Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
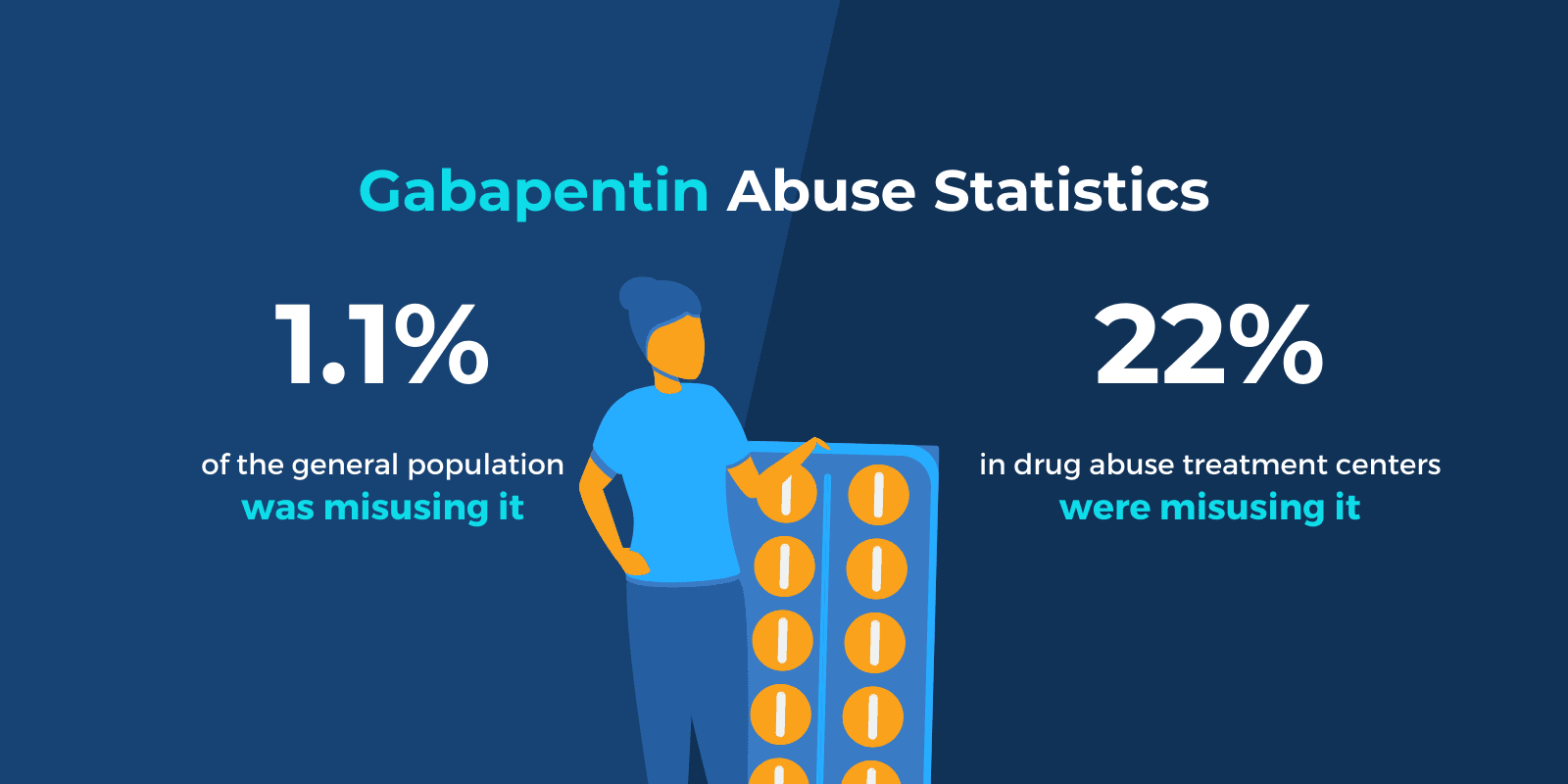
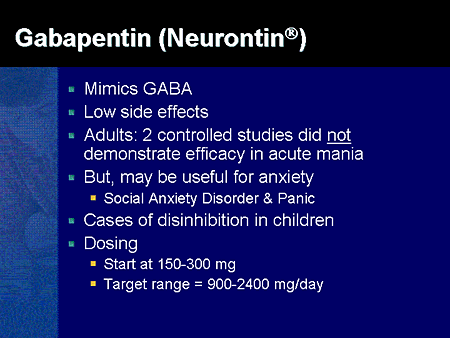
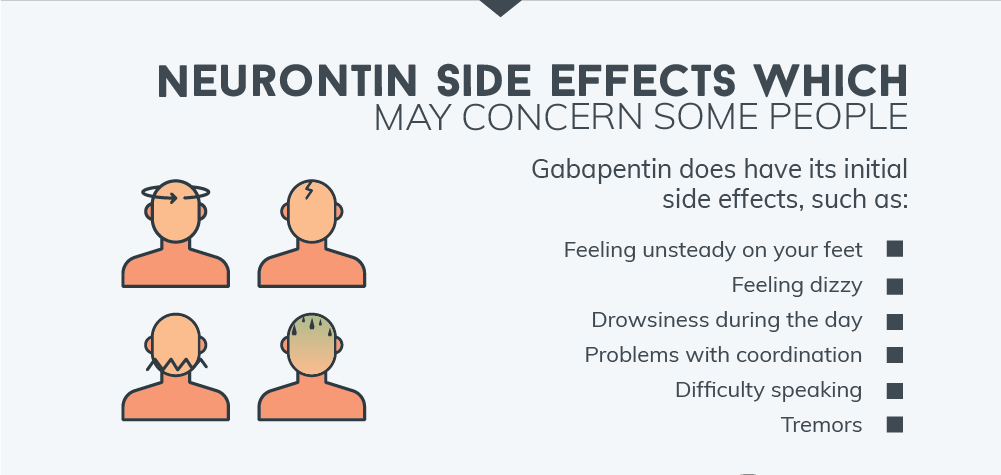
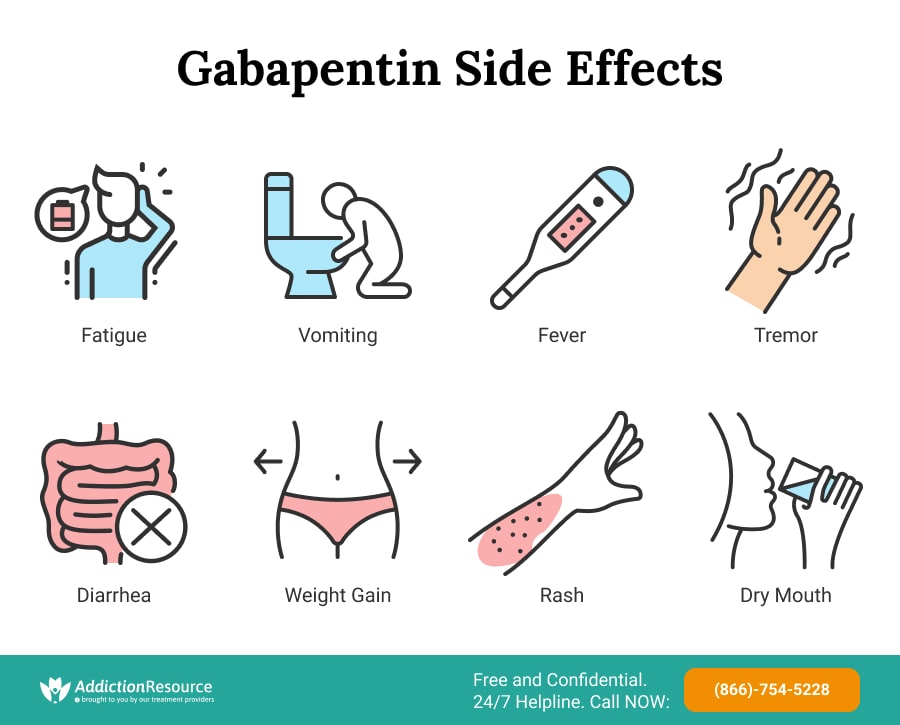
Find patient medical information for Gabapentin (Gralise, Neurontin) on WebMD including its uses, side effects and safety, interactions, pictures, warnings, and user ratings Comprehensive guide on pharmacologic management of alcohol use disorder, including treatment options and strategies for effective care. Gabapentinoid poisoning and withdrawal symptoms, including management strategies and clinical considerations, are discussed in this comprehensive resource. Gabapentin Adult Medication This information from Lexicomp ® explains what you need to know about this medication, including what it’s used for, how to take it, its side effects, and when to call your healthcare provider. Topical agents — Topically applied drugs have several potential advantages over systemic drugs for pain: delivery at the painful site of injury, significantly lower initial rates of systemic absorption and so fewer systemic effects, and patient preference. However, significant systemic concentrations and systemic side-effects are possible. Explore pharmacologic management strategies for alcohol use disorder, including treatment options and outcomes, on this comprehensive resource. Comprehensive information on antiseizure medications, including mechanisms of action, pharmacology, and adverse effects. Gabapentin may cause certain adverse effects, which are listed below. Severe reactions: The severe adverse reactions include suicidality, depression, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, anaphylaxis, angioedema, erythema multiforme, rhabdomyolysis, and withdrawal seizure or withdrawal symptoms if the drug is discontinued abruptly. Pharmacologic approaches for managing chronic non-cancer pain in adults, including treatment options and considerations. Though gabapentin has many potential uses, it can cause side effects. Read more about 13 gabapentin side effects here. Nonopioid medications provide effective options for managing acute pain in adults, offering alternatives to opioids. This strategy involves a combination of analgesic techniques and medications with differing mechanisms of action, with the goal of improving analgesia, reducing side effects, and minimizing reliance on opioids. Overview of pharmacologic management of chronic pain in adults, including medication options and treatment strategies. However, many people have no side effects or only have minor side effects. Call your doctor or get medical help if any of these side effects or any other side effects bother you or do not go away: NHS medicines information on side effects of gabapentin and what you can do to cope. Gabapentin is a medication used to treat nerve pain, seizures, and other conditions. Learn about its uses, side effects, and precautions. UpToDate UpToDate In patients with sensitivities or vulnerability to nocebo effects, consider a starting dose of 100 mg at night to minimize initial side effects. The typical effective daily dose range for immediate-release (IR) gabapentin is 1200 to 2400 mg/day on a three-times a day schedule, with a maximum daily dose of 3600 mg. Learn about the side effects of gabapentin, from common to rare, for consumers and healthcare professionals. Pharmacology Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly used first-line agents for diabetic peripheral neuropathy and other common neuropathies. Pharmacologically, both agents inhibit alpha-2-delta (α2δ) subunit of N-type voltage-gated calcium channels, a key receptor involved in regulating the excitability of neurons. 3 Peripheral nerve injury results in the upregulation of α2δ-1 receptors in
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |