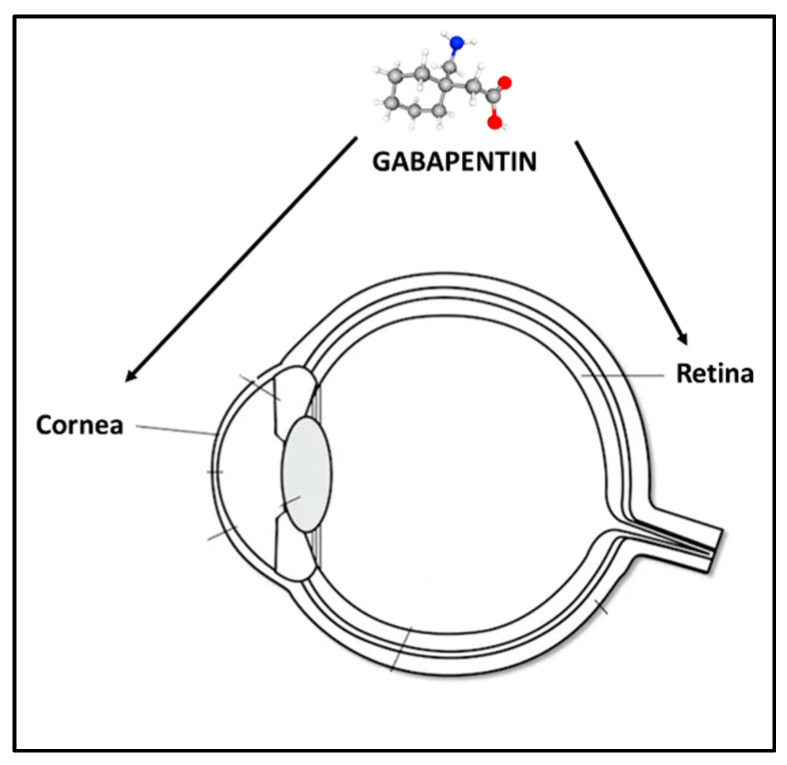
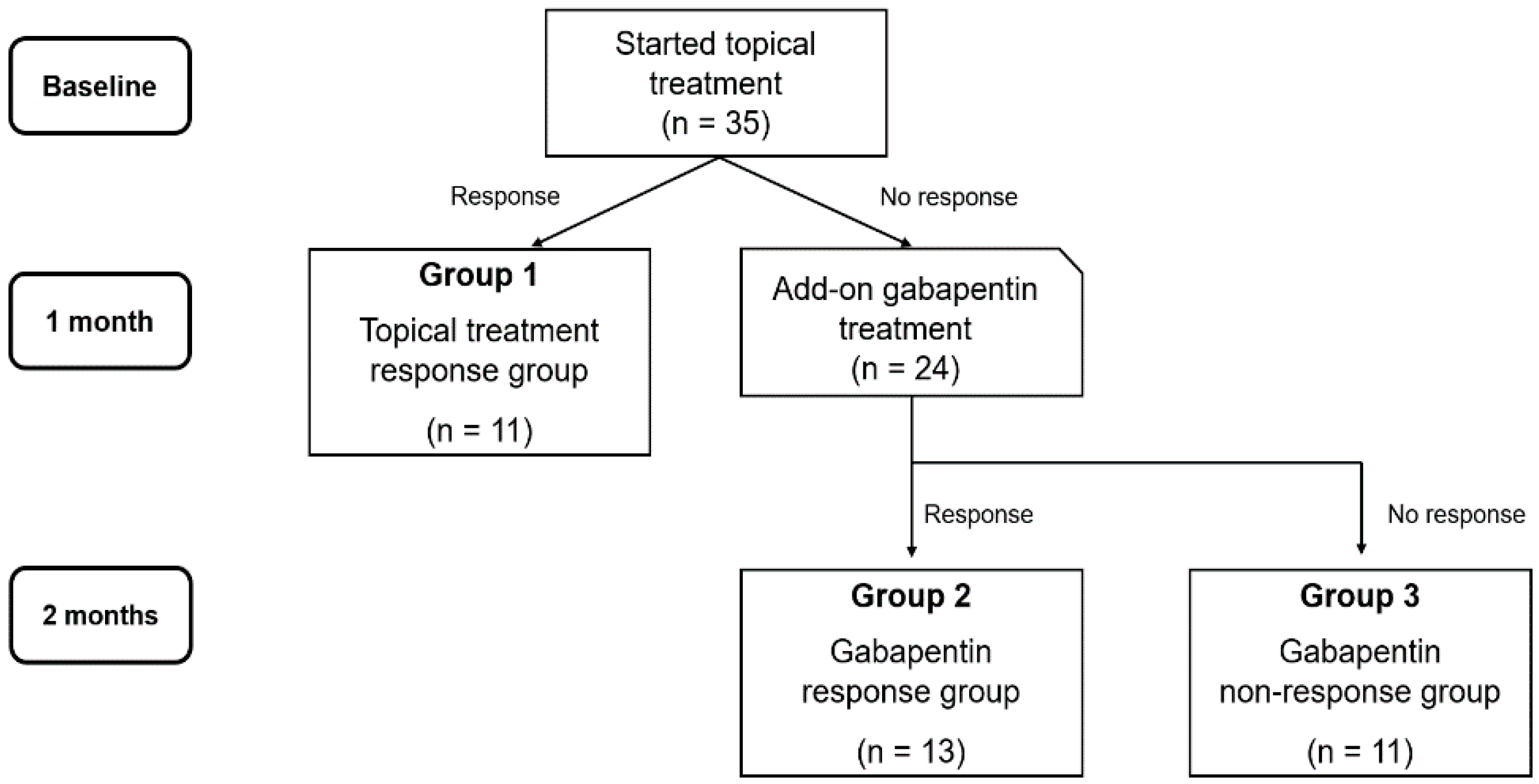
Gabapentin (GBT) is a structural analog of gamma-amino butyric acid that has been used by systemic administration to provide pain relief in glaucomatous patients. We have already shown in a rabbit model system that its topic administration as eye drops has anti-inflammatory properties. Gabapentin (GBT) is a structural analog of gamma-amino butyric acid that has been used by systemic administration to provide pain relief in glaucomatous patients. We have already shown in a rabbit model system that its topic administration as eye drops has anti-inflammatory properties. This study aims to evaluate the efficacy of gabapentin treatment in dry eye disease (DED) and neuropathic ocular pain. Our study was performed with 72 patients. The painDETECT questionnaire was used for neuropathic pain screening. Patients who were thought to have severe DED according to ocular surface disease index (OSDI) questionnaire, Schirmer’s test type 1 and tear break up time test A Challenging Dx “Pain without stain” is primarily a clinical diagnosis made for patients with corneal pain that has few-to-no clinical signs and is minimally, if at all, relieved by conventional treatments for DED. 4 Signs and symptoms. Currently, there are no standard clinical criteria and no ocular sensory tests that are diagnostic. Anat Galor, MD, MSPH, at Bascom Palmer Eye Dry eye patients should be screened for neuropathic ocular pain symptoms and individualized treatment has to be applied. Our study showed that the use of gabapentin is effective in severe dry eye patients with neuropathic ocular pain. A recent study reported that oral gabapentin may be able to successfully treat DED patients with neuropathic ocular pain—as opposed to pain mainly caused by mechanical and chemical influences—who have systemic comorbidities, including rheumatological, neurological and psychological disorders. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant and has been used to manage neuropathic pain. It was originally developed as an antiepileptic agent; however, it is now recommended as a drug of choice for the treatment of neuropathic pain. There is strong evidence that gabapentin is also effective in diabetic neuropathy and postherpetic neuralgia [1]. Corneal neuropathic pain (CNP) is a poorly defined disease entity characterised by an aberrant pain response to normally non-painful stimuli and categorised into having peripheral and central The pathophysiology of neuropathic ocular pain remains poorly understood. Clinical evaluation often reveals minimal ophthalmic exam findings, leading to an underdiagnosis of the condition by ophthalmologists. Gabapentin may be an underutilized medication in the treatment of chronic ocular pain. Purpose: To investigate the response to gabapentin treatment in patients with dry eye (DE) accompanied by features of neuropathic ocular pain (NOP), and to analyze the differences between clinical manifestations of the groups according to treatment This property is crucial for patients suffering from dry eye disease, where standard medications like artificial tears or anti-inflammatory drops fail to alleviate the full scope of symptoms. Recent studies have observed Gabapentin’s potential in reducing symptoms associated with severe dry eye and neuropathic ocular pain. A prior case report by Kavalieratos and Dimou demonstrated successful pain management of a blind glaucomatous eye with gabapentin after 6 months of treatment. 21 Similarly, we present a case of chronic ocular pain treated successfully with low-dose gabapentin. Download PDF The gabapentinoids gabapentin and pregabalin are among the most commonly prescribed drugs in North America. Now, researchers have found an association between gabapentin and the incidence of acute angle-closure glaucoma (AAG). 1 A similar association was not found for pregabalin. Both drugs are approved to treat epilepsy and selected chronic pain conditions and are widely used Learn about the side effects of gabapentin, from common to rare, for consumers and healthcare professionals. Gabapentin drug interactions: Along with side effects, gabapentin has possible interactions to know about. Gabapentin FAQs: Experts answer common questions about taking gabapentin, from if you should take it with food to what to do if you miss your dose. Is gabapentin an opioid? Learn the differences and similarities between gabapentin and an opioid medication. Abstract Purpose : Neuropathic ocular pain is a frequent occurrence in medium to severe dry eye syndrome (DES). Only palliative treatments, such as lubricants and anti-inflammatory drugs, are available to alleviate patients’ discomfort. Preclinical evidence about the efficacy of topical gabapentin on neuropathic ocular pain is provided by Cammalleri et al. in a rabbit model system in which eye drops with gabapentin exert analgesic effects coupled to stimulation of tear secretion. The patients underwent clinical examinations of the tear film, ocular surface, and meibomian gland and completed the Ocular Pain Assessment Survey (OPAS). One month after treatment with topical eye drops, add-on of gabapentin treatment was determined according to the Wong–Baker FACES Pain Rating Scale (WBFPS). Oral gabapentin is a first-line treatment for chronic systemic neuropathic pain. Although it has been used for ocular discomfort after refractive surgery and in severe, painful dry eye syndrome (DES), Analgesic drugs include gabapentin (GBT), a structural analog of gamma-amino butyric acid that has been introduced as an adjunctive therapy in epilepsy and is presently widely used to treat several kinds of neuropathic pain.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |