Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
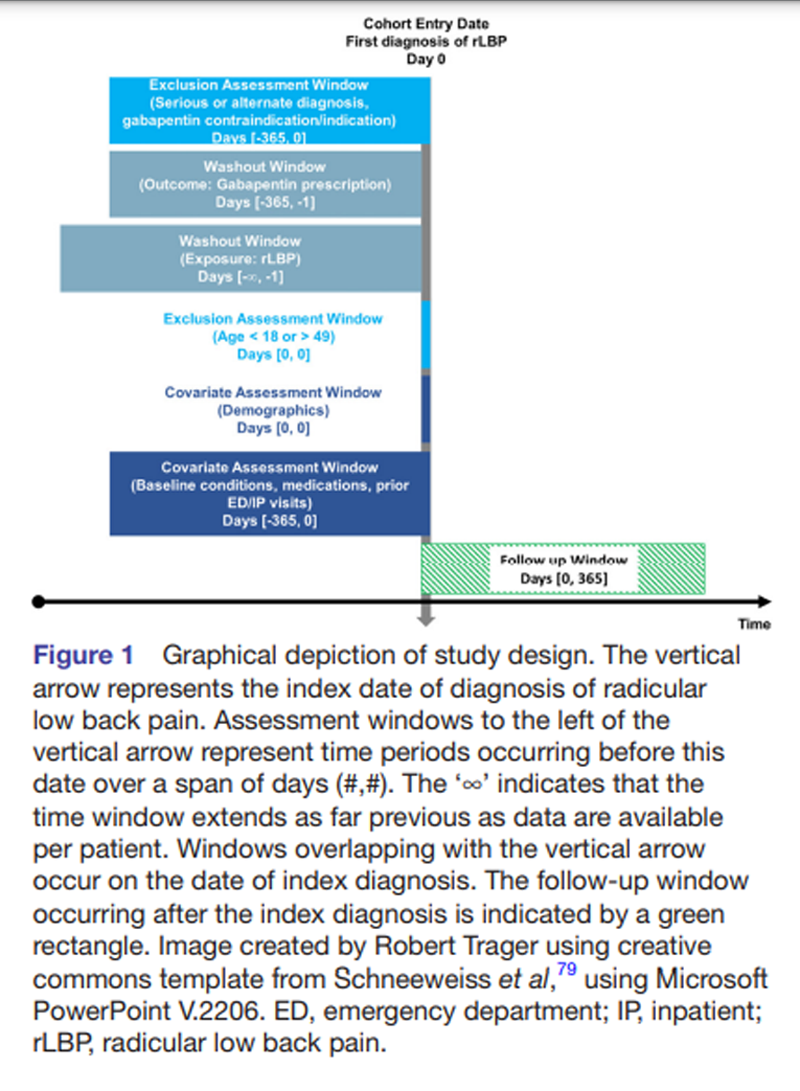
Background: The use of anticonvulsants (e.g., gabapentin, pregabalin) to treat low back pain has increased substantially in recent years despite limited supporting evidence. We aimed to determine the efficacy and tolerability of anticonvulsants in the treatment of low back pain and lumbar radicular pain compared with placebo. Methods: A search was conducted in 5 databases for studies comparing This SR aims to assess the effectiveness of pregabalin and gabapentin on pain and disability caused by acute sciatica and the adverse events associate Abstract BACKGROUND: The use of anticonvulsants (e.g., gabapentin, pregabalin) to treat low back pain has increased substantially in recent years despite limited supporting evidence. We aimed to determine the efficacy and tolerability of anticonvulsants in the treatment of low back pain and lumbar radicular pain compared with placebo. METHODS: A search was conducted in 5 databases for studies Pharmaceutical treatments for radiculopathy include opioid, antiinflammatory (steroidal and nonsteroidal), neuromodulating, topical, and adjuvant treatments. These medications act locally, peripher Discharge with pain specialist follow-up Max dosage 3600mg if patient already on gabapentin Taper dose > 7 days to discontinue [1] Pediatric Dosing Partial seizures Adjunct for partial seizures with out secondary generalization in patients> 12yo with epilepsy; also adjunctive therapy for partial seizures in patients 3-12 years Gabapentin of anticonvulsant and analgesic drugs, is one of the treatments effective in pain reduction and enhancing quality of life in patients with chronic radicular pain. However, there are not many studies on the effect of gabapentin on acute radicular pain[13]. Gabapentin may provide benefits in terms of alleviation of pain and overall quality of life in patients with chronic radiculopathy. This clinical trial is focused on studying the effects of the medication gabapentin on people experiencing radicular leg pain, which is a type of nerve pain that originates from the lower back and travels down the leg. Gabapentin is a remedy for nerve pain that’s also prescribed for back pain. See how it works and if it can help back pain from sciatica, shingles, and more. Gabapentin is prescribed frequently for chronic back pain syndromes in both primary care and specialty pain clinics, particularly when there is a ‘radicular’ or neuropathic component with pain radiating into the upper or lower legs [6]. Abstract Lumbar radiculopathy can be presented as low back pain and radiating pain. Transforaminal epidural steroid injection (TFESI) has been used to treat radicular pain, and after the injection, additional medications such as gabapentinoids including pregabalin (PGB) and gabapentin (GBP) can be administered to relieve remnant pain. However, little is known about the effectiveness of Study Design: A 4-week prospective open label single arm and single center study of patients with MRI diagnosis of spinal stenosis with radicular pain. Methods: The primary measure of efficacy was a change in average daily pain (ADP) score from baseline to completion of Gralise therapy for 4 weeks. One was a small study of high-dose gabapentin (3,600 mg per day) in 43 patients with lumbar radicular pain, and the other was a study of topiramate (300 mg per day) in 96 patients with low back pain. The efficacy of gabapentin monotherapy was investigated against both acute or chronic radicular pain caused by lumbar disk hernia (LDH) or lumbar spinal stenosis (LSS). Seventy-eight patients with radicular pain, 10 males and 68 females aged 23 to 76 years (mean 49.4 years), caused by LSS in 45 pati We included guidelines published between January 1, 2017, and January 9, 2022, written in the English language, related to radiculopathy, sciatica, and/or low back pain with leg pain, and that provided recommendations on oral medication. Is an epidural steroid injection or gabapentin (Neurontin) more effective for pain relief in patients with lumbosacral radicular pain due to a herniated disk or spinal stenosis? BACKGROUND: The use of anticonvulsants (e.g., gabapentin, pregabalin) to treat low back pain has increased substantially in recent years despite limited supporting evidence. We aimed to determine the efficacy and tolerability of anticonvulsants in the treatment of low back pain and lumbar radicular pain compared with placebo. METHODS: A search was conducted in 5 databases for studies comparing Participants: 145 people with lumbosacral radicular pain secondary to herniated disc or spinal stenosis for less than four years in duration and in whom leg pain is as severe or more severe than back pain. Interventions: Participants received either epidural steroid injection plus placebo pills or sham injection plus gabapentin. This study was carried out to determine the efficacy of gabapentin in patients with radiculopathy. Fifty patients (32 women, 18 men) with lumbosciatalgia secondary to L5 or S1 radiculopathy were ev Gabapentin is not effective for the treatment of radicular low back pain and is associated with adverse effects.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |