Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH_JessicaOlah_WhatToKnowAboutGaba_4000x2700-c7a290db74574d1eb6fab03c9008b9a0.png) |
 |  |
 |  |
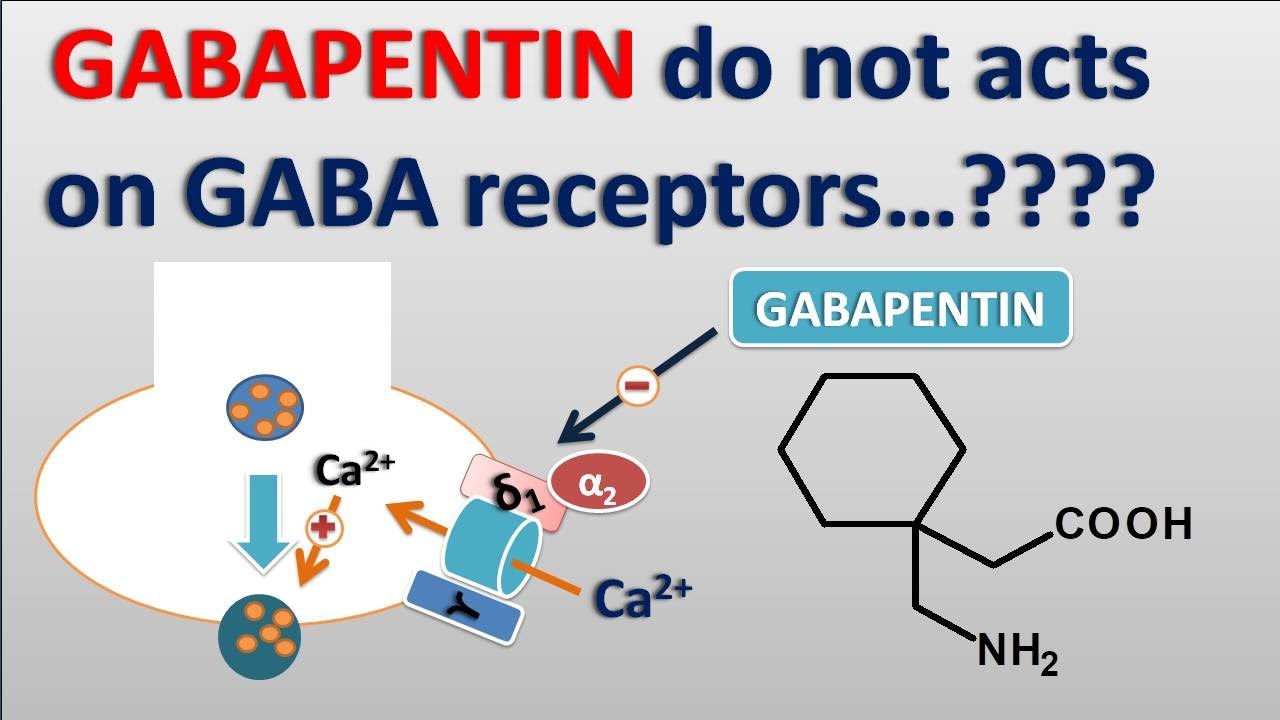
We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is a neurotransmitter with a crucial role in the human brain and body. It's recognized for its calming and relaxing effects, and many people use GABA supplements to unwind, alleviate stress, and enhance sleep. Gabapentin, while structurally similar to GABA, is a medication with distinct effects and applications. This blog post delves into the benefits of GABA Research regarding gabapentin's effects on GABA and glutamate synthetic and metabolizing enzymes reveals a complex pattern of activity and provides an incomplete explanation for its anticonvulsant effects. Limited studies have shown a possible link between GABA and lowered blood pressure. But research on GABA supplements is lacking. Researchers haven't confirmed whether or not it works for the many Difference between gabapentin and gaba supplement Looking for a natural alternative to gabapentin? Introducing GABA supplement – the safe and effective solution for managing anxiety, sleep disorders, and nerve pain. Gabapentin is a prescription medication commonly used to treat seizures, nerve pain, and certain types of mood disorders. GABA supplements generally have a more favorable safety profile, but high doses should be avoided to prevent potential adverse effects. Gabapentin, on the other hand, requires careful dosage management and regular medical oversight to monitor side effects and interactions with other medications. Key takeaways: Gabapentin (Neurontin) is a medication that’s used to treat seizures and nerve pain. Magnesium is a mineral that’s important for your health. When a magnesium-containing medication or supplement is taken with gabapentin, it can lower gabapentin’s effectiveness. It’s recommended to take gabapentin at least 2 hours after taking magnesium. GABA supplements are often promoted for their potential to alleviate anxiety and improve sleep, leveraging the body’s natural mechanisms. Gabapentin, being a prescription drug, is subject to stricter regulations and is typically used under medical supervision. GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) is a neurotransmitter in the brain. Learn about the benefits of GABA supplements and its medical significance. GABA vs. Gabapentin What's the Difference? GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) and Gabapentin are both substances that affect the central nervous system, but they have different mechanisms of action and uses. GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter in the brain that inhibits or slows down nerve activity, helping to reduce anxiety and promote relaxation. On the other hand, Gabapentin is a GABA may be able to help those with insomnia. Learn how best to try this supplement and how much to take. GABA and gabapentin are often mistakenly used interchangeably, but they are not the same. GABA is an amino acid supplement and neurotransmitter, while gabapentin is a prescription medication. While practitioners may confuse the two, it’s important to understand their differences. Key Takeaways: GABA is a natural supplement that helps alleviate anxiety and physical tension. Gabapentin is a Dosage Considerations: If someone decides to try a GABA supplement, it's essential to follow recommended dosages and guidelines. Excessive intake of GABA supplements may lead to side effects or interactions with medications. Dietary sources of Gamma-aminobutyric acid Here are you can find some food sources that contain GABA: Fermented Foods. Conclusion: Key Takeaways on GABA vs Gabapentin In conclusion, while Gamma Aminobutyric Acid and Gabapentin may share structural similarities and a focus on neurologic functions, they are distinctly different in their action, uses, and safety profiles. GABA and Gabapentin, though distinct entities share a common goal: to promote calmness and regulate neuronal activity. While GABA is a natural neurotransmitter with diverse functions, Gabapentin is a synthetic medication mimicking some of its effects for specific therapeutic purposes. Learn about the difference between GABA and gabapentin, a neurotransmitter and an inhibitory medication often used for seizures and neuropathic pain. By Forest Tennant, PNN Columnist “GABA” is short for the neurotransmitter, gamma aminobutyric acid. GABA is the natural (endogenous) biochemical substance in the brain, spinal cord, and all nerves that control electrical conduction. Without proper GABA function, we experience pain. New research GABA is not the same as gabapentin. GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) is an amino acid supplement; gabapentin is a prescription medication December 23, 2022 By Trudy Scott 53 Comments Both GABA and gabapentin are similar to each other but they have their differences. The first point of difference is their structural make-up. Gabapentin is a GABA analog, meaning that it looks very similar structurally but it is not completely the same. GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter found in the central nervous system (CNS) that Because of its importance as a neurotransmitter, pharmaceutical manufacturers have worked to design prescription GABA analogues that can cross the blood-brain barrier and mimic GABA. Gabapentin is a GABA analogue used to treat epilepsy and neurotic pain. Gabapentin causes an increase in GABA levels in the brain. Another GABA analog is gamma-hydroxybutyrate, or GHB. Also known as "liquid
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH_JessicaOlah_WhatToKnowAboutGaba_4000x2700-c7a290db74574d1eb6fab03c9008b9a0.png) |
 |  |
 |  |