Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
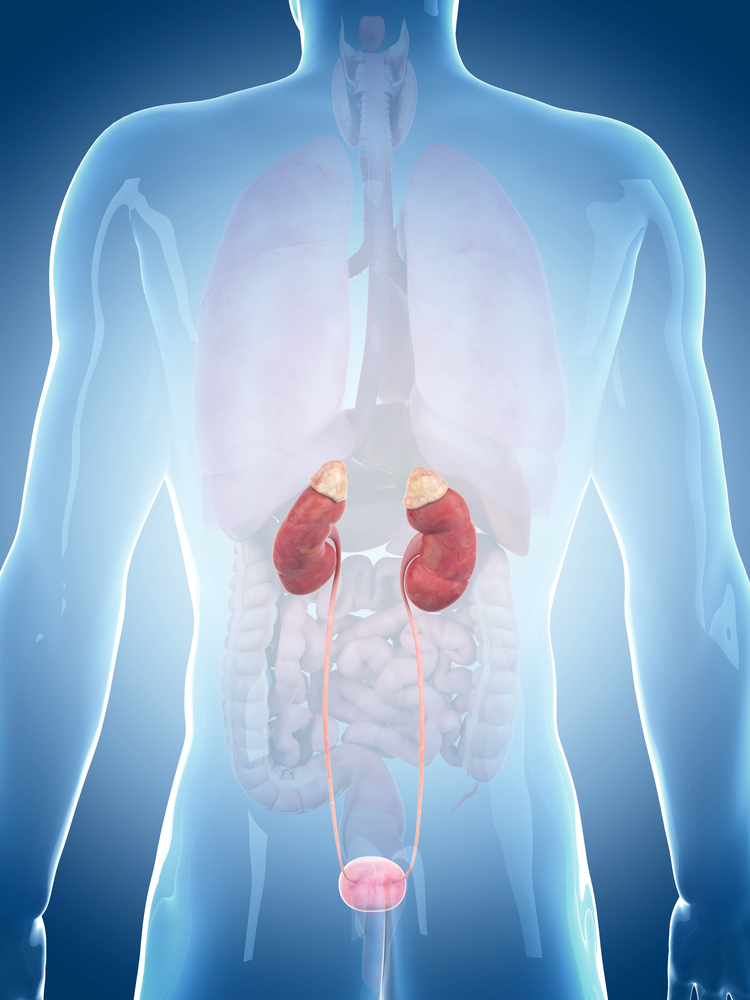
CONCLUSION: Gabapentin toxicity in patients with chronic kidney disease is underrecognized. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. Studies have shown that gabapentin toxicity can occur in patients with chronic kidney disease, particularly in those with advanced age and multiple comorbidities 4, 5. Dose Adjustment and Renal Function Dose adjustment of gabapentin is crucial in patients with decreased renal function to prevent toxicity 4, 5. Gabapentin, a medication primarily used to treat nerve pain and seizures, has garnered attention for its efficacy and safety profile. However, concerns about its potential impact on kidney health have emerged, especially among patients with pre-existing kidney conditions. Understanding the relationship between gabapentin and kidney function is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers. Rational dosing of gabapentin and pregabalin in chronic kidney disease Mena Raouf 1, Timothy J Atkinson 1, , Meredith W Crumb Abstract Background: Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Although gabapentin is well known for its favorable pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. Existing literature on such risk is lacking. Keywords: renal dose adjustment, gabapentin neuro, action myoclonus-renal failure syndrome, severe diabetic neuropathy, painful neuropathy, ckd management, pain management in ckd patients, ckd, drug-induced myoclonus, pregabalin and gabapentin treatment for peripheral neuropathy Introduction Introduction Renal dose adjustments for gabapentin and pregabalin are ubiquitously evident in the medical literature. All manufacturers for these branded and generic dosage forms list dosing recommendations relative to creatinine clearance (CrCl) for both medications (Table 1).1,2 However, the basis of these recommendations has not been well articulated. Gabapentinoids, including gabapentin and pregabalin, are frequently prescribed as opioid alternatives. Given that gabapentinoids are eliminated from the body by the kidney, we sought to determine the risk of serious adverse events in patients with chronic kidney disease who started a gabapentinoid at a higher versus a lower dose. Gabapentin is widely used in the management of pain. It is entirely excreted through the renal system so this needs to be considered in any patient becoming acutely ill and developing renal failure. Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Although gabapentin is well known for its favorable pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. Existing literature on such risk is lacking. Gabapentin can be used by kidney disease patients, but dosage adjustments are critical. Learn how to safely use gabapentin with kidney issues and discover alternative medications. Gabapentin Effects on Kidneys | Is Gabapentin Bad for Your Kidneys? In this video we talk about Gabapentin effects on kidneys. The question we’re getting a lot is, Is gabapentin bad for kidney disease? Now, gabapentin is a medication used for diabetic neuropathy or neuropathy or any type of nerve pain. It is also used for seizures, but it’s given to a lot in people that have diabetic In rare instances, gabapentin can cause DRESS (drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms) syndrome. This is a severe allergic reaction that can cause damage to major organs, including the liver and kidneys. If you have existing kidney problems, you may need a lower dose of gabapentin. Abstract Rationale & objective: Gabapentinoids are opioid substitutes whose elimination by the kidneys is reduced as kidney function declines. To inform their safe prescribing in older adults with chronic kidney disease (CKD), we examined the 30-day risk of serious adverse events according to the prescribed starting dose. Background: Gabapentin and pregabalin are well-tolerated medications primarily cleared by the kidney. Patients receiving higher gabapentinoid doses with decreased kidney function may be at an increased risk of adverse effects (AEs), but limited Discussion: Gabapentin is widely used in the management of pain. It is entirely excreted through the renal system so this needs to be considered in any patient becoming acutely ill and developing renal failure. We describe a patient who developed significant deterioration in her conscious level due to iatrogenic gabapentin overdose. Conclusion Gabapentin toxicity in patients with chronic kidney disease is underrecognized. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. INTRODUCTION Pain is one of the most common and distressing symptoms among patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) [1]. The prevalence of pain has been associated with substantially lower health-related quality of life and greater psychosocial distress, insomnia, and depressive symptoms [2-9]. As in the other 2 cases of gabapentin-induced acute renal failure and rhabdomyolysis, the patients involved had multiple illnesses and were affected by multiple medications or other factors that might lead to rhabdomyolysis and renal failure. Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Although gabapentin is well known for its favorable pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |