Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
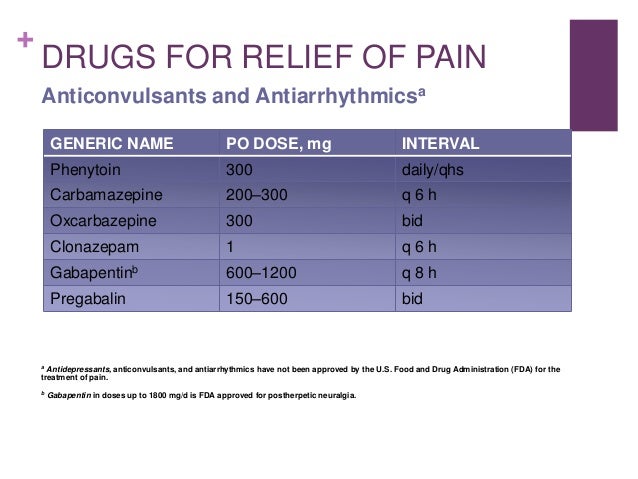
Lyrica and Gabapentin are prescription medications approved to treat partial onset seizures and various forms of neuropathic pain, including diabetic peripheral neuropathy and postherpetic neuralgia. Both belong to the class of antiepileptic drugs and work by calming overactive nerve signals. Lyrica and gabapentin are both anticonvulsants used to treat seizures and nerve pain, but have some important differences to consider when choosing one. This prospective, open-label study aimed to evaluate the efficacy of pregabalin treatment in patients suffering from trigeminal neuralgia with and without concomitant facial pain. Fifty-three patie The efficacy and safety of gabapentin vs. carbamazepine in patients with primary trigeminal neuralgia: A systematic review and meta-analysis Regarding long-term safety data for the chronic use of pregabalin and gabapentin, in the case of pregabalin for the treatment of anxiety disorders, good tolerability has been observed with effective disease management (12). The efficacy of α2δ ligands, gabapentin and pregabalin, has been assessed in seven controlled or open-label studies. Despite the low quality of evidence, the favorable tolerability profile and the possible action on concomitant continuous pain make this drug category of interest for future trials in trigeminal neuralgia. Pregabalin (Lyrica) and gabapentin (Neurontin and others) are drugs used to prevent seizures and to treat nerve pain associated with various conditions (shingles, diabetic neuropathy). Lyrica and gabapentin both cause similar side effects, including tremors, blurred or double vision, memory or concentration problems, dizziness, and drowsiness. Lyrica and gabapentin are two prescription drugs used to treat nerve pain and focal onset seizures. Find out how they’re alike and different. Lyrica and gabapentin are two prescription drugs that treat some seizures and nerve pain. Here's a comparison of how the drugs are similar and different. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of patients with trigeminal neuralgia (TN) advocate for a multidisciplinary team approach to improve the care of patients with acute and chronic TN. Evidence-based discussions and decisions are encouraged to establish care pathways for prompt diagnosis and treatment, and long-term outcomes data collection to improve care. The guidelines include Trigeminal neuralgia is a syndrome of unilateral, paroxysmal, stabbing facial pain, originating from the trigeminal nerve. Careful history of typical symptoms is crucial for diagnosis. Most cases are caused by vascular compression of the trigeminal ABSTRACT Trigeminal neuralgia (TN) is a highly disabling disorder characterised by very severe, brief and electric shock like recurrent episodes of facial pain. New diagnostic criteria, which subclassify TN on the basis of presence of trigeminal neurovascular conflict or an underlying neurological disorder, should be used as they allow better characterisation of patients and help in decision The aim of this review is to provide current, evidence-based, knowledge about the use of gabapentin and other a ligands in patients with trigeminal neuralgia. Pregabalin (Lyrica) and gabapentin (Neurontin) are both approved to treat nerve pain. How are they different, and which one is preferred? Compare both meds here. Lyrica may also be used to treat neuropathic (nerve) pain associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy or postherpetic neuralgia, spinal cord injury, and fibromyalgia Gabapentin may also be used to treat nerve pain caused by shingles (herpes zoster) and gabapentin enacarbil, brand name Horizant, is also approved for restless legs syndrome (RLS). The efficacy of α2δ ligands, gabapentin and pregabalin, has been assessed in seven controlled or open-label studies. Despite the low quality of evidence, the favorable tolerability profile and the possible action on concomitant continuous pain make this drug category of interest for future trials in trigeminal neuralgia. This article discusses the efficacy and safety of gabapentin versus carbamazepine in treating trigeminal neuralgia through a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Trigeminal neuralgia is also caused by dysfunction of neural tissue, but its management is distinct from other forms of neuropathic pain. Neuropathic pain is generally managed with a tricyclic antidepressant or with certain antiepileptic drugs. Amitriptyline hydrochloride and pregabalin are effective treatments for neuropathic pain. Corticosteroids and oxycodone reduce the pain experienced during the acute infective period. Pregabalin, gabapentin, TCAs (amitriptyline and nortriptyline), controlled release opioids, capsaicin cream (Zostrix®) and 5% lignocaine patches (Versatis®) may also help reduce the pain of PHN. Trigeminal neuralgia Gabapentin is used to treat partial seizures that occur with epilepsy and nerve pain resulting from nerve damage such as: Postherpetic neuralgia, a type of nerve pain caused by shingles Diabetic
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |