Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
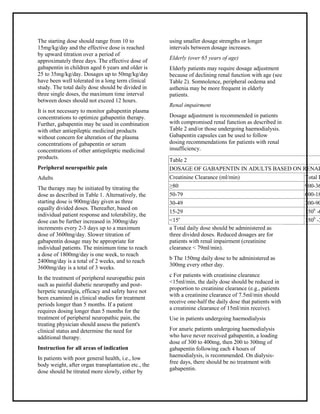
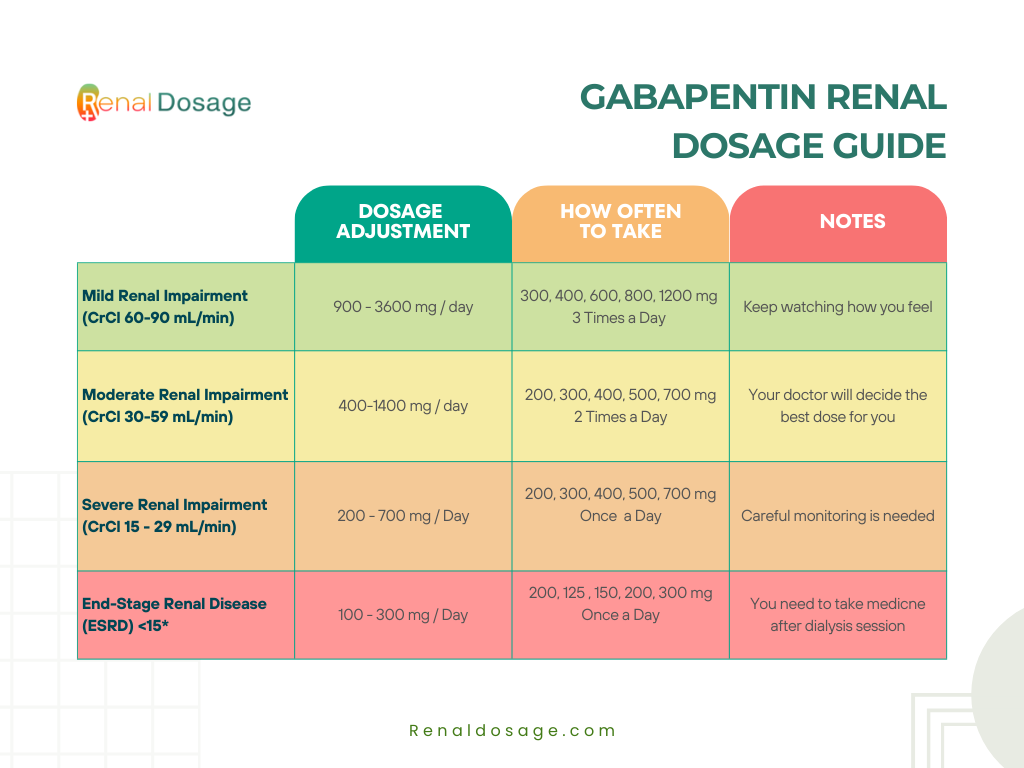
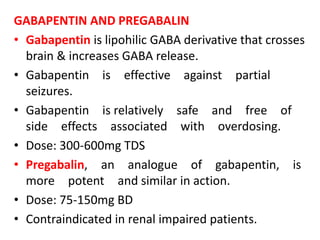
Gabapentin and pregabalin are often used in patients with CKD primarily to treat neuropathic pain and restless leg syndrome and given the high prevalence of diabetes in this population, the proportion who receive these drugs is very high. In patients with normal renal function, the maximum dose of gabapentin is 3600mg daily in divided doses. However, gabapentin is renally cleared and so the Gabapentin is eliminated in urine unmetabolized at a rate proportional to creatinine clearance. 24 In patients with renal impairment, with unaltered gastrointestinal absorption, gabapentin half-life can be prolonged up to 132 hours (without dialysis), 30 placing patients with chronic kidney disease at an increased risk for toxicity. Introduction Renal dose adjustments for gabapentin and pregabalin are ubiquitously evident in the medical literature. All manufacturers for these branded and generic dosage forms list dosing recommendations relative to creatinine clearance (CrCl) for both medications (Table 1).1,2 However, the basis of these recommendations has not been well articulated. Management of chronic pain in advanced chronic kidney disease, including pharmacologic and non-pharmacologic treatments. Clinical Pharmacology in Renal Impairment How Gabapentin Acts in the Body: Absorption: Taken by mouth, it enters your blood. Distribution: Spreads throughout your body. Metabolism: Not changed much by your body. Excretion: Removed from your body by kidneys. If kidneys are slow, gabapentin stays longer, so dosing needs to be careful. 11. Patient It is essential that a patient's renal function is taken into account when prescribing and reviewing medication. Doses often need to be reduced in renal impairment to prevent accumulation and toxicity. Examples of drugs that should be reduced in renal impairment are the gabapentinoids: gabapentin and pregabalin. Table 1 shows maximum recommended dose of gabapentin in renal impairment: Table 2 Renal dose adjustments for gabapentin and pregabalin are ubiquitously evident in the medical literature. All manufacturers for these branded and generic dosage forms list dosing recommendations relative to creatinine clearance (CrCl) for both medications (Table 1). 1,2 However, the basis of these recommendations has not been well articulated. Abstract Background: Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Although gabapentin is well known for its favorable pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. Existing literature on such risk is lacking. From the Guidelines Gabapentin generally does not worsen renal function in patients with normal kidney function, but it requires dose adjustment in those with existing kidney impairment. The medication is primarily eliminated unchanged through the kidneys, which means it can accumulate to potentially toxic levels in patients with reduced renal function if not properly dosed 1. For patients Gabapentin is widely used in the management of pain. It is entirely excreted through the renal system so this needs to be considered in any patient becoming acutely ill and developing renal failure. what is DOSE Gabapentin IN RENAL IMPAIRMENT , what IMPORTANT DRUG INTERACTIONS Gabapentin,CLINICAL USE Gabapentin , for what can Gabapentin used for Neurontin - Gabapentin Renal Dosing protocol for Adults, maintenance gabapentin dosing and additional dosing for adults undergoing dialysis 2.3 Dosage Adjustment in Patients with Renal Impairment Dosage adjustment in patients 12 years of age and older with renal impairment or undergoing hemodialysis is recommended, as follows (see dosing recommendations above for effective doses in each indication): TABLE 1. Gabapentin Dosage Based on Renal Function Gabapentin has been linked to encephalopathy, falls, and fractures in several large studies, 12,14,16,31 and the US Food and Drug Administration recently issued warnings about respiratory depression with gabapentinoids in patients at high risk, including those with CKD. 32 We defined encephalopathy as a diagnosis of delirium, disorientation For people with normal kidney function, gabapentin is safe and doesn’t cause kidney complications or trigger kidney disease. In people with renal impairment, gabapentin can be harder to clear from the body. People with kidney disease may be prescribed gabapentin, but their dose will need to be lowered based on how well their kidneys function. The clearance of both gabapentin and pregabalin decreases and half-life (t ½) increases proportionately with worsening renal function, requiring renal dose adjustment (Tables 1 and Supplementary Table 1) [106 - 108]. Both medications should be dosed post-HD. Gabapentin is a rel-atively safe medication, but in certain clinical scenarios, particularly in impaired renal functions, can lead to severe complications. Moreover, it per se can rarely lead to rhabdomyolysis and AKI. Clinical suspicion and timely decontamination are needed, and sometimes dialytic therapy may be needed. View gabapentin information, including dose, uses, side-effects, renal impairment, pregnancy, breast feeding, monitoring requirements and important safety information. Gabapentin has also been linked to causing behavioral changes such as confusion and CNS depression including somnolence and dizziness, which is more prominent in patients with renal impairment.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |