Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
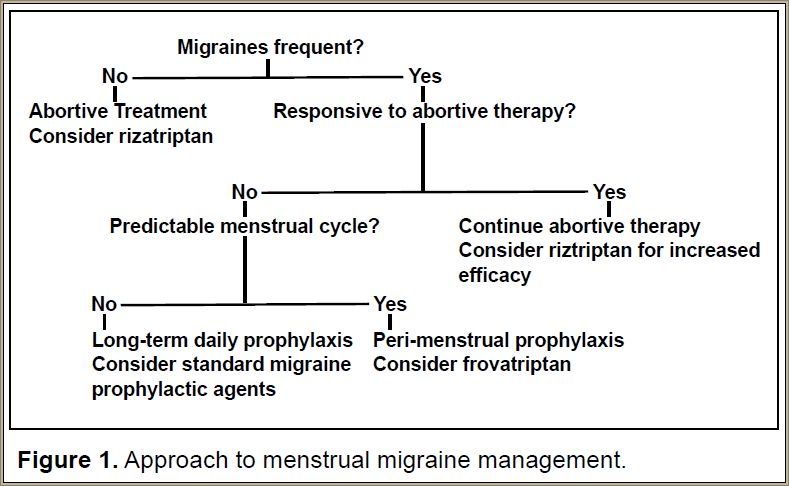
Tension-type, migraine, and cluster headaches are the most common primary headaches. Primary headaches are differentiated by clinical criteria from the International Classification of Headache Therefore, “probable migraine without aura” is used for patients who fulfill all criteria except one. 4 Migraine disorders also include hemiplegic migraine, chronic migraine, menstrual-related migraine (MRM), and complicated migraine. Table 1. Major clinical characteristics of migraine (migraine without and with aura). Background and objectives About a quarter of migraine cases among women have menstrual migraine (MM), which is usually more severe, longer lasting, and less responsive to treatment than typical migraine. Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) have evaluated the efficacy of several medication in the acute and preventive treatment of MM; this meta-analysis compared the effectiveness of these Menstrual-associated attacks typically occur in the 2 days before or 3 days after menses onset. Menstrual migraine generally begins with menarche or in adolescence. Although experiences vary, menstrual migraine commonly improves during pregnancy and may worsen during the perimenopausal period. What treatments are recommended for migraine prevention and how to follow up a person on preventative treatment, see Choice of preventative treatment and follow up. What treatments are recommended for prevention of menstrual or menstrual-related migraine, see Preventive drugs for menstrual and menstrual-related migraine. Menstrual migraine is when you have migraine attacks that are linked to your periods (menstruation). MM attacks are often longer, more severe, and harder to treat than other migraine attacks. Appropriate treatment strategies include acute treatment, short term preventive treatment, and daily preventive treatment, depending on the patient's pattern of migraine and occurrence of migraine outside the menstrual period. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication prescribed for a variety of conditions. Learn about its uses, side effects, and what you should know if you've been prescribed this medication. Migraine course is influenced by female reproductive milestones, including menstruation and perimenopause; menstrual migraine (MM) represents a distinct clinical entity. Increased susceptibility to migraine during menstruation and in perimenopause is probably due to fluctuations in estrogen levels. The present review provides suggestions for the treatment of MM and perimenopausal migraine. MM This article for healthcare providers outlines the diagnosis, mechanisms, and treatment approaches for managing menstrual migraine. Learn about the three main treatments for menstrual migraine and how to pick the best one for you, including acute and preventive treatment. Recurrent migraines can be functionally disabling and can impair quality of life. The disabling nature of migraine headaches leads to frequent visits to outpatient clinics and emergency department facilities, causing significant health and financial burdens. Headaches fall in the top five causes of emergency department visits and the top twenty reasons for outpatient visits.[1] The overall Menstrual migraines affect fewer than 10% of menstruating patients with migraine and are thought to be related to the decrease in estrogen level during the menstrual cycle. Objective A review of treatment options for menstrual migraine. Background Migraine affects ∼30 million people in the US. A subset of female migraineurs have migraines that are mainly associated w This guideline covers the diagnosis and management of tension-type headache, migraine (including migraine with aura and menstrual-related migraine), cluster headache and medication overuse headache in young people (aged 12 years and older) and adults. It aims to improve the recognition and management of headaches, with more targeted treatment to improve the quality of life for people with This is further supported by the widely reported variability of frequency and severity of migraines throughout the menstrual cycle. Stewart et al. [4] evaluated 81 women of menstruating age with a daily assessment of headaches, headache features, and days of menstruation and noted an increased incidence of migraine without aura during menses. Understanding Gabapentin for Migraine Prevention Gabapentin, originally developed as an anticonvulsant, has been found to be effective in preventing migraines. It works by stabilizing the electrical activity in the brain, reducing the likelihood of migraines. Gabapentin is thought to inhibit the release of certain neurotransmitters involved in pain signaling, thereby reducing the intensity and The use of a headache calendar will help establish a relationship between headache and the menstrual cycle and establish if headaches are menstrually triggered migraine (MM) or TMM. Women who have headache throughout their menstrual cycle should be treated with reassurance, education, and pharmacologic intervention. Gabapentin Gabapentin’s mode of action in migraine is unclear (66). It interacts with the α2δ-subunit of the calcium channel and increases the concentration and probably the syn-thesis of brain γ -aminobutyric acid (GABA). Abstract There is a wide array of options for migraine prophylaxis; many of the available drugs are clearly proven to be effective and yet are underused in Australia. “New” drugs which are gaining favour for migraine prophylaxis include topiramate, candesartan, gabapentin and botulinum toxin.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |