Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
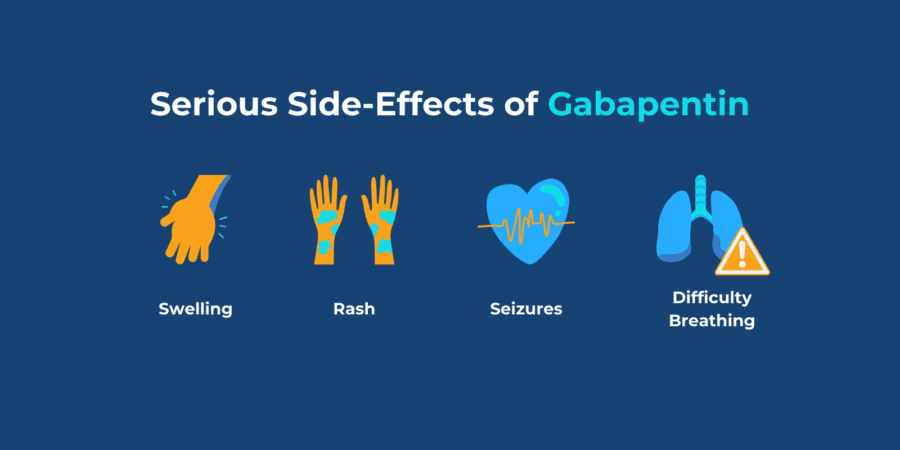
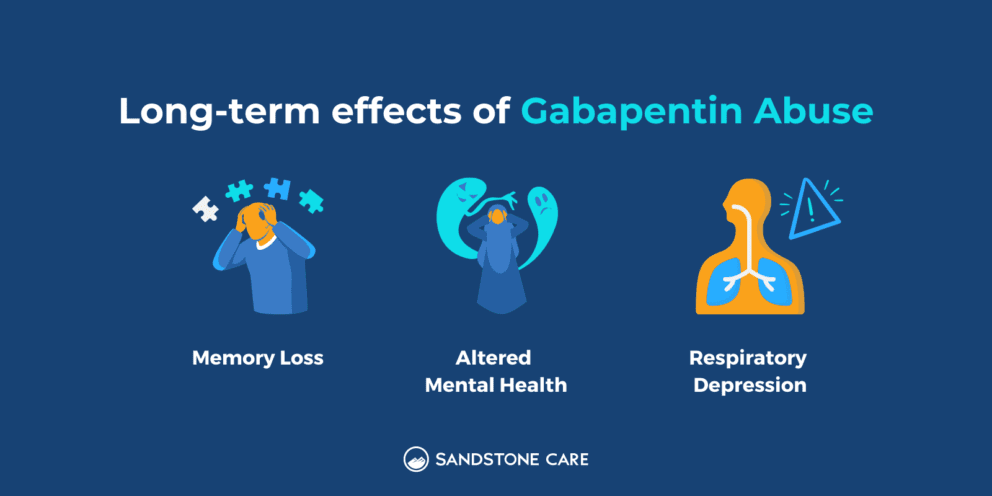
Abstract Introduction and hypothesis: Chronic pelvic pain (CPP) affects 2.1-24% of women, causing physical and psychological damage to women around the world. Based on the efficacy of gabapentin in the treatment of chronic pain, we conducted this study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of gabapentin in reducing pain in women with CPP. In some cases, the cramps that occur with fibroids cause pain in the lower back rather than in the lower abdomen, and may feel like a strained muscle. Some people have pain during sex because of fibroids. Because fibroids tend to grow, a person who didn’t have symptoms initially may slowly start experiencing them. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists has new recommendations for managing chronic pelvic pain. Gabapentin does not improve chronic pelvic pain in women, and should not be prescribed, research concludes. Chronic pelvic pain affects 2–24% of women worldwide and evidence for medical treatments is scarce. Gabapentin is effective in treating some chronic pain conditions. We aimed to measure the efficacy and safety of gabapentin in women with chronic There is minimal or no evidence for the use of gabapentin as an off-label therapy for other types of neuropathic pain, low-back pain, radiculopathy, or fibromyalgia. This study was adequately powered, but treatment with gabapentin did not result in significantly lower pain scores in women with chronic pelvic pain, and was associated with higher rates of side-effects than placebo. Given the increasing reports of abuse and evidence of potential harms associated with gabapentin use, it is important that clinicians consider alternative treatment options to off Uterine Fibroids Medicine Options This document includes the Option Grid decision aids for: Uterine Fibroid Medicine Options and Uterine Fibroid Procedure Options. This decision aid is for people with uterine fibroids that cause heavy bleeding or pain. It is not for people with cancer in the uterus. Receiving six or more prescriptions of the drug gabapentin for low back pain is associated with significantly increased risks of developing dementia and mild cognitive impairment (MCI)—29% and BackgroundThe gabapentinoid drugs gabapentin and pregabalin were originally developed as antiseizure drugs but now are prescribed mainly for treatment of pain. For gabapentin, the only pain-related indication approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is postherpetic neuralgia. For pregabalin, FDA-approved indications related to pain are limited to postherpetic neuralgia A Clinical Overview of Off-label Use of Gabapentinoid Drugs The gabapentinoid drugs gabapentin and pregabalin were originally developed as antiseizure drugs but now are prescribed mainly for treatment of pain. For gabapentin, the only pain-related indication approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is postherpetic neuralgia. Why carry out this study? Although several clinical studies have evaluated gabapentin for treatment of chronic pelvic pain (CPP) in women, the efficacy and safety of this therapy remain controversial. Therefore, there is an urgent need for specific pooled effect analysis to ascertain the methods efficacy and safety. What was learned from the study? The present meta-analysis evaluated efficacy Since the first uterine artery embolization (UAE) procedures were performed by Ravina in 1995, UAE has become accepted as a safe and effective alternate method for the treatment of uterine fibroids. 1 2 3 4 UAE is a minimally invasive method for treating fibroids and adenomyosis with shorter postoperative recovery times and faster returns to People who’d received six or more gabapentin prescriptions were more likely to be diagnosed with dementia or mild cognitive impairment within 10 years of their initial pain diagnosis, results show. Looking at age groups, researchers found that 18- to 64-year-olds prescribed gabapentin were more than twice as likely to develop dementia or MCI. The efficacy of gabapentin has been documented for other chronic pain conditions: painful diabetic neuropathy, post-herpetic neuralgia, mixed neuropathic pain conditions, spinal cord injury and phantom limb pain [5]. In some of these trials, gabapentin has also been shown to improve sleep, mood and other elements of quality of life. Gabapentin is widely used in the United States for a number of off-label indications, often as an alternative to opioid therapy. Increasing evidence has emerged suggesting that gabapentin may not be as benign as once thought and may be associated Uterine fibroids can be painful and disrupt daily life. Learn about what treatments and medications are available and how to ease the pain. Gabapentinoid drugs—specifically gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica)—are increasingly being prescribed for pain because physicians and patients seek alternatives to opioids in the Taking medications for fibroid symptoms can ease fibroid pain. However, they will not cure fibroids. Learn how medications can improve fibroid symptoms. What is Gabapentin? Gabapentin has active ingredients of gabapentin. It is often used in peripheral neuropathy. eHealthMe is studying from 322,849 Gabapentin users for the drug's side effects, drug interactions, effectiveness and more. Check Gabapentin in the real world. What is Uterine fibroids? Uterine fibroids (benign growths of the muscle inside the uterus) is found to be associated with
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |