Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
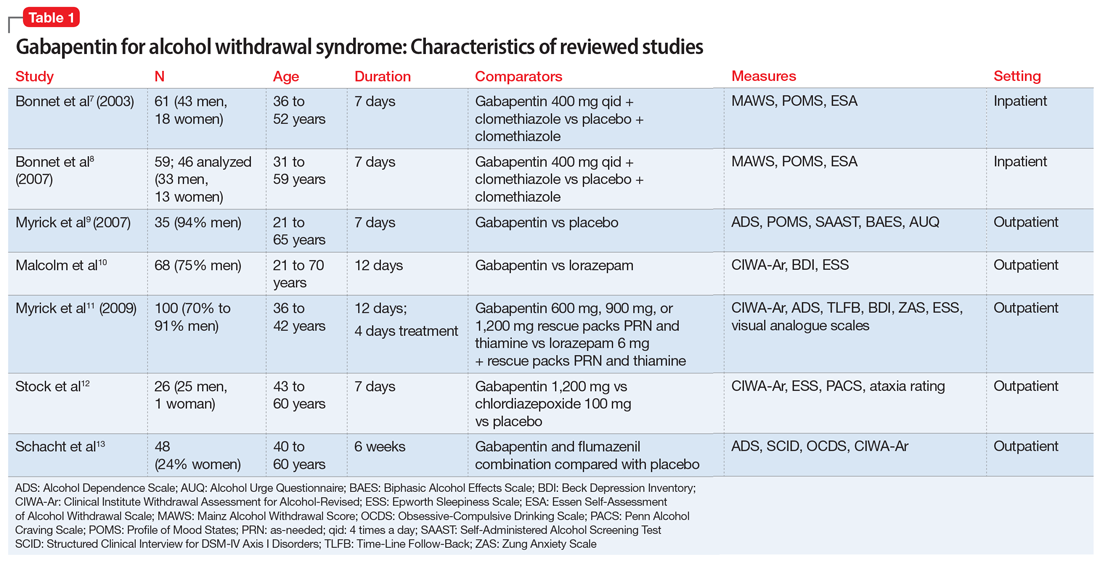
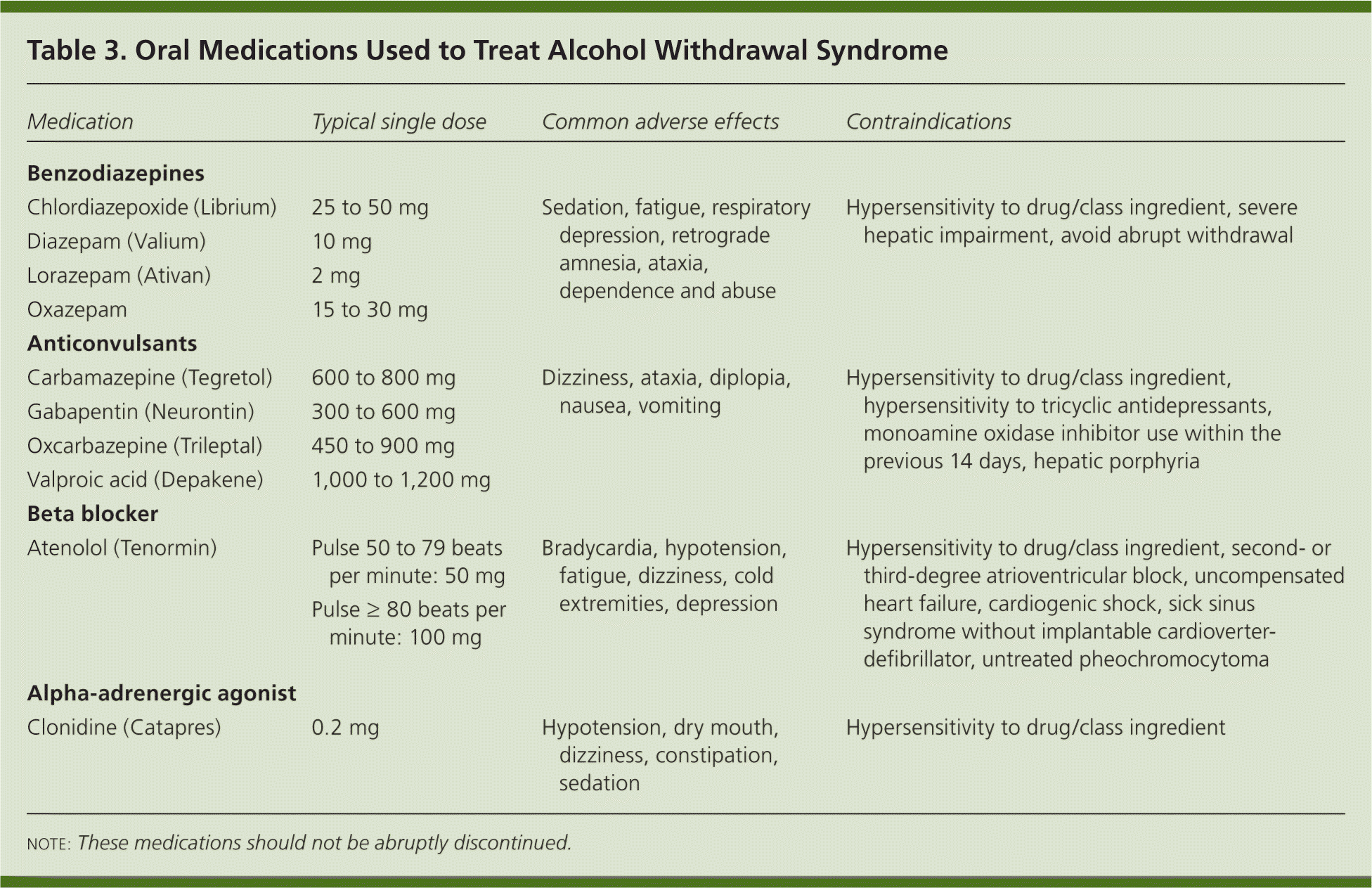
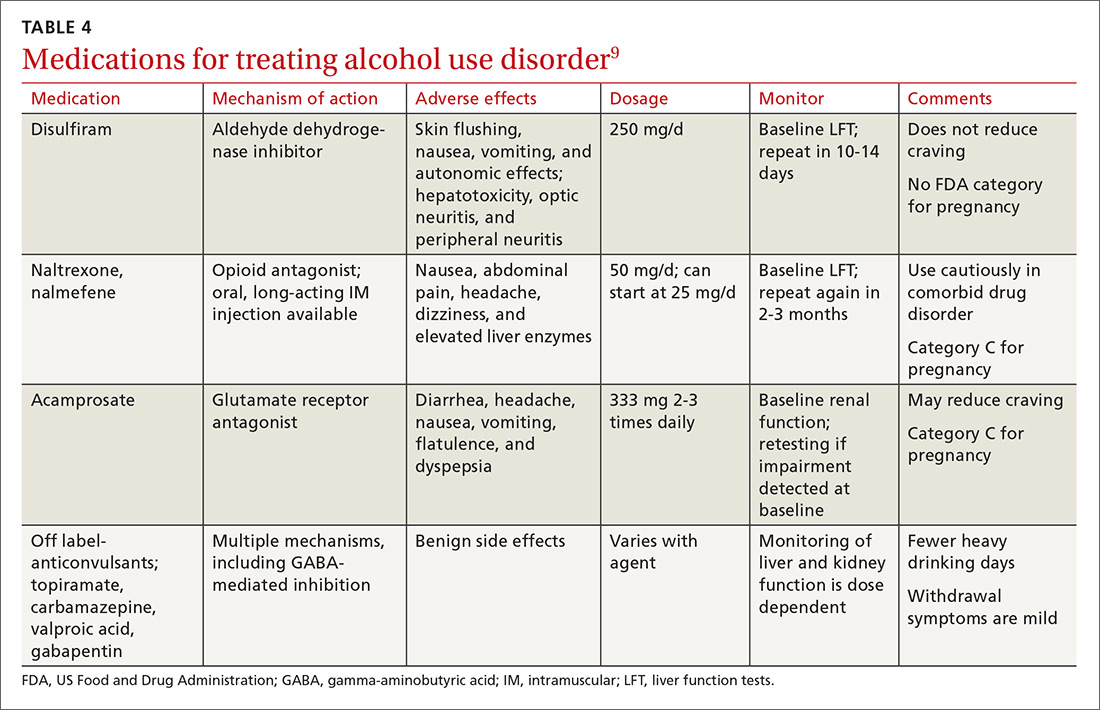
Alcohol use disorders are present across medical specialties, with alcohol-related deaths particularly prevalent in the categories of injury, cancer, cardiovascular disease, and liver cirrhosis. Nonetheless, implementation of alcohol-specific medications remains limited across most medical specialties. The anticonvulsant drug gabapentin is used off-label to treat alcohol-related withdrawal, cravings, anxiety, and insomnia. Although it is well tolerated and has demonstrated efficacy for mild alcohol withdrawal and early abstinence, there is concern about its potential for abuse. Gabapentin should be prescribed only as a second-line alternative to standard therapies, and only after screening • Taking medicine for an alcohol use disorder is not substituting one drug for another. How should I take gabapentin? • The recommended dose of gabapentin for the treatment of alcohol use disorder is 300–600 milligrams (mg) three times daily. • Gabapentin can be taken with or without food. APA’s 2018 practice guideline on AUD pharmacotherapy suggests psychiatrists consider gabapentin for patients with moderate to severe alcohol use disorder who prefer gabapentin or are intolerant to or have not responded to the FDA-approved medications naltrexone and acamprosate. A successful alcohol treatment program will include a combination of medicine and social support, like Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) meetings, counseling, individual or group therapy, and sometimes hospital treatment. What do I need to know before starting gabapentin? Gabapentin is also commonly used to treat nerve pain. Gabapentin (Neurontin) is a “novel anticonvulsant” and is FDA indicated for partial seizures and post-herpetic neuralgia. But the drug has long been heavily marketed to psychiatrists to treat a range of conditions from bipolar disorder to anxiety to alcohol withdrawal Pharmacists should bear in mind that these studies focused mainly on alcohol cravings, relapse, and abstinence. Limited data support gabapentin use in acute alcohol withdrawal symptoms, but the drug would likely be beneficial in patients after an acute withdrawal episode. Alcohol use disorder (AUD) is commonly encountered in clinical practice. A combination of psychosocial intervention and pharmacotherapy is the cornerstone of AUD treatment. Despite their efficacy, safety and cost-effectiveness, clinicians are Explore pharmacologic management strategies for alcohol use disorder, including treatment options and outcomes, on this comprehensive resource. This randomized clinical trial examines the efficacy of gabapentin as pharmacotherapy for alchohol use disorder in adults with a history of alcohol withdrawal. Find out what you need to know about gabapentin for alcohol withdrawal and discover the pros, cons, risks, and benefits, and how it may affect health. Expert opinion: Alcohol use disorder represents a challenge and large, unmet medical need. Evidence from single-site studies lend support to the safety and efficacy of gabapentin as a novel treatment for alcohol use disorder, with unique benefits for alcohol-related insomnia and negative affect, relative to available treatments. We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. A meta-analysis of the eficacy of gabapentin for treating alcohol use disorder. Addiction 2019;114(9):1547-55. Epub 2019 Jun 5. 2. Anton RF, Latham P, Voronin K, Book S, Hoffman M, Prisciandaro J, et al. Eficacy of gabapentin for the treatment of alcohol use disorder in patients with alcohol withdrawal symptoms: a random-ized clinical trial. Is gabapentin an effective treatment for alcohol use disorder (AUD)? Bottom line Gabapentin treatment avoided more heavy drinking days (> 5 standard drinks/day) than placebo (27% vs 9%). Gabapentin can be a second-line, off-label option to treat AUD. However, there is mixed evidence and concerns about abuse-misuse, and drug-related harms. Evidence P erceptions gabapentin regarding the use of for alcohol use disorder (AUD) have shifted over time.1–4 Early on, the drug was deemed to be benign and effective.4–6 But more and more, concerns are being raised about its recreational use to achieve euphoria,7 and the drug is often misused by vulnerable populations, particularly those with opioid use disorder.7–9 Given the large number of Gabapentin, available as gabapentin and as the prodrug gabapentin enacarbil, is an approved treatment for partial seizures, postherpetic neuralgia, and the restless legs syndrome. Gabapentin has been studied for diverse off-label indications, including alcohol use disorder (AUD). Gabapentin is a calcium channel GABAergic modulator that is widely used for pain. Studies showing reduced drinking and decreased craving and alcohol-related disturbances in sleep and affect in the months following alcohol cessation suggest therapeutic potential for alcohol use disorder. • Taking medicine for an alcohol use disorder is not substituting one drug for another. How should I take gabapentin? • The recommended dose of gabapentin for the treatment of alcohol use disorder is 300–600 milligrams (mg) three times daily. • Gabapentin can be taken with or without food. Is gabapentin an effective treatment for alcohol use disorder (AUD)? Gabapentin treatment avoided more heavy drinking days (> 5 standard drinks/day) than placebo (27% vs 9%). Gabapentin can be a second-line, off-label option to treat AUD. However, there is mixed evidence and concerns about abuse-
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |