Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |
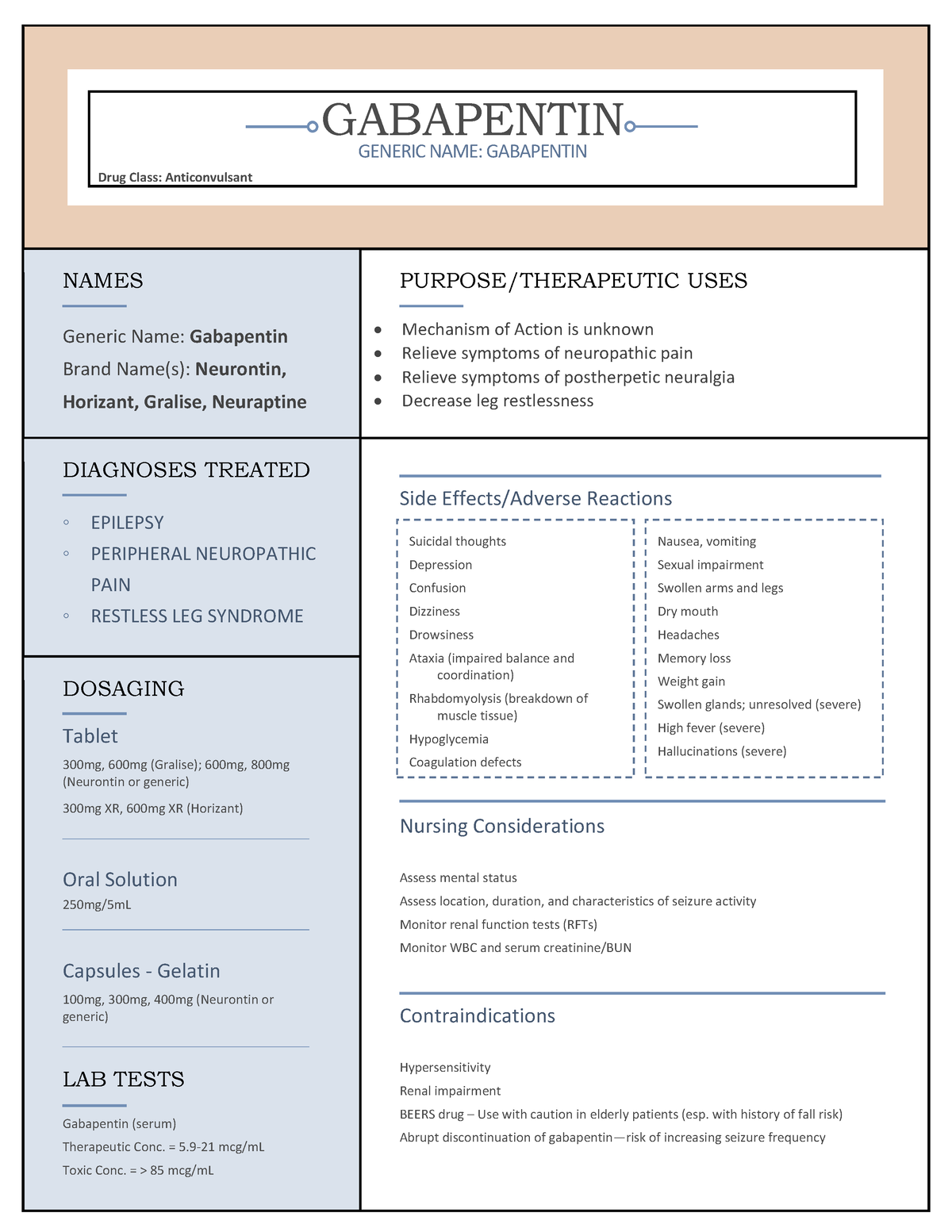
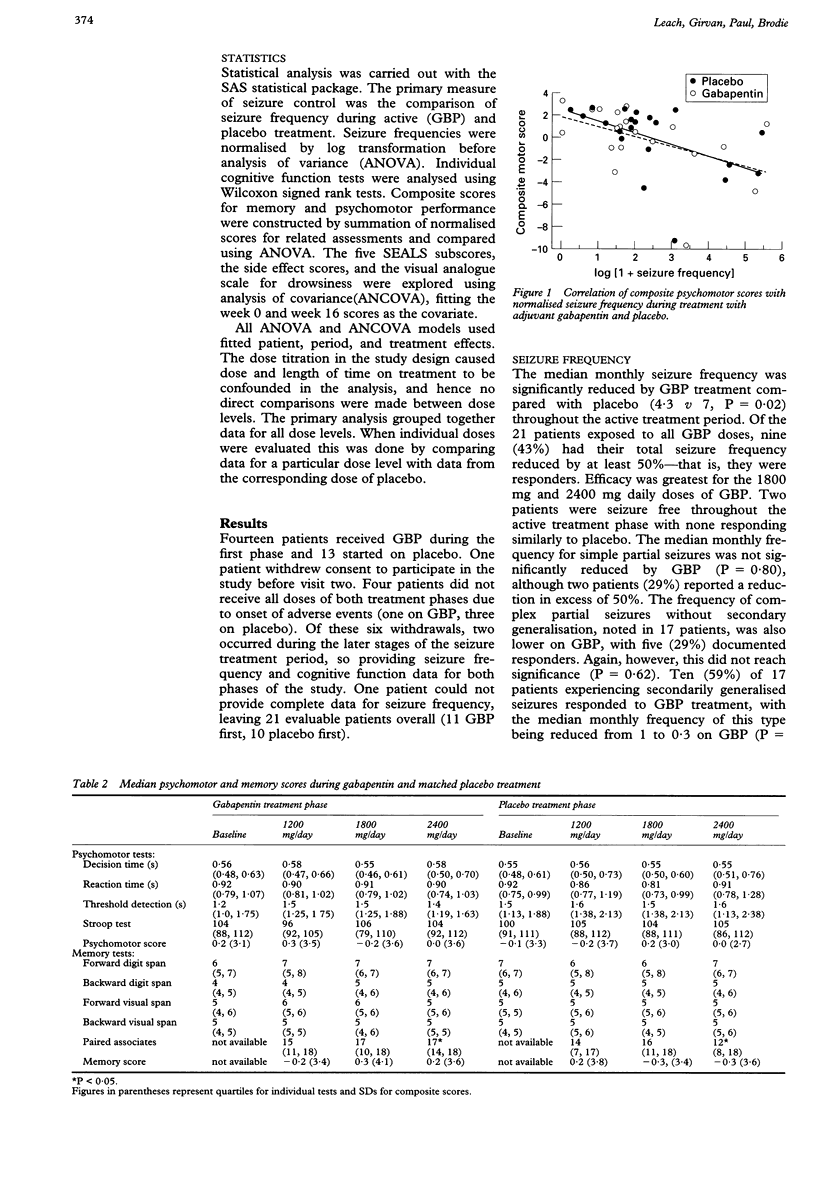
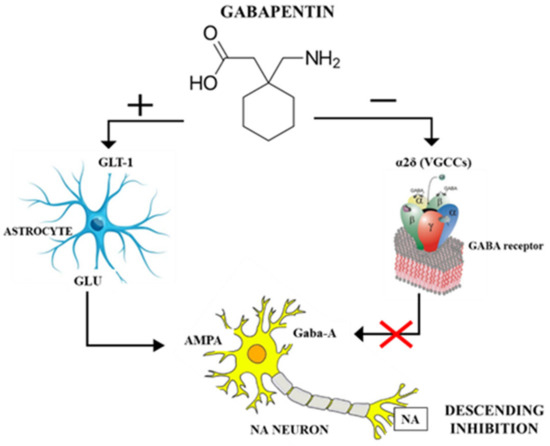
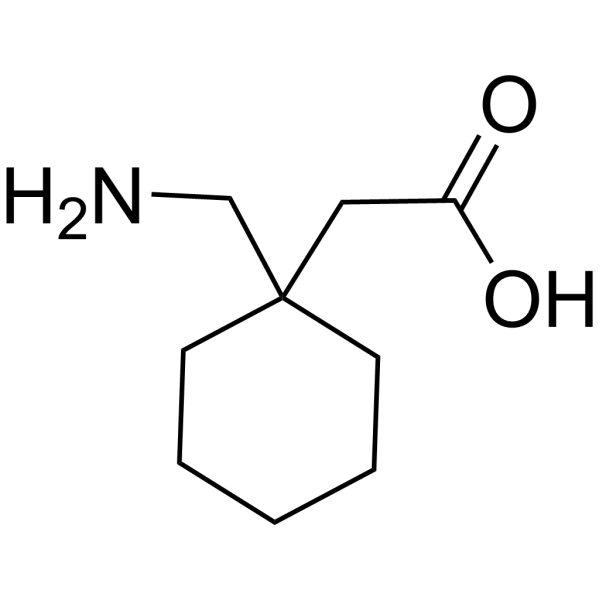
Shafigh-Ardestani MH, Karami-Horestani M, Emami B, Arjmandpour A. Evaluating the effect of oral gabapentin on the improvement of gastrointestinal symptoms in patients with functional dyspepsia resistant to conventional treatments. Gabapentin is a nonprotein amino acid and a synthetic neurotransmitter that is related to γ-aminobutyric acid1 (GABA). It was first described in 1976 West German patent DE2460891 on cyclic amino acids to Gerhard Satzinger and co-inventors at Goedecke AG (Freiburg). The corresponding US Patent is 4,024,175 (1977). gabapentin (ga-ba- pen -tin) Neurontin Classification Therapeutic: analgesic adjuncts, therapeutic, anticonvulsants, mood stabilizers Gabapentin is a gamma-amino acid that is cyclohexane substituted at position 1 by aminomethyl and carboxymethyl groups. Used for treatment of neuropathic pain and restless legs syndrome. It has a role as an anticonvulsant, a calcium channel blocker, an environmental contaminant and a xenobiotic. It is functionally related to a gamma-aminobutyric acid. Brand names: Gralise, Horizant, Neurontin Drug class: GABA-mediated Anticonvulsants Medically reviewed by Drugs.com on Jun 10, 2024. Written by ASHP. Introduction Uses Dosage Warnings Interactions Stability FAQ Introduction Anticonvulsant; structurally related to the inhibitory CNS neurotransmitter GABA; also possesses analgesic activity. Gabapentin enacarbil is a prodrug of gabapentin. Uses Gabapentin, sold under the brand name Neurontin among others, is an anticonvulsant medication primarily used to treat neuropathic pain and also for partial seizures [10][7] of epilepsy. Gabapentin is a GABA neurotransmitter analog; however, it does not inhibit GABA uptake or degradation. It appears to interact with GABA cotical neurons, but its relationship to functional activity as an anti convulsant is unknown. Used in conjunction with other anticonvulsants to control certain types of seizures in patients with epilepsy. Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Gabapentin is available in both branded and generic forms. This article details the newest Rome IV criteria for the different functional gastroduodenal disorders including functional dyspepsia and chronic nausea and vomiting syndrome and reviews data supporting management approaches to these conditions. The active ingredient in gabapentin capsules, USP is gabapentin, which has the chemical name 1- (aminomethyl)cyclohexaneacetic acid. The molecular formula of gabapentin is C9H17NO2 and the Structure of GABA: gabapentin and pregabalin. 10 Pharmacokinetics The actions of gabapentinoids are mainly at an intracellular site and require active uptake. They undergo facilitated transport across cell membranes through system l -amino acid transporters (LAT) as both drugs are structurally similar to the amino acid leucine. The effects of chronic gabapentin are blocked by an inhibitor of Gabapentin is an anticonvulsive medication that received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 and has been available in generic form in the USA since 2004. Gabapentin was originally used as a muscle relaxant and an anti-spasmodic. However, it was later discovered that gabapentin has the potential of an anticonvulsive medication and can be used as an adjunct to more Gabapentin is a new chemical compound designed as a structural analog of GABA that is effective in the treatment of partial seizures. In contrast to GABA, gabapentin readily penetrates the blood–brain barrier. In man, gabapentin has been demonstrated to increase GABA concentrations [126]. Most probably the mechanism of action is related to events modulated through its interaction with a Gabapentin is an anti-epileptic drug, also called an anticonvulsant. It is used to treat some types of seizures and nerve pain caused by shingles. Gabapentin | Deranged PhysiologyGabapentin Gabapentin extended-release tablets (Horizant) are used to treat restless legs syndrome (RLS; a condition that causes discomfort in the legs and a strong urge to move the legs, especially at night and when sitting or lying down). Gabapentin is in a class of medications called anticonvulsants. Preview text Drug: Gabapentin Drug Category: Anticonvulsant Functional Class: Anticonvulsant Chemical class: GABA analogue Method of action: Mechanism unknown; may increase seizure threshold; structurally similar to GABA but does not bind to GABAa or GABAb; gabapentin binding sites in neocortex, hippocampus Uses: Adjunct treatment of partial seizures, with/without generalization in patients Gabapentin package insert / prescribing information for healthcare professionals. Includes: indications, dosage, adverse reactions and pharmacology. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsive medication that received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 and has been available in generic form in the USA since 2004. Gabapentin was originally used as a muscle relaxant and an anti-spasmodic. However, it was later discovered that gaba Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication used in the management of peripheral neuropathic pains, postherpetic neuralgia, and partial-onset seizures.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |