Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
:.jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
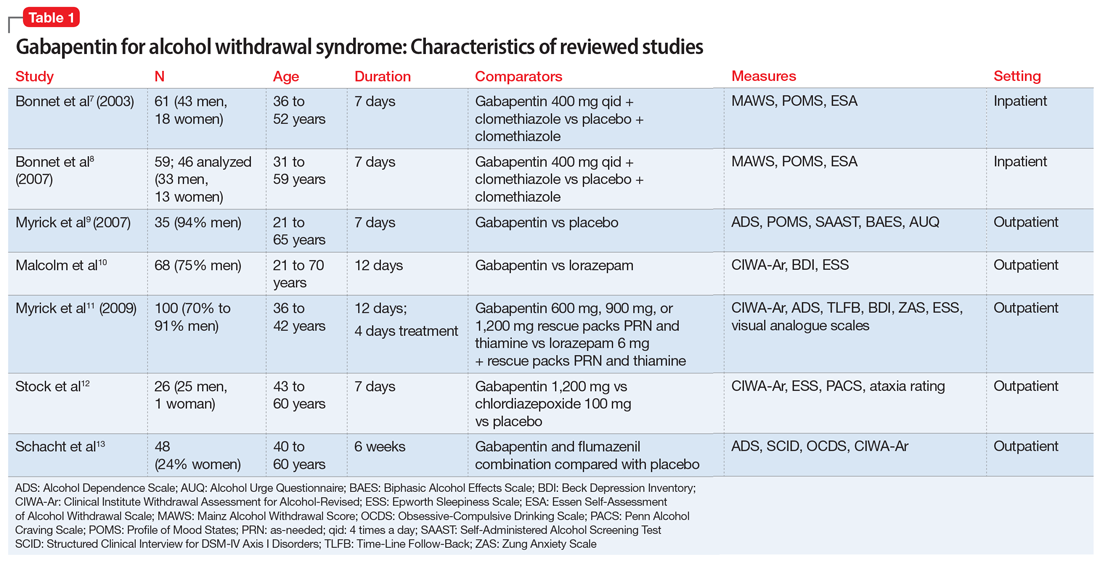
In sum, the addition of gabapentin to naltrexone for the treatment of alcohol dependence seems eficacious and well tolerated. While there are hints that this combi-nation might work best in those who have previously ex-perienced alcohol withdrawal symptoms, further study is needed to confirm this speculation. This randomized clinical trial examines the efficacy of gabapentin as pharmacotherapy for alchohol use disorder in adults with a history of alcohol withdrawal. Find out what you need to know about gabapentin for alcohol withdrawal and discover the pros, cons, risks, and benefits, and how it may affect health. The generic anticonvulsant medication gabapentin shows promise as an effective treatment for alcohol dependence, based on the results of a 150-patient clinical trial of the medication. The anticonvulsant drug gabapentin is used off-label to treat alcohol-related withdrawal, cravings, anxiety, and insomnia. Although it is well tolerated and has demonstrated efficacy for mild alcohol withdrawal and early abstinence, there is concern about its potential for abuse. Gabapentin should be prescribed only as a second-line alternative to standard therapies, and only after screening The success of gabapentin for treating alcohol/tobacco use problems was determined by calculating the success rate across studies: the total number of investigations with favorable results was divided by the total numbers of investigations for each specific disorder (eg, alcohol or tobacco dependence, or other). Expert opinion Alcohol use disorder represents a challenge and large, unmet medical need. Evidence from single-site studies lend support to the safety and efficacy of gabapentin as a novel treatment for alcohol use disorder, with unique benefits for alcohol-related insomnia and negative affect, relative to available treatments. Request PDF | Gabapentin Treatment for Alcohol Dependence A Randomized Clinical Trial | Importance Approved medications for alcohol dependence are prescribed for less than 9% of US alcoholics Expert opinion: Alcohol use disorder represents a challenge and large, unmet medical need. Evidence from single-site studies lend support to the safety and efficacy of gabapentin as a novel treatment for alcohol use disorder, with unique benefits for alcohol-related insomnia and negative affect, relative to available treatments. Gabapentin with alcohol dependence treatment can provide a smoother transition during detoxification. The medication may also help reduce alcohol cravings and support abstinence in alcohol dependence. To the Editor New treatments—both pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic—for one of the most devastating substance abuse disorders, alcoholism, are direly needed. We were therefore delighted to read an article reporting on a trial of gabapentin as a treatment option for alcohol dependence.1 Efficacy of gabapentin for the treatment of alcohol use disorder in patients with alcohol withdrawal symptoms: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med 2020;180 (5):728-36. Gabapentin may be effective in maintaining abstinence, lowering weekly alcohol intake, and reducing cravings and improving mood and sleep in patients with moderate-risk alcohol dependence; however, extrapolation of these results to the entire population may be difficult. Mason and coauthors determine if gabapentin increases rates of sustained abstinence and no heavy drinking and decreases alcohol-related insomnia, dysphoria, and craving, in a dose-dependent manner. See the Invited Commentary by Nunes. Alcohol dependence is found – and gabapentin is widely used – across medical specialties. Reported benefits of gabapentin for alcohol dependence may result in a broader interest in alcoholism treatment across diverse medical settings. Study Selection and Data Extraction: Studies were included wherein gabapentin was used as an adjunctive or primary treatment of alcohol dependence/withdrawal. Studies included participants diagnosed with alcohol use disorder using DSM-IV, DSM-IV-TR, DSM-5, or the International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10). Conclusions and relevance: Gabapentin (particularly the 1800-mg dosage) was effective in treating alcohol dependence and relapse-related symptoms of insomnia, dysphoria, and craving, with a favorable safety profile. Increased implementation of pharmacological treatment of alcohol dependence in primary care may be a major benefit of gabapentin as a treatment option for alcohol dependence. Gabapentin and Naltrexone: Treatment Options for Alcohol Dependence Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication used to treat alcohol dependence in combination with other medications. Abstract Objective: Naltrexone, an efficacious medication for alcohol dependence, does not work for everyone. Symptoms such as insomnia and mood instability that are most evident during early abstinence might respond better to a different pharmacotherapy. Gabapentin may reduce these symptoms and help prevent early relapse. This clinical trial evaluated whether the combination of naltrexone and Studies of the efficacy of gabapentin for treating alcohol use disorder (AUD) have yielded mixed findings. The aims of our study were to estimate gabapentin’s effects on six alcohol-related outcomes, test potential moderators, examine publication
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
:.jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |